Sleep environment optimisation is the next stop in the tour of foundational sleep hygiene habits. You should have already established consistent sleep and wake times, built a wind down routine that transitions your nervous system from activation to rest, sorted your light exposure, and you’re doing everything right from a behavioural standpoint. But phenomenal sleep may still feel harder than it should.
The missing piece might be the environment itself. You can have perfect sleep hygiene habits and still struggle if you’re trying to sleep in a room that’s too bright, too warm, too noisy, or simply not conducive to rest. Your bedroom environment either supports sleep or it doesn’t, and most people are trying to sleep in spaces that were never optimised for the task.
Sleep environment optimisation isn’t about creating some sterile, perfect sleep laboratory. It’s about recognising that your bedroom sends you signals all night long. Signals about temperature, light, sound, and comfort, and these signals either tell your body “this is a safe place to rest deeply” or they create subtle ongoing stress that fragments your sleep even when you’re not consciously aware of it.
This article will give you a comprehensive framework for optimising your sleep environment, covering everything from the foundational elements that matter for everyone to the individual preferences that require experimentation. Some interventions are free or nearly free. Others require investment. All of them can dramatically improve sleep quality if implemented thoughtfully, and understanding the principles allows you to make intelligent trade-offs when perfect optimisation isn’t possible.
Table of Contents
- 1 The Bedroom Sanctuary
- 2 Darkness: The Foundation of Sleep Environment Optimisation
- 3 Temperature: The Often-Overlooked Critical Factor
- 4 Noise: The Not So Silent Sleep Destroyer
- 5 Air Quality and Ventilation
- 6 Mattress Selection: Individual and Complicated
- 7 Pillow Selection: More Important Than You Think
- 8 Bedding and Blankets
- 9 Electronics and EMF Concerns
- 10 Bedroom Colours and Decor
- 11 Special Situations and Compromises
- 12 Sleep Environment Optimisation Conclusion
- 13 Author
The Bedroom Sanctuary
Before we dive into the technical elements of sleep environment optimisation, we need to address what your bedroom means to your brain. Sleep is a state of profound vulnerability. You’re unconscious, unaware of your surroundings, unable to respond to threats. For sleep to happen, your brain needs to feel safe enough to relinquish conscious control. Any signal that suggests this environment isn’t safe like loud noise, bright light, discomfort, and any associations with stress, makes sleep more difficult.
The bedroom sanctuary concept is simple: your bedroom, and specifically your bed, should be associated with only two activities: sleep and sex. Not work. Not eating. Not watching television. Not scrolling through your phone. Not having stressful conversations. Not lying awake worrying about tomorrow. Sleep and sex, that’s it.
This matters because your brain forms powerful associations with environments. If you regularly work from bed, your bed becomes associated with the arousal and focus required for work. When you then try to sleep in that same bed, your brain receives mixed signals—is this work time or sleep time? The association with wakefulness undermines your ability to relax into sleep.
This is basic stimulus control, a concept from behavioural psychology. When a stimulus (your bed) is consistently paired with a particular response (sleep), the stimulus itself begins to trigger that response. But when the same stimulus is paired with multiple responses (sleep, work, entertainment, worry), the association becomes muddled and loses its power.
Creating a bedroom sanctuary means deliberately building the association between your bedroom and rest. When you walk into your bedroom, your nervous system should begin the transition toward sleep automatically because it’s learned that this space means rest. This doesn’t happen overnight, and in reality, it requires weeks of consistent practice. But it’s one of the most powerful interventions available for chronic insomnia and sleep difficulties.
If you currently work from bed, scroll your phone in bed, eat meals in bed, or use your bed as a general relaxation space during the day, you’re actively undermining your sleep every time you do so. The solution is to stop. Use your bed only for sleep and sex. If you can’t sleep after fifteen to twenty minutes, get out of bed and go to another room. Return only when you feel sleepy. This feels counterintuitive because surely staying in bed is better than getting up? But in reality, you’re retraining your brain’s associations, and that requires consistency of stimulus.
For people in small spaces where the bed is unavoidable during waking hours, the principle must be adapted. At a minimum, don’t work from under the covers, use different positions during the day than you use for sleep (sit up against the headboard during the day, lie down only for sleep), and create psychological boundaries through rituals that signal the transition from day use to sleep use.
Darkness: The Foundation of Sleep Environment Optimisation
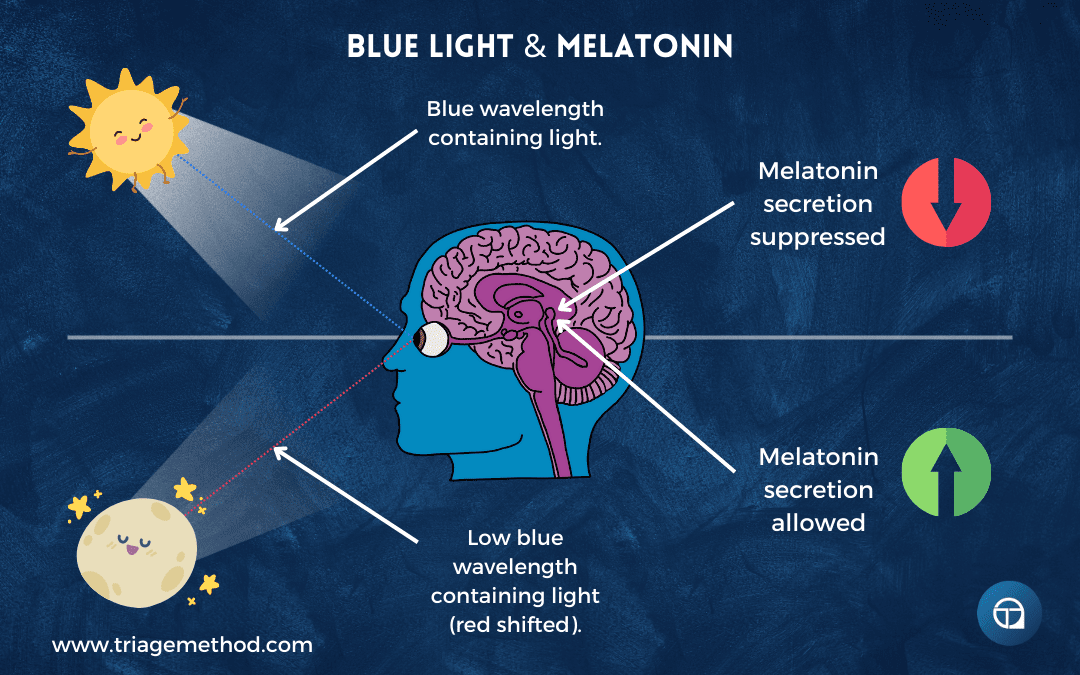
We’ve discussed light exposure management in a previous article, focusing primarily on the light you expose yourself to before bed. But what happens after you get into bed matters just as much. Even small amounts of light during sleep can disrupt sleep architecture, suppress melatonin throughout the night, and fragment sleep in ways you’re not consciously aware of.
The ideal is complete darkness. You want it so dark you literally cannot see your hand in front of your face. This might sound excessive. It’s not. Your eyes remain somewhat light-sensitive even when closed, and light that penetrates your eyelids reaches your retinas and signals your brain that it’s not fully nighttime. This affects sleep depth, REM sleep percentage, and how consolidated your sleep is.
Research shows that even dim light exposure during sleep (as little as 5-10 lux, which is about the same intensity as a streetlight through your window or the glow from electronics) can reduce slow-wave deep sleep and REM sleep whilst increasing stage 1 and stage 2 light sleep. You might sleep for eight hours, but get less restorative sleep than you would in seven hours of truly dark conditions.
The mechanism is that light exposure during sleep suppresses melatonin throughout the night, and melatonin doesn’t just help you fall asleep, it’s involved in maintaining sleep architecture and promoting the deeper stages of sleep. When it’s suppressed, your sleep becomes lighter and more fragmented. You might not fully wake and might not even remember waking, but your sleep quality suffers measurably.
This is particularly important if you live in urban areas with streetlights, if your bedroom faces east and gets early morning light, if you have a partner who wakes earlier and turns on lights, or if you have electronics in your bedroom that emit light. All of these are degrading your sleep quality, even if you’ve habituated to them and no longer consciously notice.
Achieving Complete Darkness
Blackout curtains or shades are the gold standard for sleep environment optimisation regarding darkness. Not “room darkening” curtains, which still allow significant light through, but actual blackout curtains or cellular shades that block 99-100% of light. These typically have a thick backing or multiple layers that prevent light penetration.
Installation matters. Light leaks around the edges of curtains can let in substantial light. Blackout curtains should extend beyond the window frame on all sides, or should be mounted inside the window frame with side channels that prevent light leakage. Some people use velcro or magnetic strips to seal the edges of curtains to the wall, eliminating even minor light leaks.
Cost ranges from €30-200+, depending on size and quality. This is money well spent given that you’ll use them every night for years. If your budget is severely constrained, even hanging heavy dark fabric (old blankets, dark sheets) over existing curtains provides a substantial improvement over nothing.
Light-blocking window film can supplement curtains or serve as a primary solution for windows that are difficult to cover with curtains. These films adhere directly to the window glass and block light while still allowing you to use the window during the day. They’re more permanent than curtains but often less expensive and work well for odd-shaped windows or windows in rental properties where mounting curtains is difficult.
Door draft stoppers aren’t just for insulation, they also block light that leaks under doors. If you have light from hallways or other rooms seeping under your bedroom door, a simple door draft stopper eliminates this source.
Covering electronic lights addresses the surprising amount of light emitted by chargers, smoke detectors, cable boxes, alarm clocks, and other electronics. Small pieces of black electrical tape, blackout stickers, or even small pieces of dark fabric over LEDs eliminate these light sources. Some people find this excessive and obsessive, but your sleep architecture doesn’t. Even the small LED from a phone charger can provide enough light to measurably affect sleep in a truly dark room.
Removing electronics from the bedroom entirely solves both the light problem and the temptation problem. No charging phones in the bedroom means no notification lights, no temptation to check your phone if you wake briefly, no EMF concerns (for those who have them), and no possibility of using screens when you should be sleeping. Charge devices in another room. Use an actual alarm clock rather than your phone.
Sleep masks are the fallback option when you cannot control your sleep environment. For example, if you share a bedroom with someone who keeps different hours, if you’re travelling, if you’re in temporary living situations, or if blackout curtains aren’t possible, a good sleep mask can block all light while still being comfortable enough that you forget you’re wearing it. However, this doesn’t completely eliminate the issue, as you do still sense light across your body, and not just the eyes.
Sleep Mask Considerations
Sleep masks work well for some people and are intolerable for others. The difference usually comes down to fit and quality. Cheap sleep masks that press against your eyes, shift during the night, or have elastic that’s too tight create more problems than they solve. Quality masks are worth the investment if you need them.
Contoured masks that create space around your eyes rather than pressing against them are vastly more comfortable for most people and allow you to open your eyes and blink naturally if you wake. These typically cost €15-40 but are worth every penny compared to €3 flat masks that press your eyeballs.
Material matters: silk or satin masks are cooler and create less friction against your skin than cotton or synthetic materials. Some people find certain materials irritating or sweat-inducing. Bamboo fabric offers a middle ground, as it is breathable but not as slippery as silk.
Staying in place is the make-or-break feature. Adjustable straps are essential. Some masks use velcro, some use adjustable buckles. The strap should be snug enough that the mask doesn’t shift when you move, but not so tight that it creates pressure or leaves marks on your face. Some masks have wider straps that distribute pressure more evenly.
Cost: Expect to pay €10-40 for a quality sleep mask. The €3 masks from chemists rarely work well. The €100+ luxury masks might be marginally better, but show diminishing returns. The sweet spot is €15-30 for something that actually works and lasts.
Try multiple masks if the first one doesn’t work. Individual face shapes differ enormously, and what works perfectly for one person might be uncomfortable for another. Most quality masks have return policies if they don’t work for you.
Temperature: The Often-Overlooked Critical Factor
Temperature might be the most important element of sleep environment optimisation that people consistently get wrong. Most people sleep in rooms that are too warm, and it’s costing them sleep quality they’re not aware of losing.
The optimal temperature range for most people is 15-19°C (60-67°F). This is substantially cooler than most people keep their bedrooms. This isn’t arbitrary, as it’s based on what facilitates the physiological changes required for sleep, particularly the core body temperature drop that’s necessary for sleep initiation and maintenance.
Your core body temperature needs to drop by approximately 1-2 degrees Celsius to initiate sleep and must remain lower than daytime levels to maintain deep sleep. This happens through distal vasodilation; blood flow to your extremities (hands and feet) increases, which radiates heat away from your core. This process works best when the ambient temperature is cool enough that your body can effectively offload heat.
When the room is too warm, your body struggles to lower its core temperature sufficiently. You might fall asleep eventually, but your sleep will be lighter, more fragmented, and you’ll spend less time in deep restorative sleep. You might wake frequently without fully realising it, turn repeatedly seeking a cool spot on the pillow, kick off blankets, and generally have disrupted sleep architecture.
Many people protest, “But I feel cold in a room that cool!” But here’s the thing: you should feel slightly cool when you’re awake and under minimal covering. Once you’re under blankets or a duvet, you’ll feel comfortable. The combination of cool ambient air and warm bedding creates ideal conditions, because your extremities stay warm (promoting vasodilation and heat loss), while the cool air allows your core temperature to drop.
Individual variation absolutely exists. Some people genuinely run colder and might need temperatures toward the warmer end of the range (18-19°C). Some people, particularly athletes or people with higher metabolic rates, need temperatures toward the cooler end (15-16°C). Women often run colder than men, particularly during certain phases of the menstrual cycle or when using hormonal contraceptives. Older adults often prefer warmer temperatures. So, you need to experiment within the general range to find what works for you.
Achieving Optimal Temperature
Thermostat settings are the obvious starting point if you have climate control. Set your thermostat to 16-18°C for nighttime. This feels uncomfortably cool to most people initially because they’re accustomed to warmer sleeping environments. Give it two weeks of consistent cool sleeping before deciding it doesn’t work. Most people adapt and then find they actually sleep noticeably better.
If you share a bedroom with a partner who prefers different temperatures, this becomes a negotiation. You have a few options here, such as compromising on a temperature that’s tolerable for both (usually around 17-18°C), using separate blankets of different weights, having one person wear more clothing, or investing in a dual-zone heating blanket or cooling mattress topper that allows individual temperature control.
Opening windows provides cooling and has the added benefit of improving air quality and ventilation. This works best in cooler months or climates. Obviously, this isn’t viable if external noise is problematic, if air quality is poor, if safety is a concern, or if you live in hot humid climates where opening windows just makes the room muggy.
Fans provide both cooling and white noise (which we’ll discuss in the noise section). A ceiling fan or standing fan creates air circulation that aids in heat dissipation and makes a cool room feel comfortable rather than cold. Fans are also relatively inexpensive.
Blanket weight and materials matter enormously for temperature regulation. Heavy duvets and multiple blankets trap heat, which is ideal in winter but problematic in summer. Having seasonal bedding (a heavy duvet for winter, a light cotton blanket or thin duvet for summer) allows you to maintain a consistently cool room temperature year-round while adjusting insulation.
Natural fibres (cotton, linen, bamboo, wool) breathe better than synthetic materials and regulate temperature more effectively. Egyptian cotton and linen, in particula,r are excellent for temperature regulation. Thread count matters less than you might think, although the sweet spot for sheets is typically 300-500 thread count for breathability. Higher thread counts create denser weaves that trap heat.
Clothing choices are surprisingly important. Many people wear heavy pyjamas to bed, which prevents heat dissipation. Minimal clothing (or no clothing) allows for better temperature regulation. If you need some covering for comfort or modesty, choose lightweight, breathable fabrics. Cotton or bamboo sleepwear is vastly better than flannel or fleece for most people.
Cooling mattress pads or toppers represent a more significant investment but can be transformative for people who run hot or share a bed with someone who has very different temperature preferences. These typically use phase-change materials that absorb and dissipate heat, or use active cooling systems with water circulation. They’re not necessary for most people if the room temperature is properly optimised, but they’re valuable for edge cases.
Heating mattress pads serve the opposite function for people who genuinely run cold. Electric blankets or heating mattress pads can warm the bed itself whilst the room remains cool, allowing core temperature to drop whilst preventing uncomfortable coldness. Many have timers that can turn them off after an hour or two, providing warmth for sleep onset without overheating throughout the night.
Pre-cooling the room, starting one to two hours before bed, facilitates the body temperature drop. Rather than keeping the house warm until bedtime and then trying to cool down quickly, allow the temperature to drop gradually during your wind-down period. This aids in the physiological transition to sleep and makes getting into bed feel immediately comfortable rather than initially cold.
Temperature and Hormonal Fluctuations
Women’s temperature regulation is significantly affected by hormonal fluctuations. During the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle (post-ovulation, pre-menstruation), core body temperature runs approximately 0.3-0.5°C higher, which can make sleep more difficult and increases preference for cooler sleeping environments.
Pregnancy dramatically affects temperature regulation, particularly in the second and third trimesters when metabolic rate increases and core temperature runs higher. Pregnant women almost universally need cooler sleeping environments than they did pre-pregnancy.
Menopause and perimenopause are notorious for disrupting temperature regulation through hot flashes and night sweats. During this life stage, many women need significantly cooler sleeping environments and benefit enormously from cooling mattress pads, moisture-wicking bedding, and having the ability to rapidly shed blankets without fully waking.
So, if you’re female and sleeping with a male partner, your temperature preferences might diverge significantly, and this divergence might change throughout the month or across life stages. This isn’t just preference or being difficult, it’s physiology. As such, the solution requires genuine compromise, individual temperature regulation strategies (separate blankets, different clothing), and recognition that what worked in the past might not work now.

Noise: The Not So Silent Sleep Destroyer
Noise affects sleep even when you don’t consciously wake up. Your brain continues processing sounds during sleep, and sounds above approximately 30-40 decibels can fragment sleep architecture, reduce time in deep sleep, and cause brief arousals that you’re not aware of, but that accumulate into measurably worse sleep quality.
You might believe “I sleep fine despite the noise” because you’re not waking fully. But sleep studies consistently show that people sleeping in noisy environments have more fragmented sleep, less slow-wave deep sleep, and report feeling less rested despite similar total sleep time compared to sleeping in quiet environments.
Individual sensitivity varies. Some people can sleep through virtually anything. Trains, traffic, neighbours, construction, or whatever else, they sleep through it all. Others wake to the smallest sounds; a dripping tap, a partner’s breathing, or a creaking floorboard. There’s a genetic component to noise sensitivity during sleep, but there’s also a learned hypervigilance component, particularly in people with anxiety or trauma histories who’ve learned to maintain some vigilance even during sleep.
The challenge with noise is that many sources are outside your control. You can’t eliminate traffic noise if you live on a busy street. You can’t stop construction in your neighbourhood. You can’t prevent neighbours from making noise. You can’t control aircraft if you live near an airport. This makes noise one of the most frustrating aspects of sleep environment optimisation, and no doubt, many of you know it’s affecting your sleep, but you feel powerless to change it. But there are some strategies that help here.
Managing Noise: What You Can Control
Start by identifying controllable noise sources in your own home and bedroom. Ticking clocks, creaking floorboards, rattling windows, humming electronics, squeaking bed frames, etc., as these are all fixable. Remove ticking clocks from the bedroom. Tighten loose floorboards or place rugs over creaky areas. Seal or replace rattling windows. Turn off or remove humming electronics. Oil or replace squeaky bed components.
Soft furnishings dampen sound. Heavy curtains (which you might already have for blackout purposes) absorb sound as well as blocking light. Rugs on hard floors reduce noise transmission, particularly important if you’re concerned about disturbing neighbours below you. Upholstered furniture, tapestries, acoustic panels, even bookshelves filled with books, all absorb and dampen sound.
White noise machines, fans, and air purifiers provide consistent background noise that masks intermittent, disruptive sounds. The reason this works is that your brain habituates to consistent sounds but remains alert to changes in the sound environment. A consistent 40 decibels of white noise prevents you from noticing the 50 decibel car passing by because there’s no change in your sound environment. The car is still quieter than the baseline noise.
White noise machines are cheap, and we even have a Sound Therapy Tool that you could use. Simple ones produce basic white noise (all frequencies at equal intensity), brown noise (which has lower frequencies emphasised, and is often experienced as more soothing), or pink noise (which is a balanced between white and brown). Fancier machines offer multiple sounds such as rain, ocean, fan, etc. Apps can provide these sounds for free, though phone speakers typically have lower quality than dedicated machines, and having your phone in the bedroom violates the principle of keeping screens out.
Fans serve double dutyhere, both cooling and generating white noise. A simple floor fan or ceiling fan provides consistent background sound while improving air circulation. For many people, this is sufficient noise masking without needing dedicated white noise machines.
Air purifiers provide the triple benefit of noise masking, air circulation, and improved air quality. They’re more expensive than fans (€80-800+, depending on quality and room size) but serve multiple functions that all support sleep.
Earplugs are effective when environmental noise cannot be controlled, and masking isn’t sufficient. But earplugs come with their own challenges. They can be uncomfortable, particularly for side sleepers where pressure against the pillow pushes the earplug into the ear canal. They can cause ear canal irritation with prolonged use. They can make people feel isolated or anxious about not hearing important sounds (babies, smoke alarms, break-ins). They can be difficult to insert properly, falling out during the night or not blocking sound effectively.
Types of earplugs:
- Foam earplugs (€0.20-1 per pair): Cheap, disposable, and effective when properly inserted. Many people don’t insert them correctly, as you need to roll them small, pull your ear up and back to straighten the ear canal, insert deeply, and hold while they expand. Comfort varies by brand and ear canal size.
- Wax or silicone putty earplugs (€5-15 per box): Mould to your outer ear rather than inserting into the canal. More comfortable for some people, particularly side sleepers, but they provide less noise reduction.
- Moulded silicone earplugs (€10-30): Reusable, washable, more comfortable than foam for many people. Various shapes and sizes available. Provide moderate noise reduction.
- Custom-moulded earplugs (€100-300): Made from impressions of your ear canals by an audiologist. The most comfortable and effective option, but expensive. Worth it if you need earplugs nightly long-term.
- Electronic earplugs (€150-300): Reduce harmful loud noises while allowing some ambient sound through. Useful for people who want noise reduction but not complete silence, or who are concerned about not hearing alarms or children.
You should still be able to hear smoke alarms and safety warnings while wearing earplugs. Test this. If you can’t hear your smoke alarm with earplugs in, they’re blocking too much sound for safe use.
When Noise Can’t Be Eliminated: Adaptation and Acceptance
Sometimes, despite your best efforts, noise remains problematic, and you can’t control it. You live in a city with constant traffic. Your partner snores. You have neighbours who are loud at unpredictable times. In these situations, you’re left with imperfect solutions and a need to adapt.
Chronic stress and hypervigilance can increase noise sensitivity during sleep. If you’re in a state of elevated baseline arousal from work stress, relationship difficulty, financial worry, or trauma history, you’re more likely to sleep lightly and wake to sounds that wouldn’t disturb you when you’re less stressed. Addressing the underlying stress through therapy, meditation, exercise, or other stress-management practices can reduce noise sensitivity somewhat.
This doesn’t mean the noise isn’t really affecting your sleep or that it’s “all in your head.” The noise is real. But your nervous system’s response to the noise is modulated by your overall stress state. Reducing stress won’t eliminate the impact of loud noise, but it can make you more resilient to moderate noise.
White noise masking becomes more critical when noise can’t be eliminated. Invest in a quality white noise machine or multiple machines to ensure adequate sound masking. Experiment with different sounds to find what masks your specific noise problems most effectively while not being irritating itself.
Combination strategies work better than single approaches. White noise plus earplugs provides more noise reduction than either alone. Earplugs plus addressing underlying stress works better than just one. Heavy curtains plus white noise plus earplugs might be necessary for truly problematic noise environments.
Acceptance might ultimately be necessary if you’re in a noisy environment you cannot change and cannot currently leave. This doesn’t mean giving up. It means acknowledging that your sleep won’t be perfect in this situation, that some impact on sleep quality is unavoidable, and that you’ll do what you can to mitigate while recognising the limits. Sometimes moving to a quieter environment is the only real solution, and that might be a medium-term goal rather than something possible immediately.
Air Quality and Ventilation
The air you breathe during sleep affects sleep quality in ways most people never consider. Oxygen levels, carbon dioxide levels, humidity, allergens, and air circulation all impact how well you sleep.
In a closed bedroom with poor ventilation, carbon dioxide levels can rise significantly throughout the night as you exhale CO2 that isn’t replaced with fresh air. Elevated CO2 creates subtle physiological stress, and leads to slightly faster breathing, reduced sleep depth, and increased restlessness. You don’t consciously notice this, but your sleep quality suffers as a result.
Opening windows when the weather permits is the simplest solution. Fresh air circulation maintains oxygen levels, removes excess CO2, and generally creates a more comfortable sleep environment. There are potential downsides (noise, safety, temperature control issues in extreme weather) but when possible, a window cracked open improves air quality substantially.
Air purifiers with HEPA filters remove allergens, dust, mould spores, and other particulates that can trigger allergies or respiratory irritation. They’re particularly valuable for people with asthma, allergies, or respiratory sensitivity. They also circulate air, preventing stuffiness. And as mentioned, they provide white noise masking. A quality air purifier costs €80-800, depending on room size and features.
Plants are often touted for improving air quality. But the reality is more modest, and the number of plants required to significantly impact air quality in a typical bedroom is impractically large. A few plants won’t meaningfully change oxygen or CO2 levels. That said, plants can improve psychological comfort (making the space feel more pleasant and natural), and some people find them calming. If you like plants, include them, but don’t expect them to solve air quality issues.
Avoiding irritants is crucial. Strong scents (air fresheners, scented candles, perfumes, cleaning products, etc.) can irritate airways and disrupt sleep for sensitive individuals. If you notice nasal congestion, throat irritation, or coughing during the night, consider whether scented products might be contributing. Unscented or very mildly scented products are better for bedroom use.
Smoke is an obvious irritant. Never smoke in bedrooms. If you live with smokers, ensure they smoke outside and away from bedroom windows. Smoke residue in bedding, curtains, and furnishings can continue affecting air quality long after the smoking occurred.
Dust accumulates in bedrooms and can trigger allergies or irritation. Regular cleaning, vacuuming (with a HEPA filter vacuum), washing bedding weekly, and dusting surfaces maintains better air quality.
Humidity levels between 40-60% are optimal for most people. Below 40%, the air becomes uncomfortably dry, leading to dry nasal passages, throat irritation, increased susceptibility to respiratory infections, and general discomfort. Above 60%, the air feels muggy, dust mites and mould thrive, and respiratory comfort decreases.
Humidifiers add moisture in dry climates or during winter when heating systems dry out indoor air. Cool mist humidifiers are generally preferable to warm mist (which can increase room temperature). But you do need to clean humidifiers regularly to prevent mould or bacterial growth.
Dehumidifiers remove excess moisture in humid climates or in spaces with poor ventilation and moisture problems. These are really only necessary if you live in very humid environments or have specific moisture issues in your bedroom (if you have an en suite with a shower, without excellent ventilation, moisture in the bedroom can be an issue, especially if you shower before bed).
Mattress Selection: Individual and Complicated
Unfortunately, there is no “best mattress.” Anyone telling you their mattress is perfect for everyone is selling you that mattress. What works depends on your sleeping position, body weight, temperature regulation, any pain or injury considerations, and personal preference, which varies enormously between individuals.
Sleeping position is the primary determinant. Side sleepers generally need softer mattresses that allow shoulders and hips to sink in while supporting the waist to maintain spinal alignment. Back sleepers typically prefer medium-firm mattresses that support the natural curve of the spine without allowing the hips to sink too deeply. Stomach sleepers (the least recommended position for spinal health) usually need firmer mattresses to prevent hyperextension of the lower back.
Body weight matters substantially. A mattress that feels medium-firm to someone weighing 60kg might feel much firmer to someone weighing 100kg because they compress the mattress less. Heavier individuals generally need firmer mattresses to prevent excessive sinking. Lighter individuals often find “medium-firm” mattresses too firm and prefer softer options.
Partner needs complicate things if you share a bed with someone whose body weight, sleeping position, or firmness preferences differ significantly from yours. The solutions here are to find a compromise on firmness that’s acceptable to both (usually medium or medium-firm), get a mattress with dual firmness zones, use a mattress topper on one side only, or, in extreme cases, use two separate mattresses on one frame (increasingly common in many parts of the world).
Materials include:
- Memory foam: Contours to body shape, relieves pressure points, absorbs motion (good for couples where one partner moves a lot). Can sleep hot unless infused with cooling gel or has good ventilation. This does have varying quality levels, and cheap memory foam can deteriorate quickly.
- Latex: More responsive than memory foam, doesn’t retain heat as much, durable (can last 15-20 years), naturally hypoallergenic. More expensive than memory foam. Comes in different firmness levels.
- Innerspring: Traditional coil mattresses. Good airflow (sleeps cooler), bouncy feel that some people prefer. Modern innersprings with pocketed coils reduce motion transfer better than older designs. Generally less expensive than foam or latex.
- Hybrid: Combines an innerspring base with foam or latex comfort layers. Attempts to get the benefits of both; support and cooling from coils, pressure relief from foam. Price and quality vary enormously.
Temperature regulation varies by material. Innerspring and latex sleep coolest due to better airflow. Traditional memory foam sleeps hottest. Gel-infused memory foam, open-cell foam, and various cooling technologies attempt to address this. If you sleep hot, prioritise mattresses with good temperature regulation or plan to use a cooling topper.
Durability: Mattresses deteriorate over time. Cheap foam compresses and develops body impressions within 3-5 years. Quality foam or latex can last 10-15 years. Innersprings typically last 7-10 years before springs start failing. When your mattress has visible sagging, you wake with pain that improves as the day progresses, or you sleep better on other mattresses (hotels, friends’ homes), it’s time to replace it.
Trial periods: Use them. Most online mattress companies offer 100-120 night trial periods. Most traditional mattress stores offer 30-90 day exchanges. Your body needs 2-3 weeks to adapt to a new mattress, but by 30 days, you’ll know if it’s working. Don’t keep a mattress that doesn’t work out of guilt or inertia. Sleep is too important.
Budget: Quality mattresses range from €400-2000+. This is a substantial expense, but divided over the 7-10 years you’ll use the mattress and the roughly 3,000 nights you’ll sleep on it, it’s £0.15-0.75 per night. Worth it for something that affects your health this much. Budget mattresses (under €400) can work, but often deteriorate faster or provide inadequate support. Ultra-premium mattresses (€3000+) show diminishing returns, and you’re often paying for branding rather than meaningfully better sleep.
Pillow Selection: More Important Than You Think
Pillows are crucial for maintaining proper spinal alignment during sleep, and most people use the wrong pillows for their sleeping position. The goal is to keep your head, neck, and spine in neutral alignment (e.g. the same position they’d be in if you were standing with good posture).
Side sleepers need relatively high loft (thick) pillows to fill the space between the side of their head and the mattress. The pillow needs to be firm enough to provide support without compressing too much. Side sleeping puts the most pressure on the shoulders and hips, and the pillow needs to keep the neck aligned with the spine. Many side sleepers benefit from a pillow between their knees as well, which prevents the top leg from dropping forward and rotating the pelvis, maintaining spinal alignment.
Back sleepers need medium loft pillows that support the natural curve of the neck without pushing the head too far forward. The pillow should cradle the neck while allowing the head to rest at a relatively neutral angle. Too high and you’re in chronic neck flexion. Too flat and you lose the natural cervical curve. Some back sleepers benefit from a small pillow or rolled towel under the knees to reduce lower back stress.
Stomach sleepers (not recommended, but common) need very flat or no pillows to avoid hyperextending the neck. Stomach sleeping with a thick pillow forces the neck into sustained rotation and extension, which, over time, causes pain and dysfunction. If you must sleep on your stomach, use the thinnest pillow possible or none at all, and try to train yourself to not sleep on your stomach.
Materials:
- Down: Soft, mouldable, luxurious. Expensive (€60-200+), requires fluffing regularly, may trigger allergies in sensitive individuals. Loses loft over time.
- Memory foam: Contours to the head and neck, maintains shape, good for people who need consistent support. Can sleep hot unless using gel-infused or ventilated memory foam. Solid foam pillows last longer than shredded foam.
- Latex: Responsive, cooling, durable (can last 5-7 years), naturally hypoallergenic. More expensive than memory foam (€50-150).
- Polyester fill: Inexpensive (€10-40), widely available. Compresses quickly, usually needs replacing annually. Fine for budget-conscious buyers who accept a shorter lifespan.
- Buckwheat hulls: Mouldable, cooling (excellent airflow), adjustable (you can remove hulls to reduce loft). Noisy, and it rustles when you move. Some people love them, others find the noise intolerable.
Number of pillows: One good pillow properly selected for your sleeping position is better than piling up multiple mediocre pillows. Using two or three pillows to get adequate loft usually means your head and/or neck aren’t properly aligned. Either get a thicker pillow or recognise you’re not actually a side sleeper (i.e. you may fall asleep on your side, but actually spend most of the night on your back).
Body pillows provide support along your entire body for side sleepers and can be comforting for back sleepers. They’re particularly valuable during pregnancy when maintaining a side sleeping position with support for the belly and knees improves comfort dramatically.
When to replace: Pillows should be replaced every 1-2 years, depending on the material. Down and quality memory foam or latex last toward the longer end. Polyester fill lasts 6-12 months before losing support. If your pillow is lumpy, has lost significant loft, causes you to wake with neck or shoulder pain, or you’re constantly repositioning it during the night, replace it.
Experimentation: Don’t be afraid to try different pillow configurations. Different pillows for different seasons (firmer in summer when you sleep more on your back, softer in winter). Different numbers of pillows. Different placements. What works is what allows you to wake without neck or shoulder pain while maintaining good spinal alignment.
Bedding and Blankets
The bedding and blankets you use affect temperature regulation, comfort, and even sleep quality through their impact on how you move during the night and how well they wick moisture.
Material is the most important consideration. Natural fibres (cotton, linen, bamboo, silk, wool) breathe better than synthetic materials (polyester, microfiber). They regulate temperature more effectively, wick moisture, and generally feel more comfortable against skin. The difference is substantial, and sleeping under polyester sheets versus cotton sheets in the same room temperature can mean the difference between comfortable sleep and overheated, restless sleep.
Egyptian cotton and pima cotton are considered premium for good reason. The longer fibres create softer, more durable fabric that improves with washing rather than deteriorating. Linen is exceptional for hot sleepers as it’s highly breathable, wicks moisture excellently, and actually gets softer over time. Bamboo offers a middle ground as it is soft, breathable, and more affordable than high-end cotton or linen. Silk is cooling and luxurious, but expensive and requires special care.
Thread count is overhyped. The sweet spot for cotton sheets is 300-500 thread count, as this is a tight enough weave for durability and softness, but loose enough for breathability. Higher thread counts (800+) create denser weaves that trap heat. They’re not necessarily better, just heavier and warmer.
Seasonal changes in bedding help maintain consistent body temperature throughout the year despite changing ambient temperatures. Heavy duvet in winter, light blanket or thin duvet in summer. Flannel sheets in winter, linen or lightweight cotton in summer. This might seem like unnecessary effort, but it’s one of the simplest ways to optimise temperature regulation across seasons.
Weighted blankets (typically 5-12kg) provide deep pressure stimulation that some people find calming and anxiety-reducing. The research is mixed, but many users report substantial benefits for anxiety and sleep quality. Others find them too restrictive or too hot. They’re worth trying if you have anxiety that interferes with sleep or if you enjoy the feeling of being tucked in firmly. Cost: €50-200 depending on weight and quality.
Cleanliness and hygiene matter more than most people realise. You spend eight hours per night in direct contact with your bedding, shedding skin cells, sweat, and oils. Sheets should be washed weekly. Pillowcases can be changed more frequently, roughly every 3-4 days, particularly if you have acne or oily skin. Mattress protectors prevent dust mites, allergens, and spills from reaching your mattress and should be washed monthly. Pillows should be washed or professionally cleaned every 3-6 months (depending on material).
Dust mites in particular thrive in bedding and can trigger allergies or respiratory issues even in people who don’t realise they’re sensitive. Regular washing in hot water (60°C+) kills dust mites. Hypoallergenic covers on mattresses and pillows provide barriers.
Electronics and EMF Concerns
The ideal is a bedroom completely free of electronics beyond a simple alarm clock. No phones charging on nightstands. No televisions. No laptops. No tablets. This serves multiple purposes: removes light sources from screens and charging indicators, removes temptation to use devices when you should be sleeping, and, for those concerned about electromagnetic fields (EMF), removes those sources as well.
The evidence for EMF from common household electronics affecting sleep is weak to nonexistent. The precautionary principle might suggest minimising EMF exposure anyway, but this isn’t a major health concern in the way that light and temperature are. That said, if you’re concerned, removing electronics from the bedroom is simple and has other benefits regardless of EMF considerations.
Alarm clocks should be simple, non-light-emitting or extremely dim. Many alarm clocks project bright light across the room all night, which we’ve established is terrible for sleep. Red LED displays are preferable to blue or white. Dimmable displays are ideal. Some people use alarm clocks that face away from the bed so the display doesn’t create light pollution.
Better yet, use an alarm clock that doesn’t emit light during the night. Good old-fashioned bell alarms, sunrise simulation alarms that gradually increase light only during wake-up time, or vibrating alarms that wake you through physical sensation rather than sound are all good options.
Charging devices outside the bedroom solves the problem comprehensively. Charge your phone in the bathroom or kitchen. Use an actual alarm clock. If you absolutely need your phone as an alarm (not recommended but common), put it across the room facing away from you so you can’t see the screen light, enable do-not-disturb mode, and commit to not checking it if you wake during the night.
Bedroom Colours and Decor
While less critical than darkness, temperature, and noise, the visual environment of your bedroom affects sleep quality psychologically. The room should feel calming, safe, and conducive to rest.
Calming colours like blues, greens, or soft neutrals are associated with better sleep than highly stimulating colours. This isn’t just aesthetic preference; it’s psychology. Blues and greens are subconsciously associated with nature, safety, and tranquillity. Reds, oranges, and very bright colours are associated with activation and arousal. You don’t need to repaint your bedroom if it’s not in the optimal colour scheme, but if you’re redecorating anyway, consider colours that support rest.
Minimising clutter reduces visual stress and makes the bedroom feel more like a sanctuary and less like a storage room. Cluttered spaces create low-level psychological stress. It signals unfinished tasks, things that need organising, and visual chaos. Clear surfaces, minimal visible belongings, organisation that makes the space feel calm rather than chaotic—all support the psychological transition to rest.
Artwork and aesthetics should be chosen based on what genuinely calms you. For some people, this means nature scenes, abstract art with muted colours, or minimalist design. For others, meaningful personal photographs or art that brings joy. There’s no universal prescription beyond “avoid artwork that creates stress or activation.”
Personal preference ultimately trumps rules. If you feel most restful in a maximalist bedroom filled with beloved objects, that’s more important than minimalist design principles. The goal is to create a space that feels like a sanctuary to you specifically.
Special Situations and Compromises
Shared bedroom with partner who snores: This is one of the most challenging sleep environment issues because snoring can be extremely disruptive, the snorer often can’t help it, and resentment builds quickly. The solutions here are tricky. The snorer should see a doctor to rule out sleep apnea and explore treatment options (CPAP, oral appliances, positional therapy, weight loss if relevant), the non-snoring partner can use earplugs or white noise masking. Sleeping in separate rooms is genuinely a viable option and doesn’t mean your relationship is failing (many couples sleep better and are happier when both people actually rest well).
Shared bedroom with different schedules: This requires explicit negotiation and probably won’t be perfect. The later-schedule person uses minimal light (nightlights, headlamps, reading lights) and is as quiet as possible. The earlier-schedule person uses earplugs and sleep masks if needed. Both people accept some compromise. If the schedule difference is large (one person sleeping 10pm-6am, the other 2am-10am), separate bedrooms might be necessary for both people to actually sleep well.
Shared bedroom with baby or young child: This is temporary but brutal. Do what you need to survive; co-sleeping if that’s your choice and you follow safe sleep guidelines, crib in your room, separate nursery with monitor, whatever works. Sleep deprivation with infants is unavoidable. Optimise what you can (darkness, temperature, taking turns with night wakings) and accept that this phase won’t last forever.
Small spaces: If your bedroom is also your living space, create psychological boundaries. Use room dividers, curtains, or furniture placement to partition the sleep space from the daytime space as much as possible. Follow the bed-is-for-sleep-only rule even more strictly since you can’t avoid using the bedroom during the day.
Temporary living situations: If you’re in temporary housing, traveling frequently, or in situations where you can’t control your sleep environment optimally, focus on the interventions you can implement: sleep mask for darkness, earplugs for noise, portable white noise app, fan if available, and maintaining your behavioral sleep hygiene (consistent times, wind-down routine, light exposure management) even when the physical environment isn’t ideal.
Sleep Environment Optimisation Conclusion
Sleep environment optimisation isn’t about creating some perfect, sterile sleep laboratory. It’s about recognising that sleep is a state of profound vulnerability, and your environment either supports that vulnerable state or undermines it. Every element we’ve discussed affects whether your brain feels safe enough to enter and maintain deep restorative sleep.
The modern world has created sleeping environments that systematically work against good sleep. We fill our bedrooms with electronics that emit light and create temptation. We keep them too warm because we’re uncomfortable being cool when awake. We tolerate noise because we think we’ve adapted to it. We use our beds as furniture for all purposes rather than sanctuaries for rest. And then we wonder why we feel exhausted despite spending eight hours in bed.
You can’t override your biology indefinitely. You can’t use willpower or discipline to sleep well in an environment that’s too bright, too warm, too noisy, or too uncomfortable. Your body has specific requirements for sleep, and when those requirements aren’t met, your sleep quality degrades, whether you’re consciously aware of it or not.
The interventions in this article range from free or nearly free (covering electronic lights with tape, opening windows, using your bed only for sleep) to substantial investments (blackout curtains, quality mattresses, air purifiers, cooling pads). You don’t need to implement everything. You need to identify which elements are currently undermining your sleep and address those systematically.
For most people, the highest-impact changes are achieving complete darkness through blackout curtains or sleep masks, reducing room temperature to 15-19°C, addressing noise through white noise or earplugs, and enforcing the bedroom-is-for-sleep-only rule. These four interventions probably account for 80% of the benefit of sleep environment optimisation.
But this isn’t just about sleep metrics or efficiency. It’s about creating a space that honours your fundamental need for rest, that signals to your nervous system, “This is a safe place to let go, to be vulnerable, to restore.” In a world that demands constant productivity, constant availability, and constant engagement, your bedroom should be your refuge. The one place where those demands don’t reach, where you can simply be rather than do.
You spend approximately a third of your life in your bedroom. That’s roughly 230,000 hours over a lifetime. The investment in making that space truly conducive to rest isn’t optional if you’re serious about living well. It’s foundational. Because everything else you’re trying to do with your work, your relationships, your health, your growth, your capacity to engage with life fully all depend on the quality of your sleep. And your sleep quality depends substantially on your sleep environment.
Now, I know this can be overwhelming, and I you don’t need to optimise everything at once. Start with these three interventions:
- Achieve darkness: Install blackout curtains, use window film, or purchase a quality sleep mask. Test the darkness; you should not be able to see anything without lights. Cover or remove any electronics that emit light.
- Lower the temperature: Set your thermostat to 17°C tonight. Yes, it will feel cold initially. Give it one week before deciding it doesn’t work. Most people adapt within 3-4 nights and then notice they actually sleep noticeably better. If you don’t have a thermostat, open a window (assuming it is safe to leave it open all night), and let the room cool down.
- Enforce bedroom boundaries: Starting tonight, use your bed only for sleep and sex. No screens in bed, no work in bed, no eating in bed. If you can’t sleep after 20 minutes, get up and go to another room. Return only when you feel sleepy.
These three changes will produce noticeable improvements within a week for most people. Once these are established, you can address noise, air quality, mattress quality, and the other elements we’ve discussed.
As with everything, there is always more to learn, and we haven’t even begun to scratch the surface with all this stuff. However, if you are interested in staying up to date with all our content, we recommend subscribing to our newsletter and bookmarking our free content page. We do have a lot of content on sleep in our sleep hub.
The previous article in this series was Light Exposure Management: Foundational Sleep Hygiene, and the next article in this series is Stimulant Management: Foundational Sleep Hygiene.
If you would like more help with your training (or nutrition), we do also have online coaching spaces available.
We also recommend reading our foundational nutrition articles, along with our foundational articles on exercise and stress management, if you really want to learn more about how to optimise your lifestyle. If you want even more free information on sleep, you can follow us on Instagram, YouTube or listen to the podcast, where we discuss all the little intricacies of exercise.
Finally, if you want to learn how to coach nutrition, then consider our Nutrition Coach Certification course. We do also have an exercise program design course, if you are a coach who wants to learn more about effective program design and how to coach it. We do have other courses available too, notably a sleep course. If you don’t understand something, or you just need clarification, you can always reach out to us on Instagram or via email.
References and Further Reading
Vyazovskiy, V. (2015). Sleep, recovery, and metaregulation: explaining the benefits of sleep. Nature and Science of Sleep, 171. http://doi.org/10.2147/nss.s54036
Sharma, S., & Kavuru, M. (2010). Sleep and Metabolism: An Overview. International Journal of Endocrinology, 2010, 1–12. http://doi.org/10.1155/2010/270832
Yoo, S.-S., Gujar, N., Hu, P., Jolesz, F. A., & Walker, M. P. (2007). The human emotional brain without sleep — a prefrontal amygdala disconnect. Current Biology, 17(20). http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2007.08.007
Copinschi G. Metabolic and endocrine effects of sleep deprivation. Essent Psychopharmacol. 2005;6(6):341-7. PMID: 16459757. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16459757/
Spiegel, K., Leproult, R., L’Hermite-Balériaux, M., Copinschi, G., Penev, P. D., & Cauter, E. V. (2004). Leptin Levels Are Dependent on Sleep Duration: Relationships with Sympathovagal Balance, Carbohydrate Regulation, Cortisol, and Thyrotropin. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 89(11), 5762–5771. http://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2004-1003
Nedeltcheva, A. V., Kilkus, J. M., Imperial, J., Kasza, K., Schoeller, D. A., & Penev, P. D. (2008). Sleep curtailment is accompanied by increased intake of calories from snacks. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 89(1), 126–133. http://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2008.26574
Mullington, J. M., Chan, J. L., Dongen, H. P. A. V., Szuba, M. P., Samaras, J., Price, N. J., … Mantzoros, C. S. (2003). Sleep Loss Reduces Diurnal Rhythm Amplitude of Leptin in Healthy Men. Journal of Neuroendocrinology, 15(9), 851–854. http://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2826.2003.01069.x
Leproult, R., & Cauter, E. V. (2009). Role of Sleep and Sleep Loss in Hormonal Release and Metabolism. Pediatric Neuroendocrinology Endocrine Development, 11–21. http://doi.org/10.1159/000262524
Spaeth, A. M., Dinges, D. F., & Goel, N. (2013). Effects of Experimental Sleep Restriction on Weight Gain, Caloric Intake, and Meal Timing in Healthy Adults. Sleep, 36(7), 981–990. http://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.2792
Calvin, A. D., Carter, R. E., Adachi, T., Macedo, P. G., Albuquerque, F. N., Walt, C. V. D., … Somers, V. K. (2013). Effects of Experimental Sleep Restriction on Caloric Intake and Activity Energy Expenditure. Chest, 144(1), 79–86. http://doi.org/10.1378/chest.12-2829
Markwald, R. R., Melanson, E. L., Smith, M. R., Higgins, J., Perreault, L., Eckel, R. H., & Wright, K. P. (2013). Impact of insufficient sleep on total daily energy expenditure, food intake, and weight gain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 110(14), 5695–5700. http://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1216951110
Cauter, E. V., Spiegel, K., Tasali, E., & Leproult, R. (2008). Metabolic consequences of sleep and sleep loss. Sleep Medicine, 9. http://doi.org/10.1016/s1389-9457(08)70013-3
Spiegel, K., Leproult, R., & Cauter, E. V. (1999). Impact of sleep debt on metabolic and endocrine function. The Lancet, 354(9188), 1435–1439. http://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(99)01376-8
Ness, K. M., Strayer, S. M., Nahmod, N. G., Schade, M. M., Chang, A.-M., Shearer, G. C., & Buxton, O. M. (2019). Four nights of sleep restriction suppress the postprandial lipemic response and decrease satiety. Journal of Lipid Research, 60(11), 1935–1945. http://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.p094375
Hirotsu, C., Tufik, S., & Andersen, M. L. (2015). Interactions between sleep, stress, and metabolism: From physiological to pathological conditions. Sleep Science, 8(3), 143–152. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.slsci.2015.09.002
Morselli, L., Leproult, R., Balbo, M., & Spiegel, K. (2010). Role of sleep duration in the regulation of glucose metabolism and appetite. Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 24(5), 687–702. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.beem.2010.07.005
Lamon, S., Morabito, A., Arentson-Lantz, E., Knowles, O., Vincent, G. E., Condo, D., … Aisbett, B. (2020). The effect of acute sleep deprivation on skeletal muscle protein synthesis and the hormonal environment. http://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.09.984666
Lipton, J. O., & Sahin, M. (2014). The Neurology of mTOR. Neuron, 84(2), 275–291. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.09.034
Tudor, J. C., Davis, E. J., Peixoto, L., Wimmer, M. E., Tilborg, E. V., Park, A. J., … Abel, T. (2016). Sleep deprivation impairs memory by attenuating mTORC1-dependent protein synthesis. Science Signaling, 9(425). http://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.aad4949
Dattilo, M., Antunes, H., Medeiros, A., Neto, M. M., Souza, H., Tufik, S., & Mello, M. D. (2011). Sleep and muscle recovery: Endocrinological and molecular basis for a new and promising hypothesis. Medical Hypotheses, 77(2), 220–222. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2011.04.017
Thornton, S. N., & Trabalon, M. (2014). Chronic dehydration is associated with obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Clinical Science, 128(3), 225–225. http://doi.org/10.1042/cs20140496
Rosinger, A. Y., Chang, A.-M., Buxton, O. M., Li, J., Wu, S., & Gao, X. (2018). Short sleep duration is associated with inadequate hydration: cross-cultural evidence from US and Chinese adults. Sleep, 42(2). http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/zsy210
Watson, A. M. (2017). Sleep and Athletic Performance. Current Sports Medicine Reports, 16(6), 413–418. http://doi.org/10.1249/jsr.0000000000000418
Bonnar, D., Bartel, K., Kakoschke, N., & Lang, C. (2018). Sleep Interventions Designed to Improve Athletic Performance and Recovery: A Systematic Review of Current Approaches. Sports Medicine, 48(3), 683–703. http://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-017-0832-x
Saidi, O., Davenne, D., Lehorgne, C., & Duché, P. (2020). Effects of timing of moderate exercise in the evening on sleep and subsequent dietary intake in lean, young, healthy adults: randomized crossover study. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 120(7), 1551–1562. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-020-04386-6
Abedelmalek, S., Chtourou, H., Aloui, A., Aouichaoui, C., Souissi, N., & Tabka, Z. (2012). Effect of time of day and partial sleep deprivation on plasma concentrations of IL-6 during a short-term maximal performance. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 113(1), 241–248. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-012-2432-7
Azboy, O., & Kaygisiz, Z. (2009). Effects of sleep deprivation on cardiorespiratory functions of the runners and volleyball players during rest and exercise. Acta Physiologica Hungarica, 96(1), 29–36. http://doi.org/10.1556/aphysiol.96.2009.1.3
Bird, S. P. (2013). Sleep, Recovery, and Athletic Performance. Strength and Conditioning Journal, 35(5), 43–47. http://doi.org/10.1519/ssc.0b013e3182a62e2f
Blumert, P. A., Crum, A. J., Ernsting, M., Volek, J. S., Hollander, D. B., Haff, E. E., & Haff, G. G. (2007). The Acute Effects of Twenty-Four Hours of Sleep Loss on the Performance of National-Caliber Male Collegiate Weightlifters. The Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 21(4), 1146. http://doi.org/10.1519/r-21606.1
Chase, J. D., Roberson, P. A., Saunders, M. J., Hargens, T. A., Womack, C. J., & Luden, N. D. (2017). One night of sleep restriction following heavy exercise impairs 3-km cycling time-trial performance in the morning. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, 42(9), 909–915. http://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2016-0698
Edwards, B. J., & Waterhouse, J. (2009). Effects of One Night of Partial Sleep Deprivation upon Diurnal Rhythms of Accuracy and Consistency in Throwing Darts. Chronobiology International, 26(4), 756–768. http://doi.org/10.1080/07420520902929037
Fullagar, H. H. K., Skorski, S., Duffield, R., Hammes, D., Coutts, A. J., & Meyer, T. (2014). Sleep and Athletic Performance: The Effects of Sleep Loss on Exercise Performance, and Physiological and Cognitive Responses to Exercise. Sports Medicine, 45(2), 161–186. http://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-014-0260-0
Gupta, L., Morgan, K., & Gilchrist, S. (2016). Does Elite Sport Degrade Sleep Quality? A Systematic Review. Sports Medicine, 47(7), 1317–1333. http://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-016-0650-6
Hausswirth, C., Louis, J., Aubry, A., Bonnet, G., Duffield, R., & Meur, Y. L. (2014). Evidence of Disturbed Sleep and Increased Illness in Overreached Endurance Athletes. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 46(5), 1036–1045. http://doi.org/10.1249/mss.0000000000000177
Mah, C. D., Mah, K. E., Kezirian, E. J., & Dement, W. C. (2011). The Effects of Sleep Extension on the Athletic Performance of Collegiate Basketball Players. Sleep, 34(7), 943–950. http://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.1132
Milewski, M. D., Skaggs, D. L., Bishop, G. A., Pace, J. L., Ibrahim, D. A., Wren, T. A., & Barzdukas, A. (2014). Chronic Lack of Sleep is Associated With Increased Sports Injuries in Adolescent Athletes. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics, 34(2), 129–133. http://doi.org/10.1097/bpo.0000000000000151
Mougin, F., Bourdin, H., Simon-Rigaud, M., Didier, J., Toubin, G., & Kantelip, J. (1996). Effects of a Selective Sleep Deprivation on Subsequent Anaerobic Performance. International Journal of Sports Medicine, 17(02), 115–119. http://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-972818
Oliver, S. J., Costa, R. J. S., Laing, S. J., Bilzon, J. L. J., & Walsh, N. P. (2009). One night of sleep deprivation decreases treadmill endurance performance. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 107(2), 155–161. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1103-9
Pallesen, S., Gundersen, H. S., Kristoffersen, M., Bjorvatn, B., Thun, E., & Harris, A. (2017). The Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Soccer Skills. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 124(4), 812–829. http://doi.org/10.1177/0031512517707412
Reilly, T., & Piercy, M. (1994). The effect of partial sleep deprivation on weight-lifting performance. Ergonomics, 37(1), 107–115. http://doi.org/10.1080/00140139408963628
Rossa, K. R., Smith, S. S., Allan, A. C., & Sullivan, K. A. (2014). The Effects of Sleep Restriction on Executive Inhibitory Control and Affect in Young Adults. Journal of Adolescent Health, 55(2), 287–292. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2013.12.034
Sargent, C., & Roach, G. D. (2016). Sleep duration is reduced in elite athletes following night-time competition. Chronobiology International, 33(6), 667–670. http://doi.org/10.3109/07420528.2016.1167715
Skein, M., Duffield, R., Edge, J., Short, M. J., & Mündel, T. (2011). Intermittent-Sprint Performance and Muscle Glycogen after 30 h of Sleep Deprivation. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 43(7), 1301–1311. http://doi.org/10.1249/mss.0b013e31820abc5a
Souissi, N., Sesboüé, B., Gauthier, A., Larue, J., & Davenne, D. (2003). Effects of one nights sleep deprivation on anaerobic performance the following day. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 89(3), 359–366. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-003-0793-7
Caia, J., Kelly, V. G., & Halson, S. L. (2017). The role of sleep in maximising performance in elite athletes. Sport, Recovery, and Performance, 151–167. http://doi.org/10.4324/9781315268149-11
Alley, J. R., Mazzochi, J. W., Smith, C. J., Morris, D. M., & Collier, S. R. (2015). Effects of Resistance Exercise Timing on Sleep Architecture and Nocturnal Blood Pressure. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 29(5), 1378–1385. http://doi.org/10.1519/jsc.0000000000000750
Kovacevic, A., Mavros, Y., Heisz, J. J., & Singh, M. A. F. (2018). The effect of resistance exercise on sleep: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 39, 52–68. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2017.07.002
Herrick, J. E., Puri, S., & Richards, K. C. (2017). Resistance training does not alter same-day sleep architecture in institutionalized older adults. Journal of Sleep Research, 27(4). http://doi.org/10.1111/jsr.12590
Edinger, J. D., Morey, M. C., Sullivan, R. J., Higginbotham, M. B., Marsh, G. R., Dailey, D. S., & McCall, W. V. (1993). Aerobic fitness, acute exercise and sleep in older men. Sleep, 16(4), 351-359. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/16.4.351
King, A. C. (1997). Moderate-intensity exercise and self-rated quality of sleep in older adults. A randomized controlled trial. JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association, 277(1), 32–37. http://doi.org/10.1001/jama.277.1.32
Passos, G. S., Poyares, D., Santana, M. G., Garbuio, S. A., Tufik, S., & Mello, M. T. (2010). Effect of Acute Physical Exercise on Patients with Chronic Primary Insomnia. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 06(03), 270–275. http://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.27825
Reid, K. J., Baron, K. G., Lu, B., Naylor, E., Wolfe, L., & Zee, P. C. (2010). Aerobic exercise improves self-reported sleep and quality of life in older adults with insomnia. Sleep Medicine, 11(9), 934–940. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2010.04.014
Viana, V. A. R., Esteves, A. M., Boscolo, R. A., Grassmann, V., Santana, M. G., Tufik, S., & Mello, M. T. D. (2011). The effects of a session of resistance training on sleep patterns in the elderly. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 112(7), 2403–2408. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-011-2219-2
Herring, M., Kline, C., & Oconnor, P. (2015). Effects of Exercise Training On Self-reported Sleep Among Young Women with Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD). European Psychiatry, 30, 465. http://doi.org/10.1016/s0924-9338(15)31893-9
Kredlow, M. A., Capozzoli, M. C., Hearon, B. A., Calkins, A. W., & Otto, M. W. (2015). The effects of physical activity on sleep: a meta-analytic review. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 38(3), 427–449. http://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-015-9617-6
Yang, P.-Y., Ho, K.-H., Chen, H.-C., & Chien, M.-Y. (2012). Exercise training improves sleep quality in middle-aged and older adults with sleep problems: a systematic review. Journal of Physiotherapy, 58(3), 157–163. http://doi.org/10.1016/s1836-9553(12)70106-6
Kline, C. E., Sui, X., Hall, M. H., Youngstedt, S. D., Blair, S. N., Earnest, C. P., & Church, T. S. (2012). Dose–response effects of exercise training on the subjective sleep quality of postmenopausal women: exploratory analyses of a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open, 2(4). http://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2012-001044
Fairbrother, K., Cartner, B. W., Triplett, N., Morris, D. M., & Collier, S. R. (2011). The Effects of Aerobic Exercise Timing on Sleep Architecture. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 43(Suppl 1), 879. http://doi.org/10.1249/01.mss.0000402452.16375.20
Youngstedt, S. D., & Kline, C. E. (2006). Epidemiology of exercise and sleep. Sleep and Biological Rhythms, 4(3), 215–221. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-8425.2006.00235.x
Stenholm, S., Head, J., Kivimäki, M., Hanson, L. L. M., Pentti, J., Rod, N. H., … Vahtera, J. (2018). Sleep Duration and Sleep Disturbances as Predictors of Healthy and Chronic Disease–Free Life Expectancy Between Ages 50 and 75: A Pooled Analysis of Three Cohorts. The Journals of Gerontology: Series A, 74(2), 204–210. http://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/gly01
Xiao, Q., Keadle, S. K., Hollenbeck, A. R., & Matthews, C. E. (2014). Sleep Duration and Total and Cause-Specific Mortality in a Large US Cohort: Interrelationships With Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior, and Body Mass Index. American Journal of Epidemiology, 180(10), 997–1006. http://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwu222
Reynolds, A. C., Dorrian, J., Liu, P. Y., Dongen, H. P. A. V., Wittert, G. A., Harmer, L. J., & Banks, S. (2012). Impact of Five Nights of Sleep Restriction on Glucose Metabolism, Leptin and Testosterone in Young Adult Men. PLoS ONE, 7(7). http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0041218
Åkerstedt, T., Palmblad, J., Torre, B. D. L., Marana, R., & Gillberg, M. (1980). Adrenocortical and Gonadal Steroids During Sleep Deprivation. Sleep, 3(1), 23–30. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/3.1.23
Cortés-Gallegos, V., Castañeda, G., Alonso, R., Sojo, I., Carranco, A., Cervantes, C., & Parra, A. (1983). Sleep Deprivation Reduces Circulating Androgens in Healthy Men. Archives of Andrology, 10(1), 33–37. http://doi.org/10.3109/01485018308990167
González-Santos, M. R., Gajá-Rodíguez, O. V., Alonso-Uriarte, R., Sojo-Aranda, I., & Cortés-Gallegos, V. (1989). Sleep Deprivation and Adaptive Hormonal Responses of Healthy Men. Archives of Andrology, 22(3), 203–207. http://doi.org/10.3109/01485018908986773
Penev, P. D. (2007). Association Between Sleep and Morning Testosterone Levels In Older Men. Sleep, 30(4), 427–432. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/30.4.427
Kloss, J. D., Perlis, M. L., Zamzow, J. A., Culnan, E. J., & Gracia, C. R. (2015). Sleep, sleep disturbance, and fertility in women. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 22, 78–87. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2014.10.005
Mahoney, M. M. (2010). Shift Work, Jet Lag, and Female Reproduction. International Journal of Endocrinology, 2010, 1–9. http://doi.org/10.1155/2010/813764
Labyak, S., Lava, S., Turek, F., & Zee, P. (2002). Effects Of Shiftwork On Sleep And Menstrual Function In Nurses. Health Care for Women International, 23(6-7), 703–714. http://doi.org/10.1080/07399330290107449
Pal, L., Bevilacqua, K., Zeitlian, G., Shu, J., & Santoro, N. (2008). Implications of diminished ovarian reserve (DOR) extend well beyond reproductive concerns. Menopause, 15(6), 1086–1094. http://doi.org/10.1097/gme.0b013e3181728467
Axelsson, G., Rylander, R., & Molin, I. (1989). Outcome of pregnancy in relation to irregular and inconvenient work schedules. Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 46(6), 393–398. http://doi.org/10.1136/oem.46.6.393
Bisanti, L., Olsen, J., Basso, O., Thonneau, P., & Karmaus, W. (1996). Shift Work and Subfecundity: A European Multicenter Study. Journal of Occupational & Environmental Medicine, 38(4), 352–358. http://doi.org/10.1097/00043764-199604000-00012
Rossmanith, W. G. (1998). The impact of sleep on gonadotropin secretion. Gynecological Endocrinology, 12(6), 381–389. http://doi.org/10.3109/09513599809012840
Fernando, S., & Rombauts, L. (2014). Melatonin: shedding light on infertility? – a review of the recent literature. Journal of Ovarian Research, 7(1). http://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-014-0098-y
Rocha, C., Rato, L., Martins, A., Alves, M., & Oliveira, P. (2015). Melatonin and Male Reproductive Health: Relevance of Darkness and Antioxidant Properties. Current Molecular Medicine, 15(4), 299–311. http://doi.org/10.2174/1566524015666150505155530
Song, C., Peng, W., Yin, S., Zhao, J., Fu, B., Zhang, J., … Zhang, Y. (2016). Melatonin improves age-induced fertility decline and attenuates ovarian mitochondrial oxidative stress in mice. Scientific Reports, 6(1). http://doi.org/10.1038/srep35165
Espino, J., Macedo, M., Lozano, G., Ortiz, Á., Rodríguez, C., Rodríguez, A. B., & Bejarano, I. (2019). Impact of Melatonin Supplementation in Women with Unexplained Infertility Undergoing Fertility Treatment. Antioxidants, 8(9), 338. http://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8090338
Tamura, H., Takasaki, A., Taketani, T., Tanabe, M., Kizuka, F., Lee, L., … Sugino, N. (2012). The role of melatonin as an antioxidant in the follicle. Journal of Ovarian Research, 5(1), 5. http://doi.org/10.1186/1757-2215-5-5
Saaresranta, T., & Polo, O. (2003). Sleep-disordered breathing and hormones. European Respiratory Journal, 22(1), 161–172. http://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.03.00062403
Cappuccio, F. P., Cooper, D., Delia, L., Strazzullo, P., & Miller, M. A. (2011). Sleep duration predicts cardiovascular outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. European Heart Journal, 32(12), 1484–1492. http://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehr007
Jansen, E. C., Dunietz, G. L., Tsimpanouli, M.-E., Guyer, H. M., Shannon, C., Hershner, S. D., … Baylin, A. (2018). Sleep, Diet, and Cardiometabolic Health Investigations: a Systematic Review of Analytic Strategies. Current Nutrition Reports, 7(4), 235–258. http://doi.org/10.1007/s13668-018-0240-3
Knutson, K. L., Cauter, E. V., Rathouz, P. J., Yan, L. L., Hulley, S. B., Liu, K., & Lauderdale, D. S. (2009). Association Between Sleep and Blood Pressure in Midlife. Archives of Internal Medicine, 169(11), 1055. http://doi.org/10.1001/archinternmed.2009.119
Besedovsky, L., Lange, T., & Born, J. (2011). Sleep and immune function. Pflügers Archiv – European Journal of Physiology, 463(1), 121–137. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-011-1044-0
Besedovsky, L., Lange, T., & Haack, M. (2019). The Sleep-Immune Crosstalk in Health and Disease. Physiological Reviews, 99(3), 1325–1380. http://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00010.2018
Orr, W. C., Fass, R., Sundaram, S. S., & Scheimann, A. O. (2020). The effect of sleep on gastrointestinal functioning in common digestive diseases. The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 5(6), 616–624. http://doi.org/10.1016/s2468-1253(19)30412-1
Tang, Y., Preuss, F., Turek, F. W., Jakate, S., & Keshavarzian, A. (2009). Sleep deprivation worsens inflammation and delays recovery in a mouse model of colitis. Sleep Medicine, 10(6), 597–603. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2008.12.009
Chen, Y., Tan, F., Wei, L., Li, X., Lyu, Z., Feng, X., … Li, N. (2018). Sleep duration and the risk of cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis including dose–response relationship. BMC Cancer, 18(1). http://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-5025-y
Almendros, I., Martinez-Garcia, M. A., Farré, R., & Gozal, D. (2020). Obesity, sleep apnea, and cancer. International Journal of Obesity, 44(8), 1653–1667. http://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-020-0549-z
Erren, T. C., Falaturi, P., Morfeld, P., Knauth, P., Reiter, R. J., & Piekarski, C. (2010). Shift Work and Cancer. Deutsches Aerzteblatt Online. http://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2010.0657
Bernert, R. A., Kim, J. S., Iwata, N. G., & Perlis, M. L. (2015). Sleep Disturbances as an Evidence-Based Suicide Risk Factor. Current Psychiatry Reports, 17(3). http://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-015-0554-4
Kim, J.-H., Park, E.-C., Cho, W.-H., Park, J.-Y., Choi, W.-J., & Chang, H.-S. (2013). Association between Total Sleep Duration and Suicidal Ideation among the Korean General Adult Population. Sleep, 36(10), 1563–1572. http://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.3058
Mccall, W. V., & Black, C. G. (2013). The Link Between Suicide and Insomnia: Theoretical Mechanisms. Current Psychiatry Reports, 15(9). http://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-013-0389-9
Li, S. X., Lam, S. P., Zhang, J., Yu, M. W. M., Chan, J. W. Y., Chan, C. S. Y., … Wing, Y.-K. (2016). Sleep Disturbances and Suicide Risk in an 8-Year Longitudinal Study of Schizophrenia-Spectrum Disorders. Sleep, 39(6), 1275–1282. http://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.5852
Littlewood, D. L., Gooding, P., Kyle, S. D., Pratt, D., & Peters, S. (2016). Understanding the role of sleep in suicide risk: qualitative interview study. BMJ Open, 6(8). http://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-012113
Lin, H.-T., Lai, C.-H., Perng, H.-J., Chung, C.-H., Wang, C.-C., Chen, W.-L., & Chien, W.-C. (2018). Insomnia as an independent predictor of suicide attempts: a nationwide population-based retrospective cohort study. BMC Psychiatry, 18(1). http://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-018-1702-2
Freeman, D., Sheaves, B., Waite, F., Harvey, A. G., & Harrison, P. J. (2020). Sleep disturbance and psychiatric disorders. The Lancet Psychiatry, 7(7), 628–637. http://doi.org/10.1016/s2215-0366(20)30136-x
Benca, R. M. (1992). Sleep and Psychiatric Disorders. Archives of General Psychiatry, 49(8), 651. http://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.1992.01820080059010
Breslau, N., Roth, T., Rosenthal, L., & Andreski, P. (1996). Sleep disturbance and psychiatric disorders: A longitudinal epidemiological study of young Adults. Biological Psychiatry, 39(6), 411–418. http://doi.org/10.1016/0006-3223(95)00188-3
Baglioni, C., Nanovska, S., Regen, W., Spiegelhalder, K., Feige, B., Nissen, C., … Riemann, D. (2016). Sleep and mental disorders: A meta-analysis of polysomnographic research. Psychological Bulletin, 142(9), 969–990. http://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000053
Goldstein, A. N., & Walker, M. P. (2014). The Role of Sleep in Emotional Brain Function. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 10(1), 679–708. http://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032813-153716
Postuma, R. B., Iranzo, A., Hu, M., Högl, B., Boeve, B. F., Manni, R., … Pelletier, A. (2019). Risk and predictors of dementia and parkinsonism in idiopathic REM sleep behaviour disorder: a multicentre study. Brain, 142(3), 744–759. http://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awz030
Wintler, T., Schoch, H., Frank, M. G., & Peixoto, L. (2020). Sleep, brain development, and autism spectrum disorders: Insights from animal models. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 98(6), 1137–1149. http://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.24619
Shokri-Kojori, E., Wang, G.-J., Wiers, C. E., Demiral, S. B., Guo, M., Kim, S. W., … Volkow, N. D. (2018). β-Amyloid accumulation in the human brain after one night of sleep deprivation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115(17), 4483–4488. http://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1721694115
Mantovani, S., Smith, S. S., Gordon, R., & Osullivan, J. D. (2018). An overview of sleep and circadian dysfunction in Parkinsons disease. Journal of Sleep Research, 27(3). http://doi.org/10.1111/jsr.12673
Malhotra, R. K. (2018). Neurodegenerative Disorders and Sleep. Sleep Medicine Clinics, 13(1), 63–70. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsmc.2017.09.006
Huang, L.-B., Tsai, M.-C., Chen, C.-Y., & Hsu, S.-C. (2013). The Effectiveness of Light/Dark Exposure to Treat Insomnia in Female Nurses Undertaking Shift Work during the Evening/Night Shift. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 09(07), 641–646. http://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.2824
Zhang, Y., & Papantoniou, K. (2019). Night shift work and its carcinogenicity. The Lancet Oncology, 20(10). http://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(19)30578-9
Perry-Jenkins, M., Goldberg, A. E., Pierce, C. P., & Sayer, A. G. (2007). Shift Work, Role Overload, and the Transition to Parenthood. Journal of Marriage and Family, 69(1), 123–138. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1741-3737.2006.00349.x
Rodziewicz TL, Hipskind JE. Medical Error Prevention. 2020 May 5. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan–. PMID: 29763131. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29763131/
Tanaka, K., Takahashi, M., Hiro, H., Kakinuma, M., Tanaka, M., Kamata, N., & Miyaoka, H. (2010). Differences in Medical Error Risk among Nurses Working Two- and Three-shift Systems at Teaching Hospitals: A Six-month Prospective Study. Industrial Health, 48(3), 357–364. http://doi.org/10.2486/indhealth.48.357
Admi H, Tzischinsky O, Epstein R, Herer P, Lavie P. Shift work in nursing: is it really a risk factor for nurses’ health and patients’ safety?. Nurs Econ. 2008;26(4):250-257. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18777974/
Clendon, J., & Gibbons, V. (2015). 12h shifts and rates of error among nurses: A systematic review. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 52(7), 1231–1242. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2015.03.011
Hammadah, M., Kindya, B. R., Allard‐Ratick, M. P., Jazbeh, S., Eapen, D., Tang, W. W., & Sperling, L. (2017). Navigating air travel and cardiovascular concerns: Is the sky the limit?, Clinical Cardiology, 40 (9), 660–666. http://doi.org/10.1002/clc.22741
Lieber, B. A., Han, J., Appelboom, G., Taylor, B. E., Han, B., Agarwal, N., & Connolly, E. S. (2016). Association of Steroid Use with Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Neurosurgical Patients: A National Database Analysis. World Neurosurgery, 89, 126–132. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2016.01.033
El-Menyar, A., Asim, M., & Al-Thani, H. (2017). Obesity Paradox in Patients With Deep Venous Thrombosis. Clinical and Applied Thrombosis/Hemostasis, 24(6), 986–992. http://doi.org/10.1177/1076029617727858
Klovaite, J., Benn, M., & Nordestgaard, B. G. (2014). Obesity as a causal risk factor for deep venous thrombosis: a Mendelian randomization study. Journal of Internal Medicine, 277(5), 573–584. http://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12299
Davies, H. O., Popplewell, M., Singhal, R., Smith, N., & Bradbury, A. W. (2016). Obesity and lower limb venous disease – The epidemic of phlebesity. Phlebology: The Journal of Venous Disease, 32(4), 227–233. http://doi.org/10.1177/0268355516649333
Liljeqvist, S., Helldén, A., Bergman, U., & Söderberg, M. (2008). Pulmonary embolism associated with the use of anabolic steroids. European Journal of Internal Medicine, 19(3), 214–215. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2007.03.016
Linton MF, Yancey PG, Davies SS, Jerome WG (Jay), Linton EF, Vickers KC. The Role of Lipids and Lipoproteins in Atherosclerosis. In: De Groot LJ, Chrousos G, Dungan K, et al., eds. Endotext. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK343489/.
Rescheduling of meals may ease the effects of jet lag. (2017). Nursing Standard, 31(48), 16–16. http://doi.org/10.7748/ns.31.48.16.s17
Ruscitto, C., & Ogden, J. (2016). The impact of an implementation intention to improve mealtimes and reduce jet lag in long-haul cabin crew. Psychology & Health, 32(1), 61–77. http://doi.org/10.1080/08870446.2016.1240174
Reid, K. J., & Abbott, S. M. (2015). Jet Lag and Shift Work Disorder. Sleep Medicine Clinics, 10(4), 523–535. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsmc.2015.08.006
Srinivasan, V., Spence, D. W., Pandi-Perumal, S. R., Trakht, I., & Cardinali, D. P. (2008). Jet lag: Therapeutic use of melatonin and possible application of melatonin analogs. Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease, 6(1-2), 17–28. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmaid.2007.12.002
Edwards, B. J., Atkinson, G., Waterhouse, J., Reilly, T., Godfrey, R., & Budgett, R. (2000). Use of melatonin in recovery from jet-lag following an eastward flight across 10 time-zones. Ergonomics, 43(10), 1501–1513. http://doi.org/10.1080/001401300750003934
Zee, P. C., & Goldstein, C. A. (2010). Treatment of Shift Work Disorder and Jet Lag. Current Treatment Options in Neurology, 12(5), 396–411. http://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-010-0090-9
https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/circadian-rhythm-disorders
Borodkin, K., & Dagan, Y. (2013). Diagnostic Algorithm for Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders. Encyclopedia of Sleep, 66–73. http://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-378610-4.00284-9
Lockley, S. (2013). Special Considerations and Future Directions in Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders Diagnosis. Encyclopedia of Sleep, 138–149. http://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-378610-4.00299-0
Crowley, S., & Youngstedt, S. (2013). Pathophysiology, Associations, and Consequences of Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorder. Encyclopedia of Sleep, 16–21. http://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-378610-4.00266-7
Franken, P., & Dijk, D.-J. (2009). Circadian clock genes and sleep homeostasis. European Journal of Neuroscience, 29(9), 1820–1829. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06723.x
Burgess, H. J., & Emens, J. S. (2016). Circadian-Based Therapies for Circadian Rhythm Sleep-Wake Disorders. Current Sleep Medicine Reports, 2(3), 158–165. http://doi.org/10.1007/s40675-016-0052-1
Jones, C. R., Huang, A. L., Ptáček, L. J., & Fu, Y.-H. (2013). Genetic basis of human circadian rhythm disorders. Experimental Neurology, 243, 28–33. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.07.012
Toh KL. Basic science review on circadian rhythm biology and circadian sleep disorders. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2008;37(8):662-668. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18797559/
Farhud D, Aryan Z. Circadian Rhythm, Lifestyle and Health: A Narrative Review. Iran J Public Health. 2018;47(8):1068-1076. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6123576/
Dodson, E. R., & Zee, P. C. (2010). Therapeutics for Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders. Sleep Medicine Clinics, 5(4), 701–715. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsmc.2010.08.001
Zhu, L., & Zee, P. C. (2012). Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders. Neurologic Clinics, 30(4), 1167–1191. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncl.2012.08.011
Kim MJ, Lee JH, Duffy JF. Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders. J Clin Outcomes Manag. 2013;20(11):513-528. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4212693/
Zhong, G., Naismith, S. L., Rogers, N. L., & Lewis, S. J. G. (2011). Sleep-wake disturbances in common neurodegenerative diseases: A closer look at selected aspects of the neural circuitry. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 307(1-2), 9–14. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2011.04.020
Dijk, D.-J., Boulos, Z., Eastman, C. I., Lewy, A. J., Campbell, S. S., & Terman, M. (1995). Light Treatment for Sleep Disorders: Consensus Report. Journal of Biological Rhythms, 10(2), 113–125. http://doi.org/10.1177/074873049501000204
Barion, A., & Zee, P. C. (2007). A clinical approach to circadian rhythm sleep disorders. Sleep Medicine, 8(6), 566–577. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2006.11.017
Horne JA, Ostberg O. A self-assessment questionnaire to determine morningness-eveningness in human circadian rhythms. Int J Chronobiol. 1976;4(2):97-110. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1027738/
Adan, A., & Almirall, H. (1991). Horne & Östberg morningness-eveningness questionnaire: A reduced scale. Personality and Individual Differences, 12(3), 241–253. http://doi.org/10.1016/0191-8869(91)90110-w
Urbán, R., Magyaródi, T., & Rigó, A. (2011). Morningness-Eveningness, Chronotypes and Health-Impairing Behaviors in Adolescents. Chronobiology International, 28(3), 238–247. http://doi.org/10.3109/07420528.2010.549599
https://www.thewep.org/documentations/mctq
Buysse, D. J., Reynolds, C. F., Monk, T. H., Berman, S. R., & Kupfer, D. J. (1989). The Pittsburgh sleep quality index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Research, 28(2), 193–213. http://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1781(89)90047-4
Bastien, C. (2001). Validation of the Insomnia Severity Index as an outcome measure for insomnia research. Sleep Medicine, 2(4), 297–307. http://doi.org/10.1016/s1389-9457(00)00065-4
Yang, M., Morin, C. M., Schaefer, K., & Wallenstein, G. V. (2009). Interpreting score differences in the Insomnia Severity Index: using health-related outcomes to define the minimally important difference. Current Medical Research and Opinion, 25(10), 2487–2494. http://doi.org/10.1185/03007990903167415
Morin, C. M., Belleville, G., Bélanger, L., & Ivers, H. (2011). The Insomnia Severity Index: Psychometric Indicators to Detect Insomnia Cases and Evaluate Treatment Response. Sleep, 34(5), 601–608. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/34.5.601
Castriotta RJ, Wilde MC, Lai JM, Atanasov S, Masel BE, Kuna ST. Prevalence and consequences of sleep disorders in traumatic brain injury. J Clin Sleep Med. 2007;3(4):349-356. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17694722/
Chokroverty S. Overview of sleep & sleep disorders. Indian J Med Res. 2010;131:126-140. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20308738/
Pavlova, M. K., & Latreille, V. (2019). Sleep Disorders. The American Journal of Medicine, 132(3), 292–299. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2018.09.021
Olejniczak, P. W., & Fisch, B. J. (2003). Sleep disorders. Medical Clinics of North America, 87(4), 803–833. http://doi.org/10.1016/s0025-7125(03)00006-3
https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/sleep-apnea
https://clevemed.com/what-is-sleep-apnea/patient-sleep-apnea-screener/
Spicuzza, L., Caruso, D., & Maria, G. D. (2015). Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome and its management. Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease, 6(5), 273–285. http://doi.org/10.1177/2040622315590318
Bixler, E. O., Vgontzas, A. N., Lin, H.-M., Liao, D., Calhoun, S., Fedok, F., … Graff, G. (2008). Blood Pressure Associated With Sleep-Disordered Breathing in a Population Sample of Children. Hypertension, 52(5), 841–846. http://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.108.116756
Campos, A. I., García-Marín, L. M., Byrne, E. M., Martin, N. G., Cuéllar-Partida, G., & Rentería, M. E. (2020). Insights into the aetiology of snoring from observational and genetic investigations in the UK Biobank. Nature Communications, 11(1). http://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14625-1
Morgenthaler, T. I., Kagramanov, V., Hanak, V., & Decker, P. A. (2006). Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Is It a Unique Clinical Syndrome? Sleep, 29(9), 1203–1209. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/29.9.1203
El-Ad, B., & Lavie, P. (2005). Effect of sleep apnea on cognition and mood. International Review of Psychiatry, 17(4), 277–282. http://doi.org/10.1080/09540260500104508
Morgenstern, M., Wang, J., Beatty, N., Batemarco, T., Sica, A. L., & Greenberg, H. (2014). Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America, 43(1), 187–204. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecl.2013.09.002
Sleep–Related Breathing Disorders in Adults: Recommendations for Syndrome Definition and Measurement Techniques in Clinical Research. (1999). Sleep, 22(5), 667–689. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/22.5.667
Ruehland, W. R., Rochford, P. D., O’Donoghue, F. J., Pierce, R. J., Singh, P., & Thornton, A. T. (2009). The New AASM Criteria for Scoring Hypopneas: Impact on the Apnea Hypopnea Index. Sleep, 32(2), 150–157. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/32.2.150
Selim, B. J., Koo, B. B., Qin, L., Jeon, S., Won, C., Redeker, N. S., … Yaggi, H. K. (2016). The Association between Nocturnal Cardiac Arrhythmias and Sleep-Disordered Breathing: The DREAM Study. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 12(06), 829–837. http://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.5880
Ahmed, M. H. (2010). Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and fatty liver: Association or causal link? World Journal of Gastroenterology, 16(34), 4243. http://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i34.4243
Singh, H., Pollock, R., Uhanova, J., Kryger, M., Hawkins, K., & Minuk, G. Y. (2005). Symptoms of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 50(12), 2338–2343. http://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-3058-y
Lawati, N. M. A., Patel, S. R., & Ayas, N. T. (2009). Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Consequences of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Short Sleep Duration. Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases, 51(4), 285–293. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2008.08.001
Young, T. (2004). Risk Factors for Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Adults. Jama, 291(16), 2013. http://doi.org/10.1001/jama.291.16.2013
Yaggi, H. K., Concato, J., Kernan, W. N., Lichtman, J. H., Brass, L. M., & Mohsenin, V. (2005). Obstructive Sleep Apnea as a Risk Factor for Stroke and Death. New England Journal of Medicine, 353(19), 2034–2041. http://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa043104
Redline, S., Budhiraja, R., Kapur, V., Marcus, C. L., Mateika, J. H., Mehra, R., … Quan, A. S. F. (2007). The Scoring of Respiratory Events in Sleep: Reliability and Validity. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 03(02), 169–200. http://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.26818
Basheer B, Hegde KS, Bhat SS, Umar D, Baroudi K. Influence of mouth breathing on the dentofacial growth of children: a cephalometric study. J Int Oral Health. 2014;6(6):50-55. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4295456/
Ruhle, K. H., & Nilius, G. (2008). Mouth Breathing in Obstructive Sleep Apnea prior to and during Nasal Continuous Positive Airway Pressure. Respiration, 76(1), 40–45. http://doi.org/10.1159/000111806
Izu, S. C., Itamoto, C. H., Pradella-Hallinan, M., Pizarro, G. U., Tufik, S., Pignatari, S., & Fujita, R. R. (2010). Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) in mouth breathing children. Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, 76(5), 552–556. http://doi.org/10.1590/s1808-86942010000500003
Lee, S. H., Choi, J. H., Shin, C., Lee, H. M., Kwon, S. Y., & Lee, S. H. (2007). How Does Open-Mouth Breathing Influence Upper Airway Anatomy? The Laryngoscope, 117(6), 1102–1106. http://doi.org/10.1097/mlg.0b013e318042aef7
Tuomilehto, H. P. I., Seppä, J. M., Partinen, M. M., Peltonen, M., Gylling, H., Tuomilehto, J. O. I., … Uusitupa, M. (2009). Lifestyle Intervention with Weight Reduction. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 179(4), 320–327. http://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200805-669oc
https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/obesity-overweight.htm
Neill, A. M., Angus, S. M., Sajkov, D., & Mcevoy, R. D. (1997). Effects of sleep posture on upper airway stability in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 155(1), 199–204. http://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.155.1.9001312
Loord, H., & Hultcrantz, E. (2007). Positioner–a method for preventing sleep apnea. Acta Oto-Laryngologica, 127(8), 861–868. http://doi.org/10.1080/00016480601089390
Szollosi, I., Roebuck, T., Thompson, B., & Naughton, M. T. (2006). Lateral Sleeping Position Reduces Severity of Central Sleep Apnea / Cheyne-Stokes Respiration. Sleep, 29(8), 1045–1051. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/29.8.1045
Silverberg DS, Iaina A, Oksenberg A. Treating obstructive sleep apnea improves essential hypertension and quality of life. Am Fam Physician. 2002;65(2):229-236. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11820487/
Aurora, R. N., Chowdhuri, S., Ramar, K., Bista, S. R., Casey, K. R., Lamm, C. I., … Tracy, S. L. (2012). The Treatment of Central Sleep Apnea Syndromes in Adults: Practice Parameters with an Evidence-Based Literature Review and Meta-Analyses. Sleep, 35(1), 17–40. http://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.1580
Hsu, A. A. L., & Lo, C. (2003). Continuous positive airway pressure therapy in sleep apnoea. Respirology, 8(4), 447–454. http://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1843.2003.00494.x
Patel, S. R., White, D. P., Malhotra, A., Stanchina, M. L., & Ayas, N. T. (2003). Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Therapy for Treating gess in a Diverse Population With Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Archives of Internal Medicine, 163(5), 565. http://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.163.5.565
Sundaram, S., Lim, J., & Lasserson, T. J. (2005). Surgery for obstructive sleep apnoea in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. http://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd001004.pub2
Chen, H., & Lowe, A. A. (2012). Updates in oral appliance therapy for snoring and obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep and Breathing, 17(2), 473–486. http://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-012-0712-4
Gaisl, T., Haile, S. R., Thiel, S., Osswald, M., & Kohler, M. (2019). Efficacy of pharmacotherapy for OSA in adults: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 46, 74–86. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2019.04.009
Ohayon, M., Wickwire, E. M., Hirshkowitz, M., Albert, S. M., Avidan, A., Daly, F. J., … Vitiello, M. V. (2017). National Sleep Foundations sleep quality recommendations: first report. Sleep Health, 3(1), 6–19. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleh.2016.11.006
Youngstedt, S. D., Goff, E. E., Reynolds, A. M., Kripke, D. F., Irwin, M. R., Bootzin, R. R., … Jean-Louis, G. (2016). Has adult sleep duration declined over the last 50 years? Sleep Medicine Reviews, 28, 69–85. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2015.08.004
Chaput, J.-P., Mcneil, J., Després, J.-P., Bouchard, C., & Tremblay, A. (2013). Seven to Eight Hours of Sleep a Night Is Associated with a Lower Prevalence of the Metabolic Syndrome and Reduced Overall Cardiometabolic Risk in Adults. PLoS ONE, 8(9). http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0072832
Wild, C. J., Nichols, E. S., Battista, M. E., Stojanoski, B., & Owen, A. M. (2018). Dissociable effects of self-reported daily sleep duration on high-level cognitive abilities. Sleep, 41(12). http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/zsy182
Hirshkowitz, M., Whiton, K., Albert, S. M., Alessi, C., Bruni, O., Doncarlos, L., … Hillard, P. J. A. (2015). National Sleep Foundation’s sleep time duration recommendations: methodology and results summary. Sleep Health, 1(1), 40–43. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleh.2014.12.010
Cappuccio, F. P., Delia, L., Strazzullo, P., & Miller, M. A. (2010). Sleep Duration and All-Cause Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Sleep, 33(5), 585–592. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/33.5.585
Gottlieb, D. J., Punjabi, N. M., Newman, A. B., Resnick, H. E., Redline, S., Baldwin, C. M., & Nieto, F. J. (2005). Association of Sleep Time With Diabetes Mellitus and Impaired Glucose Tolerance. Archives of Internal Medicine, 165(8), 863. http://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.165.8.863
Short, M. A., Agostini, A., Lushington, K., & Dorrian, J. (2015). A systematic review of the sleep, sleepiness, and performance implications of limited wake shift work schedules. Scandinavian Journal of Work, Environment & Health, 41(5), 425–440. http://doi.org/10.5271/sjweh.3509
Cappuccio, F. P., Taggart, F. M., Kandala, N.-B., Currie, A., Peile, E., Stranges, S., & Miller, M. A. (2008). Meta-Analysis of Short Sleep Duration and Obesity in Children and Adults. Sleep, 31(5), 619–626. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/31.5.619
Mong, J. A., & Cusmano, D. M. (2016). Sex differences in sleep: impact of biological sex and sex steroids. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 371(1688), 20150110. http://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2015.0110
Krishnan, V., & Collop, N. A. (2006). Gender differences in sleep disorders. Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine, 12(6), 383–389. http://doi.org/10.1097/01.mcp.0000245705.69440.6a
Mehta, N., Shafi, F., & Bhat, A. (2015). Unique Aspects of Sleep in Women. Missouri medicine, 112(6), 430–434. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6168103/
Moline, M. L., Broch, L., & Zak, R. (2004). Sleep in women across the life cycle from adulthood through menopause. Medical Clinics of North America, 88(3), 705–736. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2004.01.009
He, Y., Jones, C. R., Fujiki, N., Xu, Y., Guo, B., Holder, J. L., … Fu, Y.-H. (2009). The Transcriptional Repressor DEC2 Regulates Sleep Length in Mammals. Science, 325(5942), 866–870. http://doi.org/10.1126/science.1174443
Theorell-Haglöw, J., Berglund, L., Berne, C., & Lindberg, E. (2014). Both habitual short sleepers and long sleepers are at greater risk of obesity: a population-based 10-year follow-up in women. Sleep Medicine, 15(10), 1204–1211. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2014.02.014
Mezick, E. J., Wing, R. R., & Mccaffery, J. M. (2014). Associations of self-reported and actigraphy-assessed sleep characteristics with body mass index and waist circumference in adults: moderation by gender. Sleep Medicine, 15(1), 64–70. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2013.08.784
Kim, S. J. (2011). Relationship Between Weekend Catch-up Sleep and Poor Performance on Attention Tasks in Korean Adolescents. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, 165(9), 806. http://doi.org/10.1001/archpediatrics.2011.128
Kim, C.-W., Choi, M.-K., Im, H.-J., Kim, O.-H., Lee, H.-J., Song, J., … Park, K.-H. (2012). Weekend catch-up sleep is associated with decreased risk of being overweight among fifth-grade students with short sleep duration. Journal of Sleep Research, 21(5), 546–551. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2869.2012.01013.x
Sun, W., Ling, J., Zhu, X., Lee, T. M.-C., & Li, S. X. (2019). Associations of weekday-to-weekend sleep differences with academic performance and health-related outcomes in school-age children and youths. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 46, 27–53. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2019.04.003
Kang, S.-G., Lee, Y. J., Kim, S. J., Lim, W., Lee, H.-J., Park, Y.-M., … Hong, J. P. (2014). Weekend catch-up sleep is independently associated with suicide attempts and self-injury in Korean adolescents. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 55(2), 319–325. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2013.08.023
Zhao, M., Tuo, H., Wang, S., & Zhao, L. (2020). The Effects of Dietary Nutrition on Sleep and Sleep Disorders. Mediators of Inflammation, 2020, 1–7. http://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3142874
Doherty, Madigan, Warrington, & Ellis. (2019). Sleep and Nutrition Interactions: Implications for Athletes. Nutrients, 11(4), 822. http://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040822
Sutanto CN, Wang MX, Tan D, Kim JE. Association of Sleep Quality and Macronutrient Distribution: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression. Nutrients. 2020 Jan 2;12(1):126. doi: 10.3390/nu12010126. PMID: 31906452; PMCID: PMC7019667. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31906452/
Peuhkuri, K., Sihvola, N., & Korpela, R. (2012). Diet promotes sleep duration and quality. Nutrition Research, 32(5), 309–319. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2012.03.009
Afaghi, A., Oconnor, H., & Chow, C. M. (2007). High-glycemic-index carbohydrate meals shorten sleep onset. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 85(2), 426–430. http://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/85.2.426
Golem, D. L., Martin-Biggers, J. T., Koenings, M. M., Davis, K. F., & Byrd-Bredbenner, C. (2014). An Integrative Review of Sleep for Nutrition Professionals. Advances in Nutrition, 5(6), 742–759. http://doi.org/10.3945/an.114.006809
Grandner, M. A., Jackson, N., Gerstner, J. R., & Knutson, K. L. (2013). Sleep symptoms associated with intake of specific dietary nutrients. Journal of Sleep Research, 23(1), 22–34. http://doi.org/10.1111/jsr.12084
Porter, J., & Horne, J. (1981). Bed-time food supplements and sleep: Effects of different carbohydrate levels. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 51(4), 426–433. http://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4694(81)90106-1
Halson, S. L. (2014). Sleep in Elite Athletes and Nutritional Interventions to Enhance Sleep. Sports Medicine, 44(S1), 13–23. http://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-014-0147-0
Rondanelli, M., Opizzi, A., Monteferrario, F., Antoniello, N., Manni, R., & Klersy, C. (2011). The Effect of Melatonin, Magnesium, and Zinc on Primary Insomnia in Long-Term Care Facility Residents in Italy: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 59(1), 82–90. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2010.03232.x
Tahara, Y., & Shibata, S. (2014). Chrono-biology, Chrono-pharmacology, and Chrono-nutrition. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences, 124(3), 320–335. http://doi.org/10.1254/jphs.13r06cr
Landolt, H.-P., Werth, E., Borbély, A. A., & Dijk, D.-J. (1995). Caffeine intake (200 mg) in the morning affects human sleep and EEG power spectra at night. Brain Research, 675(1-2), 67–74. http://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(95)00040-w
Gottesmann, C. (2002). GABA mechanisms and sleep. Neuroscience, 111(2), 231–239. http://doi.org/10.1016/s0306-4522(02)00034-9
Campbell, S. S., Dawson, D., & Anderson, M. W. (1993). Alleviation of Sleep Maintenance Insomnia with Timed Exposure to Bright Light. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 41(8), 829–836. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.1993.tb06179.x
Zhao, J., Tian, Y., Nie, J., Xu, J., & Liu, D. (2012). Red Light and the Sleep Quality and Endurance Performance of Chinese Female Basketball Players. Journal of Athletic Training, 47(6), 673–678. http://doi.org/10.4085/1062-6050-47.6.08
Smolensky, M. H., Sackett-Lundeen, L. L., & Portaluppi, F. (2015). Nocturnal light pollution and underexposure to daytime sunlight: Complementary mechanisms of circadian disruption and related diseases. Chronobiology International, 32(8), 1029–1048. http://doi.org/10.3109/07420528.2015.1072002
Düzgün, G., & Akyol, A. D. (2017). Effect of Natural Sunlight on Sleep Problems and Sleep Quality of the Elderly Staying in the Nursing Home. Holistic Nursing Practice, 31(5), 295–302. http://doi.org/10.1097/hnp.0000000000000206
Valham, F., Sahlin, C., Stenlund, H., & Franklin, K. A. (2012). Ambient Temperature and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Effects on Sleep, Sleep Apnea, and Morning Alertness. Sleep, 35(4), 513–517. http://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.1736
Okamoto-Mizuno, K., Tsuzuki, K., & Mizuno, K. (2004). Effects of mild heat exposure on sleep stages and body temperature in older men. International Journal of Biometeorology, 49(1). http://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-004-0209-3
St-Onge, M.-P., & Shechter, A. (2014). Sleep disturbances, body fat distribution, food intake and/or energy expenditure: pathophysiological aspects. Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation, 17(1). http://doi.org/10.1515/hmbci-2013-0066
Chaput, J.-P., Després, J.-P., Bouchard, C., & Tremblay, A. (2008). The Association Between Sleep Duration and Weight Gain in Adults: A 6-Year Prospective Study from the Quebec Family Study. Sleep, 31(4), 517–523. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/31.4.517
Dekker, S. A., Noordam, R., Biermasz, N. R., Roos, A., Lamb, H. J., Rosendaal, F. R., … Mutsert, R. (2018). Habitual Sleep Measures are Associated with Overall Body Fat, and not Specifically with Visceral Fat, in Men and Women. Obesity, 26(10), 1651–1658. http://doi.org/10.1002/oby.22289
Tunnicliffe, J. M., Erdman, K. A., Reimer, R. A., Lun, V., & Shearer, J. (2008). Consumption of dietary caffeine and coffee in physically active populations: physiological interactions. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, 33(6), 1301–1310. http://doi.org/10.1139/h08-124
Mahoney, C. R., Giles, G. E., Marriott, B. P., Judelson, D. A., Glickman, E. L., Geiselman, P. J., & Lieberman, H. R. (2019). Intake of caffeine from all sources and reasons for use by college students. Clinical Nutrition, 38(2), 668–675. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2018.04.004
Binks, H., Vincent, G. E., Gupta, C., Irwin, C., & Khalesi, S. (2020). Effects of Diet on Sleep: A Narrative Review. Nutrients, 12(4), 936. http://doi.org/10.3390/nu12040936
Rao, T. P., Ozeki, M., & Juneja, L. R. (2015). In Search of a Safe Natural Sleep Aid. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 34(5), 436–447. http://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2014.926153
Abbasi B, Kimiagar M, Sadeghniiat K, Shirazi MM, Hedayati M, Rashidkhani B. The effect of magnesium supplementation on primary insomnia in elderly: A double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Res Med Sci. 2012 Dec;17(12):1161-9. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23853635/
Aspy, D. J., Madden, N. A., & Delfabbro, P. (2018). Effects of Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) and a B Complex Preparation on Dreaming and Sleep. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 003151251877032. http://doi.org/10.1177/0031512518770326
Parazzini F. Resveratrol, tryptophanum, glycine and vitamin E: a nutraceutical approach to sleep disturbance and irritability in peri- and post-menopause. Minerva Ginecol. 2015;67(1):1-5. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25660429/
Siegel JM. The neurotransmitters of sleep. J Clin Psychiatry. 2004;65 Suppl 16:4-7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15575797/
Djeridane, Y., Touitou, Y. Chronic diazepam administration differentially affects melatonin synthesis in rat pineal and Harderian glands. Psychopharmacology154, 403–407 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130000631
Betti L, Palego L, Demontis GC, Miraglia F, Giannaccini G. Hydroxyindole-O-methyltransferase (HIOMT) activity in the retina of melatonin-proficient mice. Heliyon. 2019;5(9):e02417. Published 2019 Sep 14. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02417
Haduch, A., Bromek, E., Wójcikowski, J., Gołembiowska, K., Daniel, W.. Melatonin Supports Serotonin Formation by Brain CYP2D. Drug Metabolism and DispositionMarch 1, 2016, 44 (3) 445-452; DOI: https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.115.067413
Morton, D. J. (1987). Mechanism of Inhibition of Bovine Pineal Gland Hydroxyindole-O-Methyltransferase (EC 2.1.1.4) by Divalent Cations. Journal of Pineal Research, 4(3), 295–303. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079x.1987.tb00867.x
Markova-Car, E. P., Jurišić, D., Ilić, N., & Pavelić, S. K. (2014). Running for time: circadian rhythms and melanoma. Tumor Biology, 35(9), 8359–8368. http://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1904-2
Slominski AT, Zmijewski MA, Skobowiat C, Zbytek B, Slominski RM, Steketee JD. Sensing the environment: regulation of local and global homeostasis by the skin’s neuroendocrine system. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2012;212:v-115. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-19683-6_1 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3422784/
Chalupsky, K., Kračun, D., Kanchev, I., Bertram, K., & Görlach, A. (2015). Folic Acid Promotes Recycling of Tetrahydrobiopterin and Protects Against Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension by Recoupling Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 23(14), 1076–1091. http://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2015.6329
Dianzani, I., Sanctis, L. D., Smooker, P. M., Gough, T. J., Alliaudi, C., Brusco, A., … Cotton, R. G. H. (1998). Dihydropteridine reductase deficiency: Physical structure of the QDPR gene, identification of two new mutations and genotype–phenotype correlations. Human Mutation, 12(4), 267–273. http://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1098-1004(1998)12:4<267::aid-humu8>3.0.co;2-c
Nichol, C. A., Lee, C. L., Edelstein, M. P., Chao, J. Y., & Duch, D. S. (1983). Biosynthesis of tetrahydrobiopterin by de novo and salvage pathways in adrenal medulla extracts, mammalian cell cultures, and rat brain in vivo. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 80(6), 1546–1550. http://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.80.6.1546
Titus, F., Dávalos, A., Alom, J., & Codina, A. (1986). 5-Hydroxytryptophan versus Methysergide in the Prophylaxis of Migraine. European Neurology, 25(5), 327–329. http://doi.org/10.1159/000116030
Birdsall TC. 5-Hydroxytryptophan: a clinically-effective serotonin precursor. Altern Med Rev. 1998;3(4):271-280. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9727088/
Volpi-Abadie J, Kaye AM, Kaye AD. Serotonin syndrome. Ochsner J. 2013;13(4):533-540. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3865832/
Valadas, J. S., Esposito, G., Vandekerkhove, D., Miskiewicz, K., Deaulmerie, L., Raitano, S., … Verstreken, P. (2018). ER Lipid Defects in Neuropeptidergic Neurons Impair Sleep Patterns in Parkinson’s Disease. Neuron, 98(6). http://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2018.05.022
Chung SY, Moriyama T, Uezu E, et al. Administration of phosphatidylcholine increases brain acetylcholine concentration and improves memory in mice with dementia. J Nutr. 1995;125(6):1484-1489. doi:10.1093/jn/125.6.1484 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7782901/
Montgomery, P., Burton, J. R., Sewell, R. P., Spreckelsen, T. F., & Richardson, A. J. (2014). Fatty acids and sleep in UK children: subjective and pilot objective sleep results from the DOLAB study – a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Sleep Research, 23(4), 364–388. http://doi.org/10.1111/jsr.12135
Alzoubi, K. H., Mayyas, F., & Zamzam, H. I. A. (2019). Omega-3 fatty acids protects against chronic sleep-deprivation induced memory impairment. Life Sciences, 227, 1–7. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.028
Nasehi, M., Mosavi-Nezhad, S.-M., Khakpai, F., & Zarrindast, M.-R. (2018). The role of omega-3 on modulation of cognitive deficiency induced by REM sleep deprivation in rats. Behavioural Brain Research, 351, 152–160. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2018.06.002
Jahangard, L., Sadeghi, A., Ahmadpanah, M., Holsboer-Trachsler, E., Bahmani, D. S., Haghighi, M., & Brand, S. (2018). Influence of adjuvant omega-3-polyunsaturated fatty acids on depression, sleep, and emotion regulation among outpatients with major depressive disorders – Results from a double-blind, randomized and placebo-controlled clinical trial. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 107, 48–56. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2018.09.016
Scorza, F. A., Cavalheiro, E. A., Scorza, C. A., Galduróz, J. C. F., Tufik, S., & Andersen, M. L. (2013). Sleep Apnea and Inflammation – Getting a Good Night’s Sleep with Omega-3 Supplementation. Frontiers in Neurology, 4. http://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2013.00193
Hansen, A. L., Dahl, L., Olson, G., Thornton, D., Graff, I. E., Frøyland, L., … Pallesen, S. (2014). Fish Consumption, Sleep, Daily Functioning, and Heart Rate Variability. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 10(05), 567–575. http://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.3714
Xie, L., Kang, H., Xu, Q., Chen, M. J., Liao, Y., Thiyagarajan, M., … Nedergaard, M. (2013). Sleep Drives Metabolite Clearance from the Adult Brain. Science, 342(6156), 373–377. http://doi.org/10.1126/science.1241224
Varshavsky, A. (2012). Augmented generation of protein fragments during wakefulness as the molecular cause of sleep: a hypothesis. Protein Science, 21(11), 1634–1661. http://doi.org/10.1002/pro.2148
Mackiewicz, M., Shockley, K. R., Romer, M. A., Galante, R. J., Zimmerman, J. E., Naidoo, N., … Pack, A. I. (2007). Macromolecule biosynthesis: a key function of sleep. Physiological Genomics, 31(3), 441–457. http://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00275.2006
Scharf, M. T., Naidoo, N., Zimmerman, J. E., & Pack, A. I. (2008). The energy hypothesis of sleep revisited. Progress in Neurobiology, 86(3), 264–280. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2008.08.003
Horne, J. (2009). REM sleep, energy balance and ‘optimal foraging.’ Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 33(3), 466–474. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.12.002
Berger, R. J., & Phillips, N. H. (1995). Energy conservation and sleep. Behavioural Brain Research, 69(1-2), 65–73. http://doi.org/10.1016/0166-4328(95)00002-b
Benington, J. H., & Heller, H. C. (1995). Restoration of brain energy metabolism as the function of sleep. Progress in Neurobiology, 45(4), 347–360. http://doi.org/10.1016/0301-0082(94)00057-o
Abel, T., Havekes, R., Saletin, J. M., & Walker, M. P. (2013). Sleep, Plasticity and Memory from Molecules to Whole-Brain Networks. Current Biology, 23(17). http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.07.025
Rasch, B., & Born, J. (2013). About Sleeps Role in Memory. Physiological Reviews, 93(2), 681–766. http://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00032.2012
Cirelli, C., & Tononi, G. (2008). Is Sleep Essential? PLoS Biology, 6(8). http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0060216
Siegel, J. M. (2005). Clues to the functions of mammalian sleep. Nature, 437(7063), 1264–1271. http://doi.org/10.1038/nature04285
Campbell, S. S., & Tobler, I. (1984). Animal sleep: A review of sleep duration across phylogeny. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 8(3), 269–300. http://doi.org/10.1016/0149-7634(84)90054-x
Tobler, I. (1995). Is sleep fundamentally different between mammalian species? Behavioural Brain Research, 69(1-2), 35–41. http://doi.org/10.1016/0166-4328(95)00025-o
Tononi, G., & Cirelli, C. (2006). Sleep function and synaptic homeostasis. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 10(1), 49–62. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2005.05.002
Dongen, H. P. A. V., Vitellaro, K. M., & Dinges, D. F. (2005). Individual Differences in Adult Human Sleep and Wakefulness: Leitmotif for a Research Agenda. Sleep, 28(4), 479–498. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/28.4.479
Vyazovskiy, V. V., & Delogu, A. (2014). NREM and REM Sleep. The Neuroscientist, 20(3), 203–219. http://doi.org/10.1177/1073858413518152
Mignot, E. (2008). Why We Sleep: The Temporal Organization of Recovery. PLoS Biology, 6(4). http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0060106
Siegel, J. M. (2009). Sleep viewed as a state of adaptive inactivity. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 10(10), 747–753. http://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2697
Horne, J. (2000). REM sleep — by default? Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 24(8), 777–797. http://doi.org/10.1016/s0149-7634(00)00037-3
Baran, B., Pace-Schott, E. F., Ericson, C., & Spencer, R. M. C. (2012). Processing of Emotional Reactivity and Emotional Memory over Sleep. Journal of Neuroscience, 32(3), 1035–1042. http://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2532-11.2012
Tononi, G., & Cirelli, C. (2014). Sleep and the Price of Plasticity: From Synaptic and Cellular Homeostasis to Memory Consolidation and Integration. Neuron, 81(1), 12–34. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.12.025
Li, J., Vitiello, M. V., & Gooneratne, N. S. (2018). Sleep in Normal Aging. Sleep Medicine Clinics, 13(1), 1–11. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsmc.2017.09.001
Murillo-Rodriguez, E., Arias-Carrion, O., Zavala-Garcia, A., Sarro-Ramirez, A., & Huitron-Resendiz, S. (2012). Basic Sleep Mechanisms: An Integrative Review. Central Nervous System Agents in Medicinal Chemistry, 12(1), 38–54. http://doi.org/10.2174/187152412800229107
Weber, F. D. (2018). Sleep: Eye-Opener Highlights Sleep’s Organization. Current Biology, 28(5). http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.01.054
Yetton, B. D., Mcdevitt, E. A., Cellini, N., Shelton, C., & Mednick, S. C. (2018). Quantifying sleep architecture dynamics and individual differences using big data and Bayesian networks. Plos One, 13(4). http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0194604
Colrain, I. M., Nicholas, C. L., & Baker, F. C. (2014). Alcohol and the sleeping brain. Handbook of Clinical Neurology Alcohol and the Nervous System, 415–431. http://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-444-62619-6.00024-0
Zisapel, N. (2018). New perspectives on the role of melatonin in human sleep, circadian rhythms and their regulation. British Journal of Pharmacology, 175(16), 3190–3199. http://doi.org/10.1111/bph.14116
Tosini, G., Baba, K., Hwang, C. K., & Iuvone, P. M. (2012). Melatonin: An underappreciated player in retinal physiology and pathophysiology. Experimental Eye Research, 103, 82–89. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2012.08.009
Blasiak, J., Reiter, R. J., & Kaarniranta, K. (2016). Melatonin in Retinal Physiology and Pathology: The Case of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2016, 1–12. http://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6819736
Bellingham, J., Chaurasia, S. S., Melyan, Z., Liu, C., Cameron, M. A., Tarttelin, E. E., … Lucas, R. J. (2006). Evolution of Melanopsin Photoreceptors: Discovery and Characterization of a New Melanopsin in Nonmammalian Vertebrates. PLoS Biology, 4(8). http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0040254
Zaidi, F. H., Hull, J. T., Peirson, S. N., Wulff, K., Aeschbach, D., Gooley, J. J., … Lockley, S. W. (2007). Short-Wavelength Light Sensitivity of Circadian, Pupillary, and Visual Awareness in Humans Lacking an Outer Retina. Current Biology, 17(24), 2122–2128. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2007.11.034
Legates, T. A., Altimus, C. M., Wang, H., Lee, H.-K., Yang, S., Zhao, H., … Hattar, S. (2012). Aberrant light directly impairs mood and learning through melanopsin-expressing neurons. Nature, 491(7425), 594–598. http://doi.org/10.1038/nature11673
Sikka, G., Hussmann, G. P., Pandey, D., Cao, S., Hori, D., Park, J. T., … Berkowitz, D. E. (2014). Melanopsin mediates light-dependent relaxation in blood vessels. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(50), 17977–17982. http://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1420258111
Buhr, E. D., Yoo, S.-H., & Takahashi, J. S. (2010). Temperature as a Universal Resetting Cue for Mammalian Circadian Oscillators. Science, 330(6002), 379–385. http://doi.org/10.1126/science.1195262
Robbins, R., Grandner, M. A., Buxton, O. M., Hale, L., Buysse, D. J., Knutson, K. L., … Jean-Louis, G. (2019). Sleep myths: an expert-led study to identify false beliefs about sleep that impinge upon population sleep health practices. Sleep Health, 5(4), 409–417. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleh.2019.02.002
Damiola, F. (2000). Restricted feeding uncouples circadian oscillators in peripheral tissues from the central pacemaker in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Genes & Development, 14(23), 2950–2961. http://doi.org/10.1101/gad.183500
Abel, T., Havekes, R., Saletin, J. M., & Walker, M. P. (2013). Sleep, Plasticity and Memory from Molecules to Whole-Brain Networks. Current Biology, 23(17). http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.07.025
Muzet, A., Ehrhart, J., Candas, V., Libert, J. P., & Vogt, J. J. (1983). Rem Sleep and Ambient Temperature in Man. International Journal of Neuroscience, 18(1-2), 117–125. http://doi.org/10.3109/00207458308985885
Saini, C., Morf, J., Stratmann, M., Gos, P., & Schibler, U. (2012). Simulated body temperature rhythms reveal the phase-shifting behavior and plasticity of mammalian circadian oscillators. Genes & Development, 26(6), 567–580. http://doi.org/10.1101/gad.183251.111
Franco P, Szliwowski H, Dramaix M, Kahn A. Influence of ambient temperature on sleep characteristics and autonomic nervous control in healthy infants. Sleep. 2000 May 1;23(3):401-7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10811384/
Libert JP, Candas V, Muzet A, Ehrhart J. Thermoregulatory adjustments to thermal transients during slow wave sleep and REM sleep in man. J Physiol (Paris). 1982;78(3):251-7 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7166740/
Palca, J. W., Walker, J. M., & Berger, R. J. (1986). Thermoregulation, metabolism, and stages of sleep in cold-exposed men. Journal of Applied Physiology, 61(3), 940–947. http://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.1986.61.3.940
Lack. (2009). Chronotype differences in circadian rhythms of temperature, melatonin, and sleepiness as measured in a modified constant routine protocol. Nature and Science of Sleep, 1. http://doi.org/10.2147/nss.s6234
Samson, D. R., Crittenden, A. N., Mabulla, I. A., Mabulla, A. Z. P., & Nunn, C. L. (2017). Chronotype variation drives night-time sentinel-like behaviour in hunter–gatherers. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 284(1858), 20170967. http://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2017.0967
Walker, R. J., Kribs, Z. D., Christopher, A. N., Shewach, O. R., & Wieth, M. B. (2014). Age, the Big Five, and time-of-day preference: A mediational model. Personality and Individual Differences, 56, 170–174. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2013.09.003
Bjorness, T., & Greene, R. (2009). Adenosine and Sleep. Current Neuropharmacology, 7(3), 238–245. http://doi.org/10.2174/157015909789152182
Dworak, M., Diel, P., Voss, S., Hollmann, W., & Strüder, H. (2007). Intense exercise increases adenosine concentrations in rat brain: Implications for a homeostatic sleep drive. Neuroscience, 150(4), 789–795. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.09.062
Rainnie, D., Grunze, H., Mccarley, R., & Greene, R. (1994). Adenosine inhibition of mesopontine cholinergic neurons: implications for EEG arousal. Science, 263(5147), 689–692. http://doi.org/10.1126/science.8303279
Daly, J. W., Shi, D., Nikodijevic, O., & Jacobson, K. A. (1994). The role of adenosine receptors in the central action of caffeine. Pharmacopsychoecologia, 7(2), 201–213. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4373791/

