Exercise reduces risk of kidney disease, and also plays a role in improving kidney function and reducing morbidity and mortality for those with established disease.
In this episode, we discuss kidney physiology, risk factors for disease, disease progression, dialysis, and transplant. All of this is discussed in the context of the question “what role might exercise play here?”.
If you or someone you know has been affected by kidney disease, make sure to give this episode a listen.
Podcast Notes
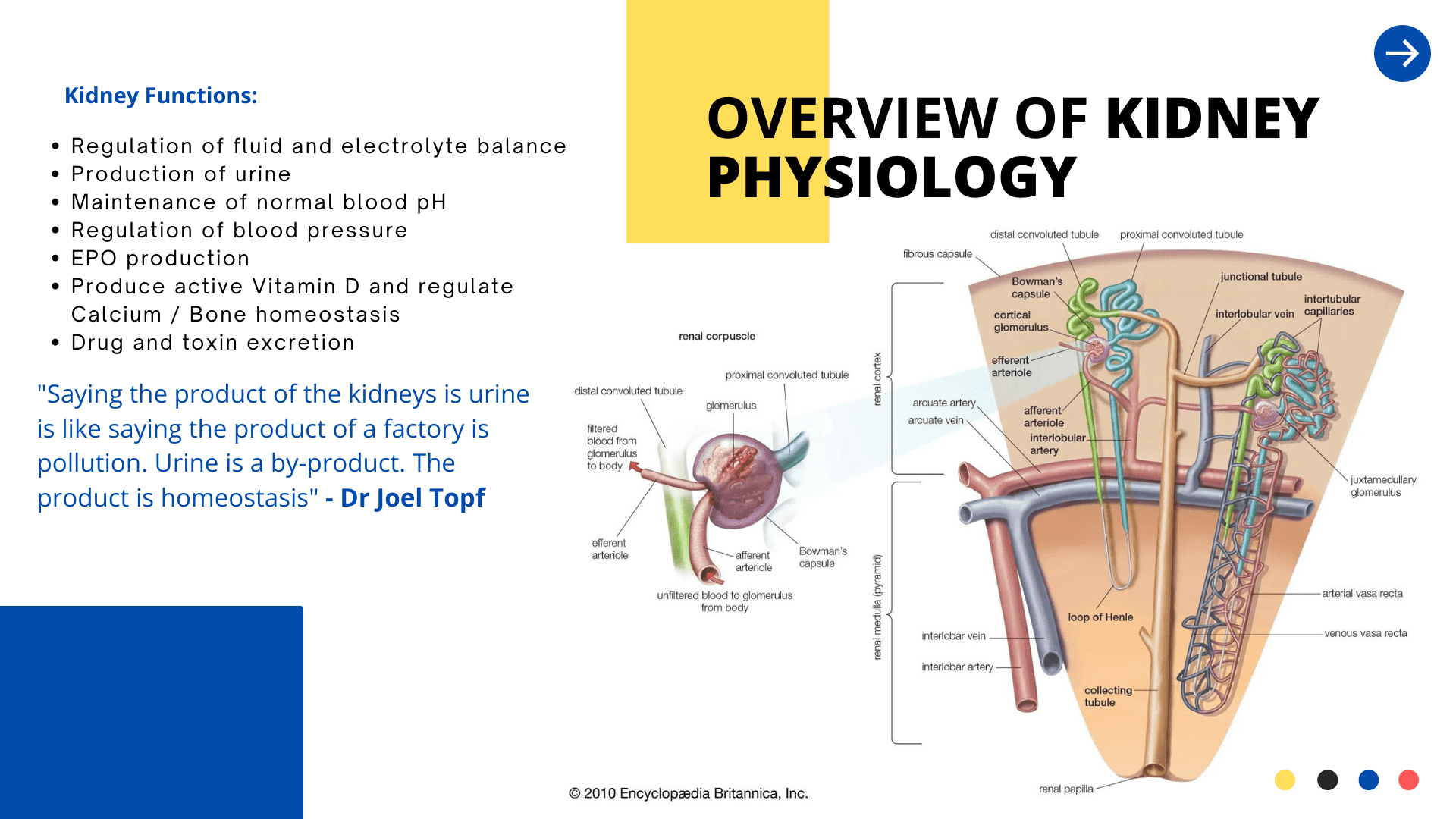
Introduction to the Kidneys
The functions of the kidney include:
- Regulation of fluid and electrolyte balance
- Production of urine
- Maintenance of normal blood pH
- Regulation of blood pressure
- EPO production
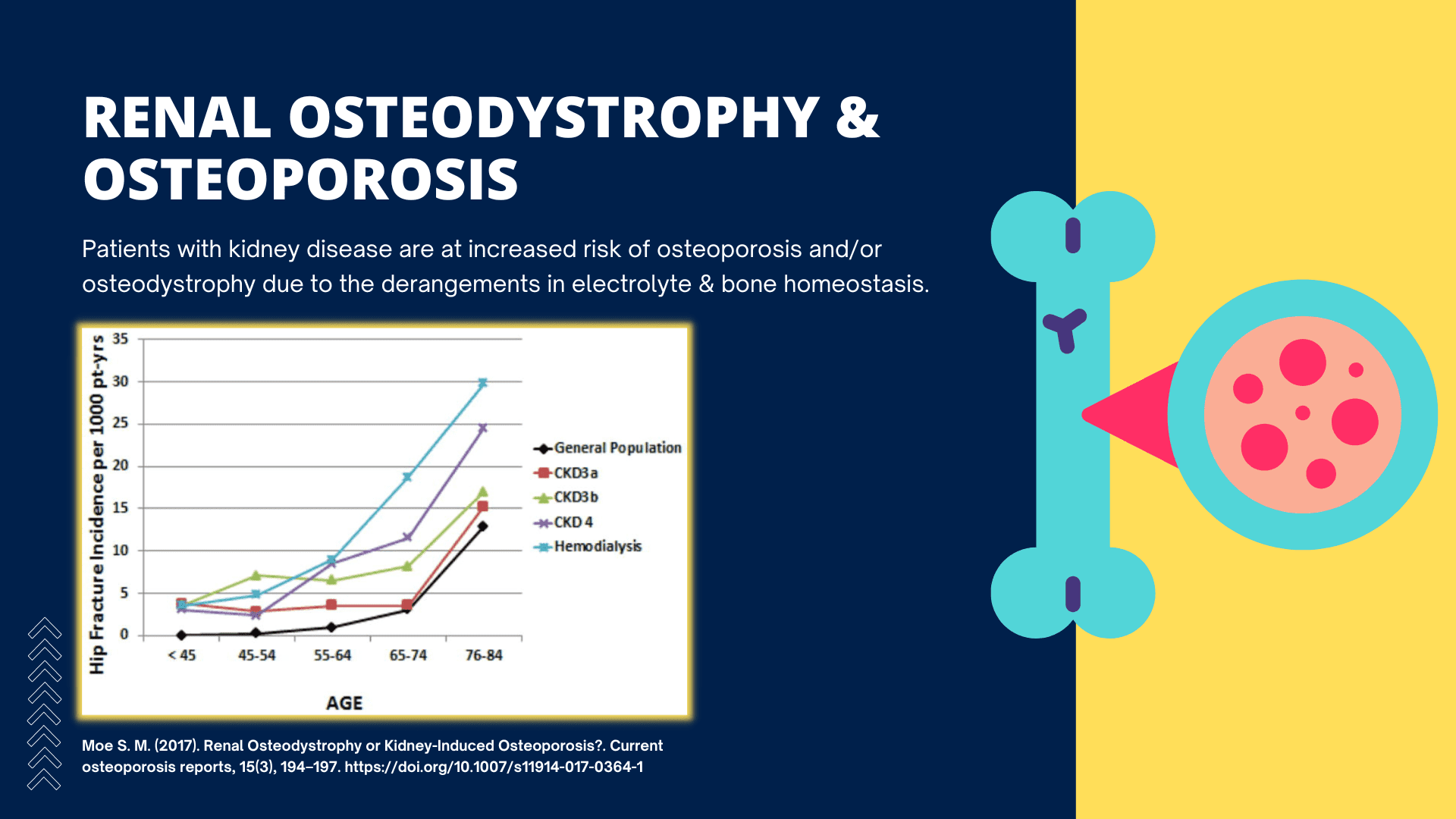
- Produce active Vitamin D and regulate Calcium / Bone homeostasis
- Drug and toxin excretion
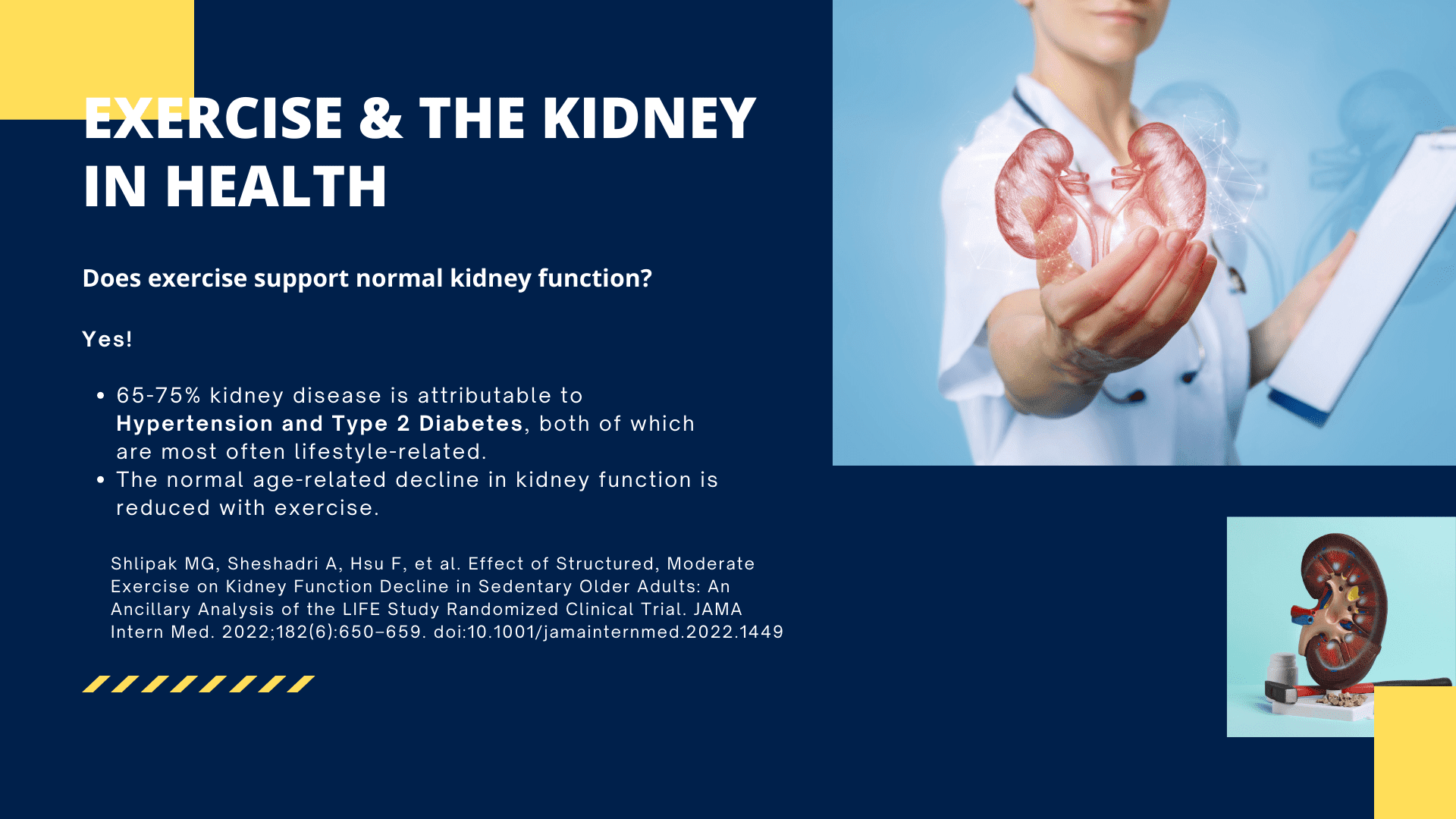
In a state of health, exercise supports normal kidney physiology, and slows the expected age-related decline in kidney function with age.
Kidney Disease
Diabetes and high blood pressure are responsible for up to two-thirds of the cases of kidney disease. Other causes are either genetic or more specific issues (such as frequent UTIs, obstructions, autoimmune etc).
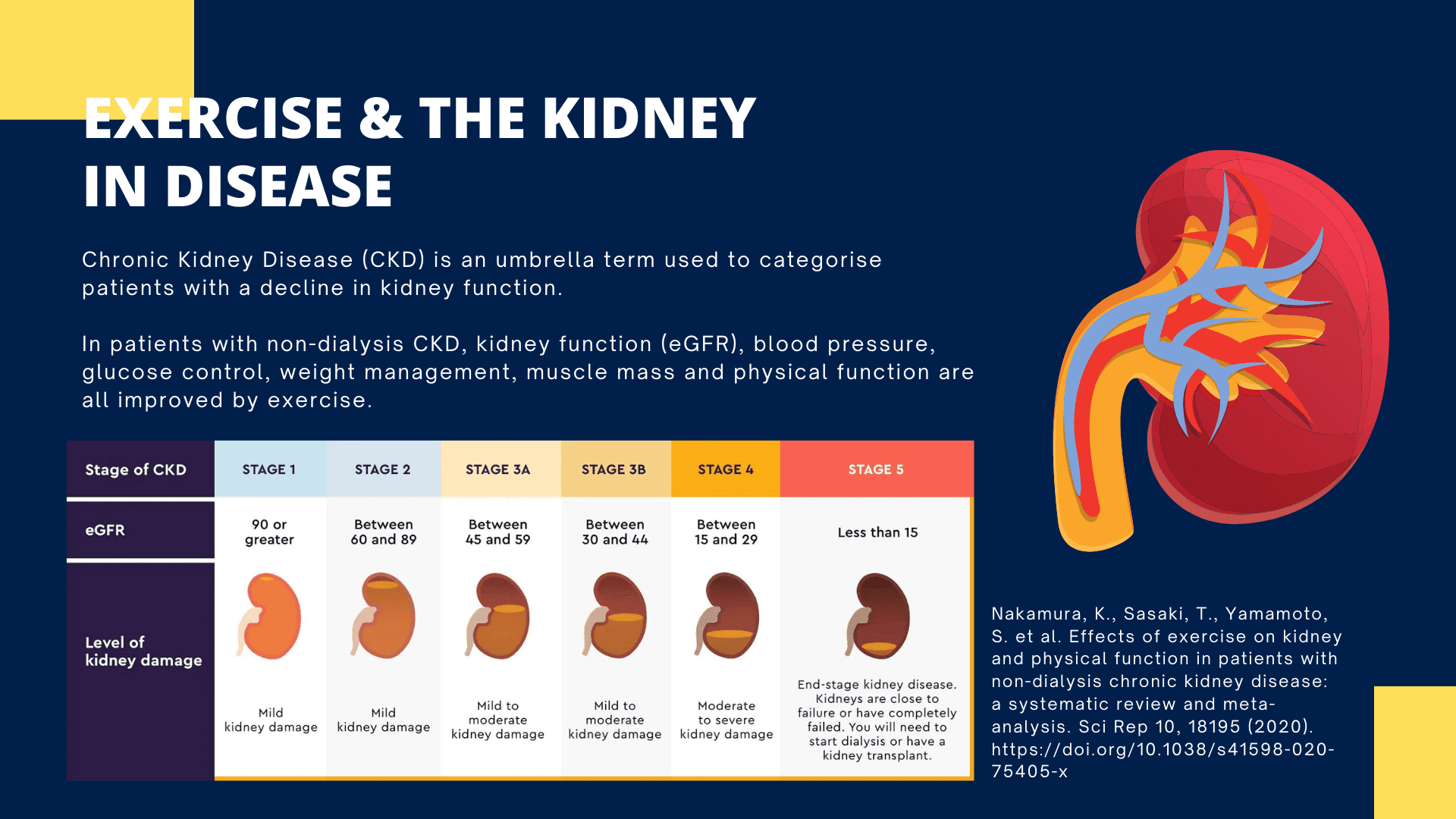
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is an umbrella term used to categorise patients with a decline in kidney function:
- Stage 1 with normal or high GFR (GFR > 90 mL/min)
- Stage 2 Mild CKD (GFR = 60-89 mL/min)
- Stage 3A Moderate CKD (GFR = 45-59 mL/min)
- Stage 3B Moderate CKD (GFR = 30-44 mL/min)
- Stage 4 Severe CKD (GFR = 15-29 mL/min)
- Stage 5 End Stage CKD (GFR <15 mL/min)
In patients with non-dialysis CKD, kidney function (eGFR), blood pressure, glucose control, weight management, muscle mass and physical function are all improved by exercise.
Nakamura, K., Sasaki, T., Yamamoto, S. et al. Effects of exercise on kidney and physical function in patients with non-dialysis chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sci Rep 10, 18195 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-75405-x
Exercise guidelines are not specified for those with kidney disease, but the same guidelines generally apply. Some express concerns related to increased blood pressure during resistance training, but is this of concern?
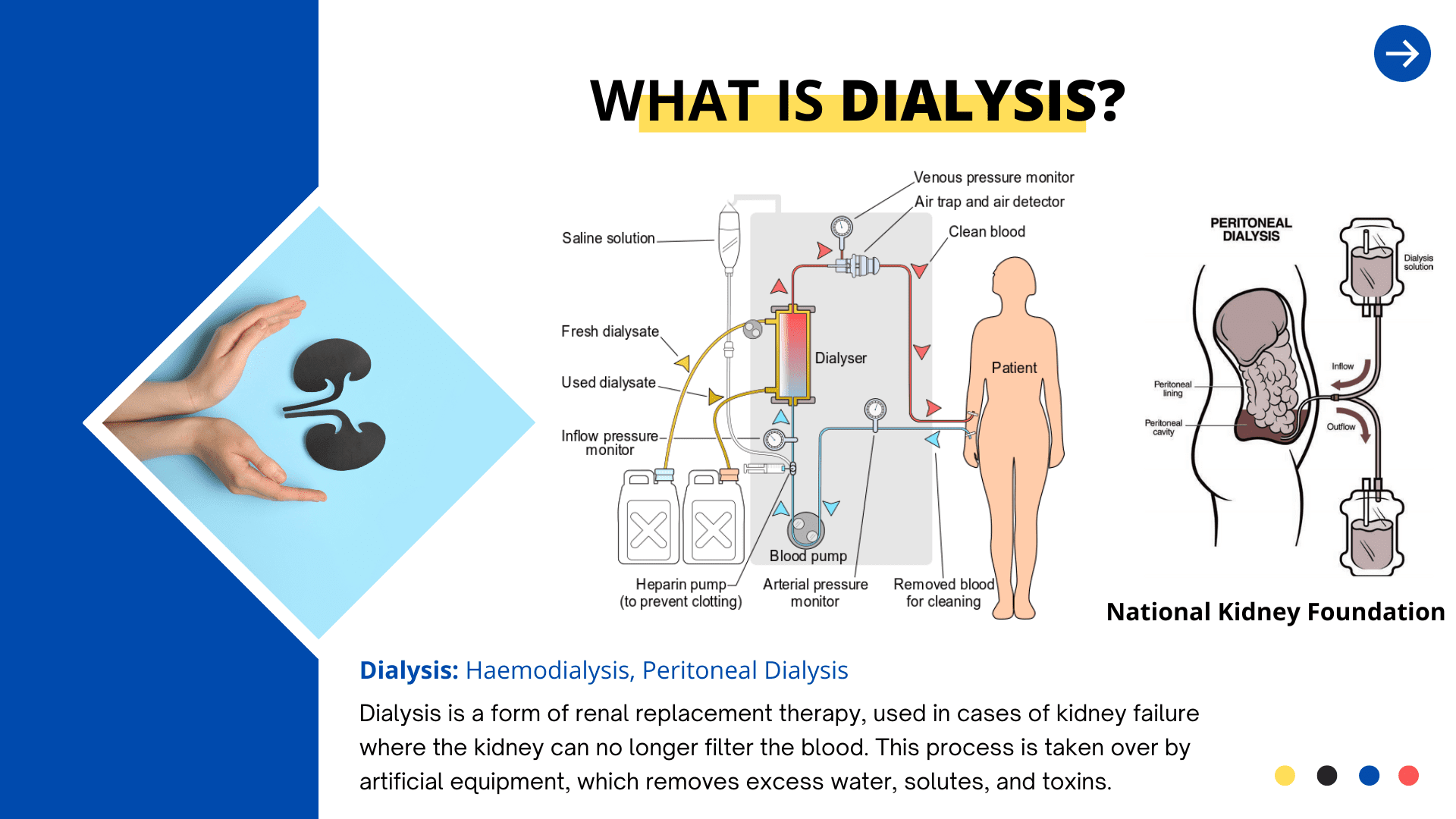
Dialysis
Dialysis is a form of renal replacement therapy, used in cases of kidney failure where the kidney can no longer filter the blood. This process is taken over by artificial equipment, which removes excess water, solutes, and toxins.
Most patients on dialysis do not exercise, with major barriers including tiredness, muscle fatigue, and fear of arteriovenous fistula injury.
Cardiovascular
Cardiac complications are a core feature of kidney disease, and exercise improves cardiac function, autonomic regulation, and arterial hypertension.
Muscular Benefits
Muscle atrophy, deconditioning, and loss of function is common in dialysis patients. Exercise can prevent and reverse these muscular and systemic effects.
Contraindications
Transplant
Stefan De Smet, Amaryllis H. Van Craenenbroeck, Exercise training in patients after kidney transplantation, Clinical Kidney Journal, Volume 14, Issue Supplement_2, April 2021, Pages ii15–ii24, https://doi.org/10.1093/ckj/sfab022
Contraindications include contact sports and other barriers depending on wound healing and other co-morbidities.
Other References:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27334146/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15974634/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/24899042/
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26447795/
More From Triage…
Join the Email List
forms.aweber.com/form/77/857616677.htm
Interested in coaching with Triage?
Email info@TriageMethod.com and the Triage Team will get back to you!
Or you can read more and fill in a contact form at triagemethod.com/online-coaching/
Interested in getting certified as a Nutrition Coach?
Check out our course here: triagemethod.com/nutrition-certificate/
Have you followed us on social media?
Youtube: www.youtube.com/channel/UCzYO5nzz50kOAxo6BOvJ_sQ
Instagram: www.instagram.com/triagemethod/
Facebook: www.facebook.com/triagemethod/