Stimulant management is crucial if you are to get good sleep. Unfortunately, people often skip it. They do everything else right with their sleep hygiene, but then they pay no attention to their stimulant intake or timing, and as a result, they still struggle with sleep. They lie awake despite being exhausted, or they fall asleep but wake unrefreshed, or they sleep poorly and then drag through the next day feeling depleted.
What is often sabotaging everything else they’re doing right is stimulant management. More specifically, the lack of it. Most people are using stimulants (primarily caffeine, but increasingly stronger compounds) in patterns that systematically destroy their sleep while creating the very exhaustion that makes them feel they need more stimulants. It’s a vicious cycle, and breaking it might be the single most impactful change you can make for your sleep quality.
This is the intervention people least want to hear about because it requires genuine sacrifice. You like your afternoon coffee. You’ve built your entire workday around strategic caffeine doses. You’ve convinced yourself that you “handle caffeine well” because you can drink espresso at 8pm and still fall asleep. And I’m about to explain why none of that matters, why your stimulant use is almost certainly undermining your sleep more than you realise, and what proper stimulant management actually looks like.
This article will be covering how stimulants work, why even morning caffeine affects nighttime sleep, the genetic factors that make some people far more sensitive than others, and most importantly, how to actually implement changes that work without making yourself miserable. Because the thing is, most people know they should reduce caffeine. They don’t because previous attempts have been brutal, and they couldn’t sustain the change. We need to address that. So, let’s get stuck into understanding stimulant management for sleep.
Table of Contents
Understanding Stimulants: What We’re Actually Talking About
When we talk about stimulant management in the context of sleep, we’re primarily discussing compounds that increase central nervous system activity, arousal, and wakefulness. The most common by far is caffeine, which we’ll explore in depth. But the category also includes nicotine, prescription stimulants (methylphenidate, amphetamines, modafinil), over-the-counter stimulants, and various compounds in pre-workout supplements and energy drinks.
These substances work through different mechanisms, but they all share the property of increasing arousal and alertness when you want to be awake, and unfortunately, maintaining some level of that arousal when you want to be asleep. The effects persist far longer than most people realise, and the impact on sleep architecture (the structure and quality of your sleep) exists even when you successfully fall asleep.
This all creates a doom loop that destroys sleep for millions of people. You sleep poorly, so you feel exhausted in the morning and reach for coffee. The caffeine gets you through the day, but it’s still in your system at bedtime, fragmenting your sleep and reducing sleep quality. You sleep poorly again, wake even more exhausted, and need even more caffeine to function. The cycle continues, each iteration making you more dependent on stimulants while simultaneously making your sleep worse, which increases your dependence further.
Breaking this cycle requires understanding how stimulants actually work, acknowledging the ways you’re currently using them that undermine sleep, and implementing proper stimulant management strategies that allow you to maintain function while recovering sleep quality. It’s not easy, but it’s worth it.
Caffeine: The Stimulant Nearly Everyone Uses
Caffeine is the world’s most widely consumed psychoactive drug, used by approximately 90% of adults in Western countries. It’s so normalised that most people don’t think of it as a drug at all; it’s just coffee, or tea, or energy drinks. But caffeine is absolutely a drug, with specific pharmacology, individual variation in response, tolerance development, and withdrawal symptoms. Understanding how it works is essential for proper stimulant management.
Caffeine is an adenosine receptor antagonist. You see, throughout your day, as your neurons fire and consume energy, they produce a molecule called adenosine as a metabolic byproduct. Adenosine accumulates in your brain, and when it binds to adenosine receptors, it creates the sensation of tiredness and sleepiness. This is your sleep pressure, and it’s why the longer you’re awake, the more adenosine accumulates, and the sleepier you feel.
Caffeine molecules are structurally similar enough to adenosine that they can bind to the same receptors, but without activating them. They essentially block the parking spaces that adenosine would normally occupy. This is called competitive inhibition. The adenosine is still accumulating, and your sleep debt is still growing, but you can’t feel it because the signal is being blocked.
Caffeine doesn’t give you energy. It doesn’t reduce your sleep debt. It doesn’t make you less tired. It just blocks your brain’s ability to detect that you’re tired. The fatigue is still there, accumulating in the background, and when the caffeine wears off, you feel the full weight of it all at once. This is why caffeine “crashes” happen. The caffeine wasn’t providing energy that’s now gone. The adenosine that accumulated while you were caffeinated is suddenly able to bind to its receptors. So it hits you all at once.
Caffeine has a half-life of approximately 3-7 hours, with 5 hours being average for most adults. This means that five hours after consuming caffeine, roughly half of it is still in your system. If you have 200mg of caffeine (a large coffee) at 2pm, you still have approximately 100mg in your system at 7pm, 50mg at midnight, and 25mg at 5am.
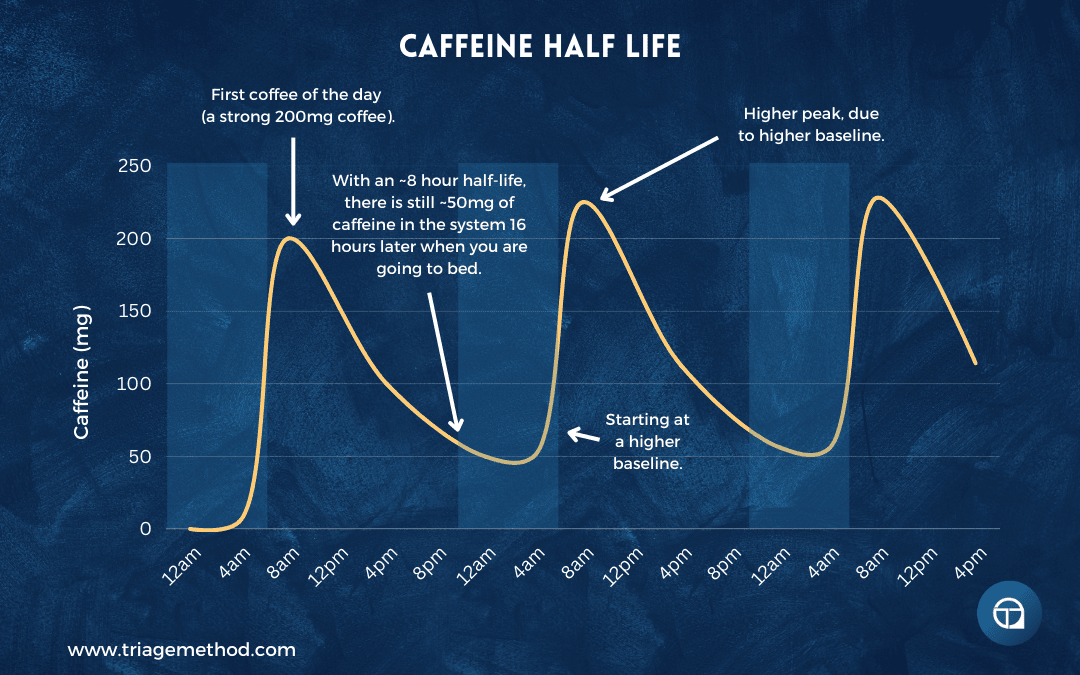
But it’s actually worse than that for sleep, because it’s not just about when caffeine is completely eliminated, it’s about when levels drop low enough to no longer interfere with sleep. Even 25-50mg of caffeine can measurably disrupt sleep architecture. This is why the “quarter-life” matters as much or more than the half-life. It takes roughly 12-15 hours for caffeine to be reduced to levels that don’t meaningfully affect sleep for most people.
If you consume 200mg of caffeine at noon and try to sleep at 10pm (10 hours later), you still have approximately 60-70mg of caffeine in your system, which is equivalent to a cup of tea or half a cup of coffee. This is enough to reduce deep sleep, fragment sleep architecture, and make sleep less restorative, even if you fall asleep without difficulty.
But it gets more complicated, especially when you try to compare different individuals. Caffeine is primarily metabolised by an enzyme called CYP1A2, and genetic variation in the gene encoding this enzyme creates enormous individual differences in how quickly you clear caffeine from your system.
Fast metabolisers have highly active CYP1A2 and clear caffeine rapidly, as their caffeine half-life might be 3-4 hours. These people genuinely can have afternoon coffee without major sleep disruption because by bedtime, most of the caffeine is gone. Slow metabolizers have less active CYP1A2 and clear caffeine slowly, as their caffeine half-life might be 7-8 hours or longer. For these people, even morning coffee can still be affecting their sleep at night.
You can’t determine your metaboliser status by how caffeine feels. Fast metabolisers might feel a strong acute effect that wears off quickly. Slow metabolisers might feel a milder effect that persists. Both experiences are real, but they mean different things for sleep. The only way to know definitively is genetic testing (23andMe and similar services report CYP1A2 variants), but you can infer it from your experience: if you’ve ever had coffee after 2pm and had trouble sleeping, you’re probably a slow metaboliser. If you regularly have afternoon coffee with no sleep issues, you might be a fast metaboliser, although even then, your sleep architecture might be affected without you noticing.
Age effects: CYP1A2 activity declines with age, meaning you become a slower caffeine metaboliser as you get older. The afternoon coffee you tolerated fine at 25 might be disrupting your sleep at 45, because your caffeine clearance can change across the lifespan. This is why older adults often need to move their caffeine cutoff earlier in the day.
Sex differences and hormonal effects: Women, on average, metabolise caffeine slightly slower than men, particularly during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle (after ovulation, before menstruation) when progesterone is elevated. Hormonal contraceptives can significantly slow caffeine metabolism, and some studies show oral contraceptives increase caffeine half-life by 30-40%. Pregnancy drastically slows caffeine metabolism, particularly in the third trimester, when half-life can extend to 10-15 hours.
If you’re a woman on hormonal birth control and you’re struggling with sleep, caffeine timing is even more critical than for the average person. What might be a safe afternoon coffee for someone else could be disrupting your sleep because you’re clearing it much more slowly.
Medication interactions: Certain medications affect CYP1A2 activity. Fluvoxamine (an antidepressant) dramatically inhibits it, making you an ultra-slow metaboliser while you’re taking it. Fluoroquinolone antibiotics (ciprofloxacin, levofloxacin) reduce caffeine clearance. Some heart medications affect it. If you’re on any prescription medications and your response to caffeine has changed, this might be why.
Sources of Caffeine: An Audit You Need to Do
Most people dramatically underestimate their caffeine intake because they’re only counting coffee while ignoring the substantial amounts they’re getting from other sources. Proper stimulant management starts with accurate accounting.
Coffee: 80-200mg per cup, but this varies wildly based on brewing method, bean type, and serving size. A small drip coffee from a chain might be 80-100mg. A large “venti” from Starbucks can be 300-400mg. Cold brew often has higher caffeine due to longer extraction time, and some bottles contain 200mg+. Instant coffee is typically lower, 60-80mg per cup. Decaf isn’t zero, and it contains 2-15mg per cup.
Espresso: 60-80mg per shot. A double espresso (doppio) is 120-160mg. Americanos, lattes, cappuccinos, and other espresso-based drinks contain the same caffeine as their espresso shot count would suggest, as the milk and/or extra water doesn’t dilute the caffeine.
Tea: This is where people get surprised. Black tea contains 40-70mg per cup, green tea 25-50mg, white tea 15-30mg, and oolong 30-50mg. A large mug of strong English breakfast tea can easily contain 60-70mg of caffeine, which is nearly as much as a small coffee. If you’re drinking multiple cups of tea throughout the afternoon and evening, you’re getting substantial caffeine without realising it.
This is particularly relevant in British and Irish contexts where tea consumption is cultural and constant. “Just a cup of tea before bed” might seem innocuous, and most people rationalise that it’s not coffee, after all. But the reality is that you’re still consuming 40-50mg of caffeine right before sleep. If you’re having three or four cups of tea between 6pm and 10pm, you’re getting 150-200mg of caffeine during exactly the hours when you should be avoiding it entirely.
Herbal teas are caffeine-free (chamomile, peppermint, rooibos), but “tea” made from actual tea leaves (Camellia sinensis) contains caffeine regardless of whether it’s black, green, white, or oolong.
Soft drinks: Cola drinks contain 30-50mg per can (330ml). Some “energy” colas contain more (70-80mg per can). If you’re drinking multiple cans throughout the day, particularly in the afternoon or evening, you’re getting significant caffeine intake.
Energy drinks: Energy drinks typically contain 80-200mg per can, but some contain far more. A 500ml can of Monster or Red Bull contains about 160mg of caffeine. Some “extra strength” energy drinks contain 300mg+ per can. The large cans people drink over several hours might contain 240-300mg of caffeine.
Even worse, energy drinks often combine caffeine with other stimulants (guarana, taurine, various amino acids) that create synergistic effects, meaning the total stimulant load is higher than caffeine content alone would suggest. Energy drinks are probably worse for sleep than equivalent caffeine from coffee or tea, and most people don’t seem to realise this.
Pre-workout supplements: Many contain 150-300mg of caffeine per serving, plus additional stimulants. Some contain 400mg+ of caffeine, which is equivalent to four cups of coffee in a single dose. If you’re taking pre-workout in the afternoon or early evening before a gym session, you’re essentially guaranteeing poor sleep that night, which generally means you will get worse results from your exercise.
Chocolate: Contains modest amounts of caffeine; clocking in at 10-30mg per 50g serving for dark chocolate, less for milk chocolate. Not enough to worry about for most people, but it adds up if you’re eating substantial amounts in the evening.
Caffeine pills: Over-the-counter stimulants sold for alertness typically contain 100-200mg per pill. Some students and shift workers use these in addition to coffee, easily exceeding 600-800mg of daily caffeine without realising the total.
Hidden sources: Some pain medications contain caffeine (Excedrin, Panadol Extra). Some weight loss supplements. Even some flavoured waters now contain caffeine. Always check labels on anything you’re consuming, particularly medications and supplements.
The Audit Process
For proper stimulant management, you need to actually track your caffeine intake for a week. Write down every source of caffeine, the approximate amount, and the time consumed. Most people are shocked by the results. They thought they had “just two coffees a day” and often discover they’re actually consuming 400-600mg from coffee, tea, and soft drinks combined, with half of it after 2pm.
Common discoveries from caffeine audits:
- The afternoon tea habit is providing 150-200mg of caffeine between 4pm and 9pm
- The “small” coffees from shops are actually 200mg+ due to serving size
- Pre-workout supplements are adding 200-300mg in the early evening
- Multiple sources combine to far exceed intended intake
- Caffeine is being consumed much later in the day than previously realised
Once you know your actual intake and timing, you can make informed decisions about changes. Most people need to reduce both the total amount and move the cutoff time earlier (8-12 hours before sleep).
Caffeine Tolerance: The Trap Everyone Falls Into
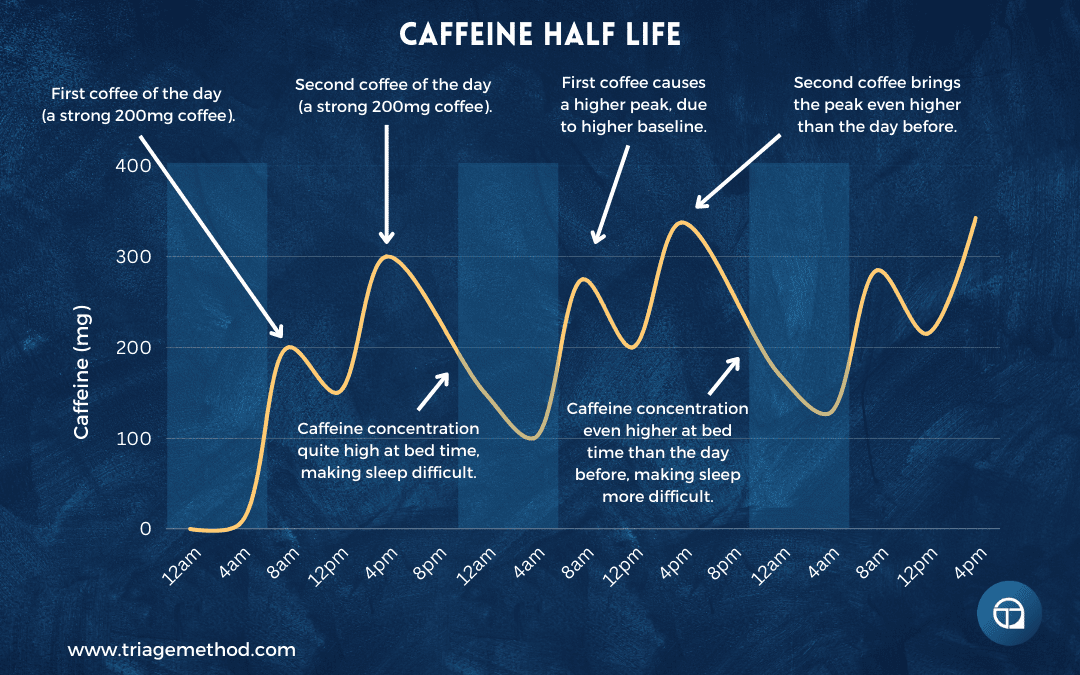
With regular caffeine use, your brain adapts by producing more adenosine receptors. This is tolerance development. Now you need more caffeine to occupy enough receptors to feel the alertness effect. What started as one coffee in the morning becomes two, then three, then you’re adding afternoon coffee, then you’re considering pre-workout supplements.
The insidious thing is that tolerance develops to the alertness and performance effects, but not to the sleep-disrupting effects. Your brain adapts by becoming less sensitive to caffeine’s acute stimulation, but caffeine still blocks adenosine receptors at bedtime, still fragments sleep architecture, and still reduces deep sleep. You need caffeine just to feel normal (because you have more adenosine receptors and therefore experience adenosine signalling more strongly without caffeine), but you’re not actually more alert than you would be without caffeine, as you’ve just shifted your baseline. And you’re still destroying your sleep.
This is why people who consume large amounts of caffeine daily often report feeling constantly tired despite high caffeine intake. They’re tired because their sleep is terrible because of the caffeine they’re taking because they’re tired. The tolerance hasn’t protected them from sleep disruption. It’s just made them dependent on caffeine to feel baseline normal.
Withdrawal symptoms demonstrate this dependence. When regular caffeine users stop consuming caffeine, they experience:
- Headaches (the primary symptom, which can be severe)
- Fatigue and excessive sleepiness
- Irritability and mood disturbance
- Difficulty concentrating
- Flu-like symptoms (muscle aches, nausea)
These symptoms typically begin 12-24 hours after the last caffeine dose, peak around 24-48 hours, and gradually resolve over 2-9 days, depending on prior intake levels and individual factors. The severity correlates with habitual intake, and someone consuming 600mg daily will have worse withdrawal than someone consuming 200mg daily.
The headaches deserve special mention because they can be genuinely debilitating. The mechanism is that caffeine causes vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels in the brain), and when you remove caffeine, rebound vasodilation occurs, triggering headache. For people with high habitual intake, withdrawal headaches can be severe enough to interfere with work and require medication.
This is why most people who try to quit caffeine fail. The withdrawal is miserable, and it’s easy to make it stop by just having some caffeine. Then you’re back to baseline, and you’ve reinforced the idea that you “need” caffeine to function.
Recommended Stimulant Management Practices
If you’re serious about sleep quality, here are the non-negotiable principles of proper stimulant management:
1. Total daily limit: Keep total daily caffeine intake below 400mg, and ideally below 300mg. For many people, particularly slow metabolisers, women on hormonal contraceptives, or anyone with sleep difficulties, 200mg or less might be appropriate. We are just trying to not overwhelm your system’s ability to clear caffeine before bedtime.
2. Hard cutoff time: No caffeine within 8-12 hours of your target bedtime, minimum. If you sleep at 10:30pm, no caffeine after 2:30pm (8 hours) or ideally after 10:30am (12 hours). This feels extreme. It’s not. Remember, caffeine’s quarter-life means meaningful amounts persist for 12-15 hours. The 8-hour cutoff is the bare minimum for fast metabolisers. Most people should use a 10-12 hour cutoff.
For slow metabolisers, the cutoff needs to be even earlier, and potentially have all caffeine confined to before noon. If you suspect you’re a slow metaboliser (caffeine keeps you wired for hours, afternoon coffee disrupts sleep, you’re on medications that slow clearance), experiment with a noon cutoff.
3. Morning front-loading: If you’re going to consume caffeine, consume most of it early in the day when it’s least likely to interfere with sleep. If you want 300mg daily, better to have two large coffees before 10am than to spread smaller doses throughout the day into the afternoon.
This also aligns with your natural cortisol rhythm. Cortisol is naturally high in the morning (especially the first hour after waking), and adding caffeine to this creates a strong alertness signal. Taking caffeine when cortisol is already elevated is more effective than taking it in the afternoon when cortisol has declined.
4. Awareness of all sources: Count everything. That afternoon tea matters. That piece of chocolate after dinner matters. The soft drink with lunch matters. Hidden sources in medications and supplements matter. If you’re trying to maintain a 2pm cutoff, you can’t have “just a cup of tea” at 4pm and pretend it doesn’t count.
5. Strategic use vs. habitual use: Ideally, use caffeine strategically for situations where you genuinely need enhanced alertness (early morning meeting, long drive, demanding task) rather than habitually throughout the day just to feel normal. This reduces tolerance development and makes caffeine more effective when you actually need it.
This isn’t practical for everyone as many people have built their lives around steady caffeine intake. But it’s worth considering whether you’re using caffeine because it helps or because you’re addicted and can’t function without it.
6. Experiment with lower doses: Most people are consuming more caffeine than they actually need. Try reducing each dose by 25-30% and see if you notice a meaningful difference in alertness. Often you won’t, which suggests you’ve been consuming excess purely out of habit or tolerance.
Breaking the Caffeine-Sleep Doom Loop
If you recognise yourself in the pattern of poor sleep leading to high caffeine intake leading to worse sleep leading to higher caffeine intake, then breaking the cycle is hard but essential. Here’s the realistic approach:
Step 1: Recognise the pattern and commit to change. Acknowledge that your current approach isn’t working, that you’re tired despite high caffeine intake, and that continuing this pattern will only make things worse. Commit to temporary discomfort for long-term improvement.
Step 2: Track your baseline. Do a week-long caffeine audit. Record every source, amount, and timing. This gives you a baseline to work from and often reveals consumption patterns you weren’t aware of.
Step 3: Implement the cutoff first. Before reducing total intake, move your cutoff time earlier. If you currently drink coffee until 6pm, move it to 4pm for a week, then 2pm, then noon if needed. This immediately improves sleep quality, which makes the next steps easier.
Step 4: Gradually reduce total intake. Once your cutoff is established, start reducing total daily intake by 10-25% every 3-5 days. If you’re at 600mg daily, reduce to 500mg for 3-4 days, then 400mg for 3-4 days, then 300mg, and so on. Gradual reduction minimises withdrawal symptoms.
The key is “gradual.” Cold turkey from 600mg to zero might seem admirable, but the withdrawal will be brutal, you’ll be non-functional for several days, and you’re likely to give up and return to your previous intake. Gradual reduction over 2-4 weeks is sustainable.
Step 5: Manage withdrawal symptoms. Even with gradual reduction, you’ll likely experience some headaches, fatigue, and irritability. Strategies:
- Stay well-hydrated (helps with headaches)
- Get extra sleep if possible (your body is catching up)
- Use over-the-counter pain medication for severe headaches (just make sure they don’t have caffeine in them!)
- Increase physical activity (helps with energy and mood)
- Be patient; it gets better, usually within a week
Step 6: Improve sleep to reduce need. As your sleep quality improves (which it will once caffeine is properly managed), you’ll naturally need less caffeine because you’re less tired. This creates a positive feedback loop where better sleep means less caffeine need, which means better sleep.
Step 7: Maintain the change. This is the hardest part. Once you’ve successfully reduced intake and moved your cutoff earlier, the temptation to backslide is constant. “Just one afternoon coffee won’t hurt.” Yes, it will. You’re not different. You’re not an exception. If you’re a slow metaboliser, afternoon caffeine will disrupt your sleep, and once you disrupt your sleep, you’ll want caffeine the next day, and you’re back in the doom loop.
Maintenance requires vigilance and boundary-setting with yourself and others. “Would you like tea?” “No thanks, I don’t drink caffeine after noon.” This feels socially awkward initially. It becomes normal quickly, and your sleep is worth it.
Other Stimulants: Beyond Caffeine
While caffeine is by far the most common stimulant affecting sleep, other compounds deserve attention for proper stimulant management.
Nicotine is a potent stimulant that disrupts sleep architecture even when it doesn’t prevent sleep onset. Smokers and vapers who use nicotine in the hours before bed experience reduced deep sleep, more nighttime awakenings, and worse overall sleep quality. Nicotine also creates its own dependency cycle, and nicotine withdrawal during sleep can cause awakenings, which reinforces the pattern of using nicotine.
If you use nicotine, avoid it within 2-3 hours of bedtime at a minimum. Better, work toward quitting entirely. While it can be used responsibly with minimal negative health effects, most people simply do not do this.
Prescription stimulants (methylphenidate/Ritalin, amphetamine/Adderall, dextroamphetamine/Dexedrine, modafinil/Provigil, armodafinil/Nuvigil) are increasingly common for ADHD, narcolepsy, and increasingly for “off-label” cognitive enhancement. These are powerful stimulants with long durations of action, and some formulations last 10-12+ hours.
If you take prescription stimulants:
- Take them as early in the day as possible
- Work with your prescriber to optimise timing and dosing for your sleep
- Understand that sleep disruption is an expected side effect, and you may need to accept the trade-off or work to minimise dose
- Implement every other sleep hygiene practice obsessively because you’re already at a disadvantage
- Never take extra doses or doses later in the day, thinking you’ll “just push through”, as you’re destroying your sleep and will just have a rough time the next day
Some people genuinely need prescription stimulants for medical conditions. If that’s you, the goal isn’t to stop the medication but to optimise everything else to mitigate the sleep impact as much as possible.
Over-the-counter stimulants, including things marketed for weight loss, alertness, or energy, often contain caffeine (which we’ve covered), but also ephedrine analogues (synephrine), guarana (which is just caffeine under a different name), yerba mate (also caffeine), and various other compounds. Some contain dangerous substances like DMAA that have been banned but still appear in unregulated supplements.
The stimulant management principle: if it’s marketed for energy, alertness, or fat burning, assume it contains stimulants and avoid it in the afternoon/evening. Better, avoid it entirely unless you have a specific reason to use it and understand exactly what’s in it.
Energy drinks deserve special mention again because they combine high caffeine with other stimulants, plus sugar or artificial sweeteners. The stimulant combination creates synergistic effects, and the total impact is greater than caffeine alone. Energy drinks are marketed heavily to young people and increasingly normalised as “just a drink” rather than recognised as significant stimulant doses in beverage form.
Energy drinks are categorically worse for sleep than equivalent caffeine from coffee. The combination of stimulants, the liquid sugar crash, and the tendency to consume them quickly and late in the day makes them particularly problematic. If you’re serious about sleep, eliminate energy drinks entirely, or choose the sugar free version and only have them earlier in the day.
Pre-workout supplements are similar, as they have very high caffeine plus additional stimulants, and are consumed right before exercise, which is itself somewhat stimulating. If you exercise in the afternoon or evening and use pre-workout, you’re all-but guaranteeing poor sleep that night. The ideal solution is to exercise earlier in the day, use stimulant-free pre-workout, or use nothing and accept that your workout might be slightly less intense, but your sleep will be dramatically better. Exercising earlier may not be possible, but you certainly can reduce your stimulant use.
Special Populations
There are some special considerations for different populations when we consider stimulant management to improve sleep.
Adolescents are more sensitive to caffeine’s effects and more vulnerable to developing problematic use patterns. Their sleep requirements are higher, their circadian rhythms are naturally shifted later (making sleep problems more severe), and they’re heavily targeted by energy drink marketing. Adolescents should minimise caffeine intake and avoid it entirely after early afternoon.
Parents: if your teenager is drinking energy drinks or multiple coffees daily, this is contributing to their sleep problems (which are already substantial due to school start times and circadian shifts), their mood problems, and potentially their academic performance despite using stimulants to try to improve it. This is a hard conversation to have, but it’s necessary.
Pregnant and breastfeeding women should limit caffeine to 200mg daily maximum (some guidelines suggest 150mg), taken as early in the day as possible. Caffeine crosses the placenta and is secreted in breast milk. Fetal/infant caffeine metabolism is extremely slow, meaning caffeine persists much longer in their systems. Beyond sleep concerns, high caffeine intake during pregnancy is associated with pregnancy complications.
Slow metabolisers need to be even more conservative with caffeine timing and amount. If you’ve identified yourself as a slow metaboliser (through genetic testing or experience), you need a stricter cutoff time of around noon or maybe even earlier, and you likely need to lower total intake. A reasonable 2pm cutoff for a fast metaboliser might mean a 10am cutoff for you.
People with anxiety disorders often find caffeine worsens their anxiety, creates physical symptoms of arousal that they misinterpret as panic, and disrupts sleep, which exacerbates anxiety. If you have an anxiety disorder and consume significant caffeine, you’re making things harder for yourself. Many people find substantial anxiety reduction with caffeine elimination or dramatic reduction.
Alternatives to Caffeine for Energy
When you reduce caffeine, you’ll need strategies for maintaining energy and alertness. The good news: most of these are better for you than caffeine, and several of them directly improve sleep quality, creating a positive rather than negative feedback loop.
Morning light exposure is the most powerful natural alertness cue available. Getting bright outdoor light within 30-60 minutes of waking provides a cortisol boost, entrains your circadian rhythm, and increases daytime alertness far more effectively than most people realise. This is free, improves sleep, and doesn’t create tolerance or withdrawal.
Morning exercise increases alertness through multiple mechanisms (cortisol and adrenaline release, increased blood flow, and metabolic activation). Even 10-20 minutes of movement in the morning provides several hours of enhanced alertness. Unlike caffeine, exercise actually improves sleep rather than disrupting it.
Cold exposure (cold shower, cold water face splash, stepping outside in winter) provides acute alertness through sympathetic nervous system activation. The effect is brief but immediate. Some people use this strategically when they feel themselves dragging in the morning.
Brief walks throughout the day, particularly outdoor walks, provide alertness resets without the drawbacks of caffeine. When you feel yourself fading in the afternoon, a 10-minute walk often provides more sustainable alertness than coffee would.
Strategic breaks from demanding cognitive work prevent the accumulated fatigue that makes people reach for caffeine. Work in focused 60-90 minute blocks with genuine breaks between, rather than grinding through hours of continuous work while dosing caffeine to maintain function.
Better sleep is ultimately the real solution. When you’re actually well-rested from consistent, high-quality sleep, you need dramatically less caffeine. Most people are using caffeine to compensate for sleep deprivation. Fix the sleep, and the caffeine need largely disappears.
Addressing underlying fatigue: If you’re consistently exhausted despite adequate sleep, this might indicate medical issues like anaemia, thyroid dysfunction, sleep apnea, depression, or chronic illness. Using caffeine to mask these symptoms just delays diagnosis and treatment. If you’re perpetually tired despite sleeping 7-9 hours consistently, see a doctor.
Troubleshooting Common Objections
Look, I have helped a lot of people with this stuff, and I know you are going to have a lot of very specific reasons why you simply can’t do this and why you are different or have special circumstances. Unfortunately, this just often isn’t the case. So, lets go through some of the common objections I hear from people when we go about trying to improve stimulant management.
“I can drink coffee at 8pm and sleep fine.” No, you can’t. You can fall asleep, which is different from sleeping fine. Studies consistently show that even when people successfully fall asleep after late caffeine, their sleep architecture is disrupted. They get less deep sleep, more light sleep, and more brief awakenings they don’t remember. You feel less rested the next day, even if you got your usual hours. You’re habituated to poor sleep and don’t remember what genuinely restorative sleep feels like.
Try this experiment: stop all caffeine after noon for two weeks. Track how you feel. Most people report substantially better sleep quality, even though they thought their sleep was “fine” before. You’ve been sleeping poorly for so long that you’ve normalised it.
“I need it for work. I can’t function without it.” You need it for work because you’re sleep-deprived, because you’re using caffeine that disrupts your sleep. You’ve created a dependency that feels like necessity. Yes, if you reduce caffeine, you’ll have a few days or weeks where function is reduced while your sleep catches up and your tolerance resets. Then you’ll function better than you did on high caffeine, without the side effects, without the disrupted sleep, without the afternoon crashes.
This requires accepting temporary decreased performance for lasting improvement. Most people aren’t willing to do this, which is why they stay stuck in the doom loop.
The alternative approach if you genuinely can’t afford reduced function is to reduce gradually, optimise timing, and improve other sleep factors simultaneously. You might maintain acceptable function throughout while still improving sleep.
“I’m addicted. I can’t quit.” You probably are dependent, which is slightly different from addicted, but functionally similar. The withdrawal is real, but it’s temporary. A few days to a week of discomfort, then it’s over. Gradual reduction makes it manageable. And staying dependent means continuing to destroy your sleep, which affects your health, mood, relationships, and long-term function far more than a week of caffeine withdrawal headaches.
It helps to reframe this. You’re not losing something you need. You’re freeing yourself from dependence on something that’s actively harming you. This is recovery, not deprivation.
“I’ll be useless without it.” Temporarily, yes. Then you’ll sleep better, have more natural energy, and function better than you did on caffeine—without the anxiety, jitters, sleep disruption, or afternoon crashes. The transition is hard. The destination is worth it.
Many people who’ve successfully eliminated or dramatically reduced caffeine report after a month: “I can’t believe I thought I needed it. I feel so much better without it.” But you have to get through the transition to experience the benefits on the other side.
Stimulant Management Conclusion
Stimulant management isn’t about moral virtue or proving you can live without caffeine. It’s about recognising that stimulants create a false energy that masks underlying sleep debt while actively making that sleep debt worse. You’re borrowing from tomorrow’s energy to feel functional today, and the interest compounds.
The modern world encourages this pattern. Caffeine is cheap, legal, socially acceptable, and available everywhere. You’re surrounded by cultural narratives about coffee as a personality trait, energy drinks as normal beverages, and working long hours powered by stimulants as admirable hustle. And meanwhile, you’re exhausted, anxious, sleeping poorly, and increasingly dependent on the very substances causing the problem.
Breaking free from this requires seeing through the narrative and recognising what’s actually happening: you’re chemically disrupting your sleep, then using more chemicals to mask the consequences, in an endless cycle that erodes your wellbeing while making you feel like you’re managing.
Proper stimulant management (e.g. consuming less, consuming it earlier, and ideally breaking the dependence entirely) restores your sleep quality, which restores your natural energy, which reduces your need for stimulants, which improves your sleep further. It’s a positive feedback loop instead of a destructive one.
This isn’t about perfection. It’s about recognising that every cup of coffee after 2pm, every energy drink in the afternoon, every bit of caffeine in your evening tea is a vote for worse sleep tonight and more exhaustion tomorrow. You’re making a choice, usually unconsciously, and usually because you haven’t connected the dots, but a choice nonetheless.
You can make a different choice. You can implement proper stimulant management. You can accept the temporary discomfort of reducing caffeine, improving your sleep, and finding that you have more natural energy than you’ve had in years. You can stop borrowing from tomorrow’s energy to get through today.
Here’s your implementation plan:
Week 1: Establish the cutoff. No caffeine after 2pm, regardless of total intake. Track your sleep quality. Most people notice improvement within a few days.
Week 2: Move cutoff to noon. Track sleep again. If you’re a slow metaboliser, this will produce dramatic improvement. If you’re a fast metaboliser, you’ll still see benefits.
Week 3: Reduce total intake. If you’re currently above 300mg daily, reduce to 250mg. All before noon. Track sleep and daytime energy.
Week 4: Continue gradual reduction. Reduce another 50mg. Notice that as your sleep improves, you need less caffeine to feel functional.
If you’re really committed, eliminate all caffeine for 30 days and notice how you feel. You’ll have a rough first week. By week three, most people report feeling significantly better. Better sleep, more stable energy, less anxiety, no afternoon crashes. Then you can decide if you want to reintroduce caffeine in a limited, strategic way, or maintain caffeine-free life.
Unfortunately, you cannot optimise sleep while maintaining high caffeine intake late into the day. It’s not possible. Fix this first, and everything else becomes easier.
You’re not weak for being dependent on caffeine. You’re human, living in a culture that normalises and encourages stimulant use while creating conditions (early work start times, long hours, insufficient sleep) that make stimulants feel necessary. But you don’t have to stay trapped in this pattern. You can choose differently, starting tomorrow morning.
As with everything, there is always more to learn, and we haven’t even begun to scratch the surface with all this stuff. However, if you are interested in staying up to date with all our content, we recommend subscribing to our newsletter and bookmarking our free content page. We do have a lot of content on sleep in our sleep hub.
The previous article in this series was Sleep Environment Optimisation: Foundational Sleep Hygiene, and the next article in this series is Exercise and Sleep: Foundational Sleep Hygiene.
If you would like more help with your training (or nutrition), we do also have online coaching spaces available.
We also recommend reading our foundational nutrition articles, along with our foundational articles on exercise and stress management, if you really want to learn more about how to optimise your lifestyle. If you want even more free information on sleep, you can follow us on Instagram, YouTube or listen to the podcast, where we discuss all the little intricacies of exercise.
Finally, if you want to learn how to coach nutrition, then consider our Nutrition Coach Certification course. We do also have an exercise program design course, if you are a coach who wants to learn more about effective program design and how to coach it. We do have other courses available too, notably a sleep course. If you don’t understand something, or you just need clarification, you can always reach out to us on Instagram or via email.
References and Further Reading
Vyazovskiy, V. (2015). Sleep, recovery, and metaregulation: explaining the benefits of sleep. Nature and Science of Sleep, 171. http://doi.org/10.2147/nss.s54036
Sharma, S., & Kavuru, M. (2010). Sleep and Metabolism: An Overview. International Journal of Endocrinology, 2010, 1–12. http://doi.org/10.1155/2010/270832
Yoo, S.-S., Gujar, N., Hu, P., Jolesz, F. A., & Walker, M. P. (2007). The human emotional brain without sleep — a prefrontal amygdala disconnect. Current Biology, 17(20). http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2007.08.007
Copinschi G. Metabolic and endocrine effects of sleep deprivation. Essent Psychopharmacol. 2005;6(6):341-7. PMID: 16459757. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16459757/
Spiegel, K., Leproult, R., L’Hermite-Balériaux, M., Copinschi, G., Penev, P. D., & Cauter, E. V. (2004). Leptin Levels Are Dependent on Sleep Duration: Relationships with Sympathovagal Balance, Carbohydrate Regulation, Cortisol, and Thyrotropin. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 89(11), 5762–5771. http://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2004-1003
Nedeltcheva, A. V., Kilkus, J. M., Imperial, J., Kasza, K., Schoeller, D. A., & Penev, P. D. (2008). Sleep curtailment is accompanied by increased intake of calories from snacks. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 89(1), 126–133. http://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.2008.26574
Mullington, J. M., Chan, J. L., Dongen, H. P. A. V., Szuba, M. P., Samaras, J., Price, N. J., … Mantzoros, C. S. (2003). Sleep Loss Reduces Diurnal Rhythm Amplitude of Leptin in Healthy Men. Journal of Neuroendocrinology, 15(9), 851–854. http://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2826.2003.01069.x
Leproult, R., & Cauter, E. V. (2009). Role of Sleep and Sleep Loss in Hormonal Release and Metabolism. Pediatric Neuroendocrinology Endocrine Development, 11–21. http://doi.org/10.1159/000262524
Spaeth, A. M., Dinges, D. F., & Goel, N. (2013). Effects of Experimental Sleep Restriction on Weight Gain, Caloric Intake, and Meal Timing in Healthy Adults. Sleep, 36(7), 981–990. http://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.2792
Calvin, A. D., Carter, R. E., Adachi, T., Macedo, P. G., Albuquerque, F. N., Walt, C. V. D., … Somers, V. K. (2013). Effects of Experimental Sleep Restriction on Caloric Intake and Activity Energy Expenditure. Chest, 144(1), 79–86. http://doi.org/10.1378/chest.12-2829
Markwald, R. R., Melanson, E. L., Smith, M. R., Higgins, J., Perreault, L., Eckel, R. H., & Wright, K. P. (2013). Impact of insufficient sleep on total daily energy expenditure, food intake, and weight gain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 110(14), 5695–5700. http://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1216951110
Cauter, E. V., Spiegel, K., Tasali, E., & Leproult, R. (2008). Metabolic consequences of sleep and sleep loss. Sleep Medicine, 9. http://doi.org/10.1016/s1389-9457(08)70013-3
Spiegel, K., Leproult, R., & Cauter, E. V. (1999). Impact of sleep debt on metabolic and endocrine function. The Lancet, 354(9188), 1435–1439. http://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(99)01376-8
Ness, K. M., Strayer, S. M., Nahmod, N. G., Schade, M. M., Chang, A.-M., Shearer, G. C., & Buxton, O. M. (2019). Four nights of sleep restriction suppress the postprandial lipemic response and decrease satiety. Journal of Lipid Research, 60(11), 1935–1945. http://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.p094375
Hirotsu, C., Tufik, S., & Andersen, M. L. (2015). Interactions between sleep, stress, and metabolism: From physiological to pathological conditions. Sleep Science, 8(3), 143–152. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.slsci.2015.09.002
Morselli, L., Leproult, R., Balbo, M., & Spiegel, K. (2010). Role of sleep duration in the regulation of glucose metabolism and appetite. Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, 24(5), 687–702. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.beem.2010.07.005
Lamon, S., Morabito, A., Arentson-Lantz, E., Knowles, O., Vincent, G. E., Condo, D., … Aisbett, B. (2020). The effect of acute sleep deprivation on skeletal muscle protein synthesis and the hormonal environment. http://doi.org/10.1101/2020.03.09.984666
Lipton, J. O., & Sahin, M. (2014). The Neurology of mTOR. Neuron, 84(2), 275–291. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.09.034
Tudor, J. C., Davis, E. J., Peixoto, L., Wimmer, M. E., Tilborg, E. V., Park, A. J., … Abel, T. (2016). Sleep deprivation impairs memory by attenuating mTORC1-dependent protein synthesis. Science Signaling, 9(425). http://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.aad4949
Dattilo, M., Antunes, H., Medeiros, A., Neto, M. M., Souza, H., Tufik, S., & Mello, M. D. (2011). Sleep and muscle recovery: Endocrinological and molecular basis for a new and promising hypothesis. Medical Hypotheses, 77(2), 220–222. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2011.04.017
Thornton, S. N., & Trabalon, M. (2014). Chronic dehydration is associated with obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome. Clinical Science, 128(3), 225–225. http://doi.org/10.1042/cs20140496
Rosinger, A. Y., Chang, A.-M., Buxton, O. M., Li, J., Wu, S., & Gao, X. (2018). Short sleep duration is associated with inadequate hydration: cross-cultural evidence from US and Chinese adults. Sleep, 42(2). http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/zsy210
Watson, A. M. (2017). Sleep and Athletic Performance. Current Sports Medicine Reports, 16(6), 413–418. http://doi.org/10.1249/jsr.0000000000000418
Bonnar, D., Bartel, K., Kakoschke, N., & Lang, C. (2018). Sleep Interventions Designed to Improve Athletic Performance and Recovery: A Systematic Review of Current Approaches. Sports Medicine, 48(3), 683–703. http://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-017-0832-x
Saidi, O., Davenne, D., Lehorgne, C., & Duché, P. (2020). Effects of timing of moderate exercise in the evening on sleep and subsequent dietary intake in lean, young, healthy adults: randomized crossover study. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 120(7), 1551–1562. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-020-04386-6
Abedelmalek, S., Chtourou, H., Aloui, A., Aouichaoui, C., Souissi, N., & Tabka, Z. (2012). Effect of time of day and partial sleep deprivation on plasma concentrations of IL-6 during a short-term maximal performance. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 113(1), 241–248. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-012-2432-7
Azboy, O., & Kaygisiz, Z. (2009). Effects of sleep deprivation on cardiorespiratory functions of the runners and volleyball players during rest and exercise. Acta Physiologica Hungarica, 96(1), 29–36. http://doi.org/10.1556/aphysiol.96.2009.1.3
Bird, S. P. (2013). Sleep, Recovery, and Athletic Performance. Strength and Conditioning Journal, 35(5), 43–47. http://doi.org/10.1519/ssc.0b013e3182a62e2f
Blumert, P. A., Crum, A. J., Ernsting, M., Volek, J. S., Hollander, D. B., Haff, E. E., & Haff, G. G. (2007). The Acute Effects of Twenty-Four Hours of Sleep Loss on the Performance of National-Caliber Male Collegiate Weightlifters. The Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 21(4), 1146. http://doi.org/10.1519/r-21606.1
Chase, J. D., Roberson, P. A., Saunders, M. J., Hargens, T. A., Womack, C. J., & Luden, N. D. (2017). One night of sleep restriction following heavy exercise impairs 3-km cycling time-trial performance in the morning. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, 42(9), 909–915. http://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2016-0698
Edwards, B. J., & Waterhouse, J. (2009). Effects of One Night of Partial Sleep Deprivation upon Diurnal Rhythms of Accuracy and Consistency in Throwing Darts. Chronobiology International, 26(4), 756–768. http://doi.org/10.1080/07420520902929037
Fullagar, H. H. K., Skorski, S., Duffield, R., Hammes, D., Coutts, A. J., & Meyer, T. (2014). Sleep and Athletic Performance: The Effects of Sleep Loss on Exercise Performance, and Physiological and Cognitive Responses to Exercise. Sports Medicine, 45(2), 161–186. http://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-014-0260-0
Gupta, L., Morgan, K., & Gilchrist, S. (2016). Does Elite Sport Degrade Sleep Quality? A Systematic Review. Sports Medicine, 47(7), 1317–1333. http://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-016-0650-6
Hausswirth, C., Louis, J., Aubry, A., Bonnet, G., Duffield, R., & Meur, Y. L. (2014). Evidence of Disturbed Sleep and Increased Illness in Overreached Endurance Athletes. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 46(5), 1036–1045. http://doi.org/10.1249/mss.0000000000000177
Mah, C. D., Mah, K. E., Kezirian, E. J., & Dement, W. C. (2011). The Effects of Sleep Extension on the Athletic Performance of Collegiate Basketball Players. Sleep, 34(7), 943–950. http://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.1132
Milewski, M. D., Skaggs, D. L., Bishop, G. A., Pace, J. L., Ibrahim, D. A., Wren, T. A., & Barzdukas, A. (2014). Chronic Lack of Sleep is Associated With Increased Sports Injuries in Adolescent Athletes. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics, 34(2), 129–133. http://doi.org/10.1097/bpo.0000000000000151
Mougin, F., Bourdin, H., Simon-Rigaud, M., Didier, J., Toubin, G., & Kantelip, J. (1996). Effects of a Selective Sleep Deprivation on Subsequent Anaerobic Performance. International Journal of Sports Medicine, 17(02), 115–119. http://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-972818
Oliver, S. J., Costa, R. J. S., Laing, S. J., Bilzon, J. L. J., & Walsh, N. P. (2009). One night of sleep deprivation decreases treadmill endurance performance. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 107(2), 155–161. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1103-9
Pallesen, S., Gundersen, H. S., Kristoffersen, M., Bjorvatn, B., Thun, E., & Harris, A. (2017). The Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Soccer Skills. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 124(4), 812–829. http://doi.org/10.1177/0031512517707412
Reilly, T., & Piercy, M. (1994). The effect of partial sleep deprivation on weight-lifting performance. Ergonomics, 37(1), 107–115. http://doi.org/10.1080/00140139408963628
Rossa, K. R., Smith, S. S., Allan, A. C., & Sullivan, K. A. (2014). The Effects of Sleep Restriction on Executive Inhibitory Control and Affect in Young Adults. Journal of Adolescent Health, 55(2), 287–292. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jadohealth.2013.12.034
Sargent, C., & Roach, G. D. (2016). Sleep duration is reduced in elite athletes following night-time competition. Chronobiology International, 33(6), 667–670. http://doi.org/10.3109/07420528.2016.1167715
Skein, M., Duffield, R., Edge, J., Short, M. J., & Mündel, T. (2011). Intermittent-Sprint Performance and Muscle Glycogen after 30 h of Sleep Deprivation. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 43(7), 1301–1311. http://doi.org/10.1249/mss.0b013e31820abc5a
Souissi, N., Sesboüé, B., Gauthier, A., Larue, J., & Davenne, D. (2003). Effects of one nights sleep deprivation on anaerobic performance the following day. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 89(3), 359–366. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-003-0793-7
Caia, J., Kelly, V. G., & Halson, S. L. (2017). The role of sleep in maximising performance in elite athletes. Sport, Recovery, and Performance, 151–167. http://doi.org/10.4324/9781315268149-11
Alley, J. R., Mazzochi, J. W., Smith, C. J., Morris, D. M., & Collier, S. R. (2015). Effects of Resistance Exercise Timing on Sleep Architecture and Nocturnal Blood Pressure. Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research, 29(5), 1378–1385. http://doi.org/10.1519/jsc.0000000000000750
Kovacevic, A., Mavros, Y., Heisz, J. J., & Singh, M. A. F. (2018). The effect of resistance exercise on sleep: A systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 39, 52–68. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2017.07.002
Herrick, J. E., Puri, S., & Richards, K. C. (2017). Resistance training does not alter same-day sleep architecture in institutionalized older adults. Journal of Sleep Research, 27(4). http://doi.org/10.1111/jsr.12590
Edinger, J. D., Morey, M. C., Sullivan, R. J., Higginbotham, M. B., Marsh, G. R., Dailey, D. S., & McCall, W. V. (1993). Aerobic fitness, acute exercise and sleep in older men. Sleep, 16(4), 351-359. https://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/16.4.351
King, A. C. (1997). Moderate-intensity exercise and self-rated quality of sleep in older adults. A randomized controlled trial. JAMA: The Journal of the American Medical Association, 277(1), 32–37. http://doi.org/10.1001/jama.277.1.32
Passos, G. S., Poyares, D., Santana, M. G., Garbuio, S. A., Tufik, S., & Mello, M. T. (2010). Effect of Acute Physical Exercise on Patients with Chronic Primary Insomnia. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 06(03), 270–275. http://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.27825
Reid, K. J., Baron, K. G., Lu, B., Naylor, E., Wolfe, L., & Zee, P. C. (2010). Aerobic exercise improves self-reported sleep and quality of life in older adults with insomnia. Sleep Medicine, 11(9), 934–940. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2010.04.014
Viana, V. A. R., Esteves, A. M., Boscolo, R. A., Grassmann, V., Santana, M. G., Tufik, S., & Mello, M. T. D. (2011). The effects of a session of resistance training on sleep patterns in the elderly. European Journal of Applied Physiology, 112(7), 2403–2408. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-011-2219-2
Herring, M., Kline, C., & Oconnor, P. (2015). Effects of Exercise Training On Self-reported Sleep Among Young Women with Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD). European Psychiatry, 30, 465. http://doi.org/10.1016/s0924-9338(15)31893-9
Kredlow, M. A., Capozzoli, M. C., Hearon, B. A., Calkins, A. W., & Otto, M. W. (2015). The effects of physical activity on sleep: a meta-analytic review. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 38(3), 427–449. http://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-015-9617-6
Yang, P.-Y., Ho, K.-H., Chen, H.-C., & Chien, M.-Y. (2012). Exercise training improves sleep quality in middle-aged and older adults with sleep problems: a systematic review. Journal of Physiotherapy, 58(3), 157–163. http://doi.org/10.1016/s1836-9553(12)70106-6
Kline, C. E., Sui, X., Hall, M. H., Youngstedt, S. D., Blair, S. N., Earnest, C. P., & Church, T. S. (2012). Dose–response effects of exercise training on the subjective sleep quality of postmenopausal women: exploratory analyses of a randomised controlled trial. BMJ Open, 2(4). http://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2012-001044
Fairbrother, K., Cartner, B. W., Triplett, N., Morris, D. M., & Collier, S. R. (2011). The Effects of Aerobic Exercise Timing on Sleep Architecture. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise, 43(Suppl 1), 879. http://doi.org/10.1249/01.mss.0000402452.16375.20
Youngstedt, S. D., & Kline, C. E. (2006). Epidemiology of exercise and sleep. Sleep and Biological Rhythms, 4(3), 215–221. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-8425.2006.00235.x
Stenholm, S., Head, J., Kivimäki, M., Hanson, L. L. M., Pentti, J., Rod, N. H., … Vahtera, J. (2018). Sleep Duration and Sleep Disturbances as Predictors of Healthy and Chronic Disease–Free Life Expectancy Between Ages 50 and 75: A Pooled Analysis of Three Cohorts. The Journals of Gerontology: Series A, 74(2), 204–210. http://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/gly01
Xiao, Q., Keadle, S. K., Hollenbeck, A. R., & Matthews, C. E. (2014). Sleep Duration and Total and Cause-Specific Mortality in a Large US Cohort: Interrelationships With Physical Activity, Sedentary Behavior, and Body Mass Index. American Journal of Epidemiology, 180(10), 997–1006. http://doi.org/10.1093/aje/kwu222
Reynolds, A. C., Dorrian, J., Liu, P. Y., Dongen, H. P. A. V., Wittert, G. A., Harmer, L. J., & Banks, S. (2012). Impact of Five Nights of Sleep Restriction on Glucose Metabolism, Leptin and Testosterone in Young Adult Men. PLoS ONE, 7(7). http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0041218
Åkerstedt, T., Palmblad, J., Torre, B. D. L., Marana, R., & Gillberg, M. (1980). Adrenocortical and Gonadal Steroids During Sleep Deprivation. Sleep, 3(1), 23–30. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/3.1.23
Cortés-Gallegos, V., Castañeda, G., Alonso, R., Sojo, I., Carranco, A., Cervantes, C., & Parra, A. (1983). Sleep Deprivation Reduces Circulating Androgens in Healthy Men. Archives of Andrology, 10(1), 33–37. http://doi.org/10.3109/01485018308990167
González-Santos, M. R., Gajá-Rodíguez, O. V., Alonso-Uriarte, R., Sojo-Aranda, I., & Cortés-Gallegos, V. (1989). Sleep Deprivation and Adaptive Hormonal Responses of Healthy Men. Archives of Andrology, 22(3), 203–207. http://doi.org/10.3109/01485018908986773
Penev, P. D. (2007). Association Between Sleep and Morning Testosterone Levels In Older Men. Sleep, 30(4), 427–432. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/30.4.427
Kloss, J. D., Perlis, M. L., Zamzow, J. A., Culnan, E. J., & Gracia, C. R. (2015). Sleep, sleep disturbance, and fertility in women. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 22, 78–87. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2014.10.005
Mahoney, M. M. (2010). Shift Work, Jet Lag, and Female Reproduction. International Journal of Endocrinology, 2010, 1–9. http://doi.org/10.1155/2010/813764
Labyak, S., Lava, S., Turek, F., & Zee, P. (2002). Effects Of Shiftwork On Sleep And Menstrual Function In Nurses. Health Care for Women International, 23(6-7), 703–714. http://doi.org/10.1080/07399330290107449
Pal, L., Bevilacqua, K., Zeitlian, G., Shu, J., & Santoro, N. (2008). Implications of diminished ovarian reserve (DOR) extend well beyond reproductive concerns. Menopause, 15(6), 1086–1094. http://doi.org/10.1097/gme.0b013e3181728467
Axelsson, G., Rylander, R., & Molin, I. (1989). Outcome of pregnancy in relation to irregular and inconvenient work schedules. Occupational and Environmental Medicine, 46(6), 393–398. http://doi.org/10.1136/oem.46.6.393
Bisanti, L., Olsen, J., Basso, O., Thonneau, P., & Karmaus, W. (1996). Shift Work and Subfecundity: A European Multicenter Study. Journal of Occupational & Environmental Medicine, 38(4), 352–358. http://doi.org/10.1097/00043764-199604000-00012
Rossmanith, W. G. (1998). The impact of sleep on gonadotropin secretion. Gynecological Endocrinology, 12(6), 381–389. http://doi.org/10.3109/09513599809012840
Fernando, S., & Rombauts, L. (2014). Melatonin: shedding light on infertility? – a review of the recent literature. Journal of Ovarian Research, 7(1). http://doi.org/10.1186/s13048-014-0098-y
Rocha, C., Rato, L., Martins, A., Alves, M., & Oliveira, P. (2015). Melatonin and Male Reproductive Health: Relevance of Darkness and Antioxidant Properties. Current Molecular Medicine, 15(4), 299–311. http://doi.org/10.2174/1566524015666150505155530
Song, C., Peng, W., Yin, S., Zhao, J., Fu, B., Zhang, J., … Zhang, Y. (2016). Melatonin improves age-induced fertility decline and attenuates ovarian mitochondrial oxidative stress in mice. Scientific Reports, 6(1). http://doi.org/10.1038/srep35165
Espino, J., Macedo, M., Lozano, G., Ortiz, Á., Rodríguez, C., Rodríguez, A. B., & Bejarano, I. (2019). Impact of Melatonin Supplementation in Women with Unexplained Infertility Undergoing Fertility Treatment. Antioxidants, 8(9), 338. http://doi.org/10.3390/antiox8090338
Tamura, H., Takasaki, A., Taketani, T., Tanabe, M., Kizuka, F., Lee, L., … Sugino, N. (2012). The role of melatonin as an antioxidant in the follicle. Journal of Ovarian Research, 5(1), 5. http://doi.org/10.1186/1757-2215-5-5
Saaresranta, T., & Polo, O. (2003). Sleep-disordered breathing and hormones. European Respiratory Journal, 22(1), 161–172. http://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.03.00062403
Cappuccio, F. P., Cooper, D., Delia, L., Strazzullo, P., & Miller, M. A. (2011). Sleep duration predicts cardiovascular outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective studies. European Heart Journal, 32(12), 1484–1492. http://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehr007
Jansen, E. C., Dunietz, G. L., Tsimpanouli, M.-E., Guyer, H. M., Shannon, C., Hershner, S. D., … Baylin, A. (2018). Sleep, Diet, and Cardiometabolic Health Investigations: a Systematic Review of Analytic Strategies. Current Nutrition Reports, 7(4), 235–258. http://doi.org/10.1007/s13668-018-0240-3
Knutson, K. L., Cauter, E. V., Rathouz, P. J., Yan, L. L., Hulley, S. B., Liu, K., & Lauderdale, D. S. (2009). Association Between Sleep and Blood Pressure in Midlife. Archives of Internal Medicine, 169(11), 1055. http://doi.org/10.1001/archinternmed.2009.119
Besedovsky, L., Lange, T., & Born, J. (2011). Sleep and immune function. Pflügers Archiv – European Journal of Physiology, 463(1), 121–137. http://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-011-1044-0
Besedovsky, L., Lange, T., & Haack, M. (2019). The Sleep-Immune Crosstalk in Health and Disease. Physiological Reviews, 99(3), 1325–1380. http://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00010.2018
Orr, W. C., Fass, R., Sundaram, S. S., & Scheimann, A. O. (2020). The effect of sleep on gastrointestinal functioning in common digestive diseases. The Lancet Gastroenterology & Hepatology, 5(6), 616–624. http://doi.org/10.1016/s2468-1253(19)30412-1
Tang, Y., Preuss, F., Turek, F. W., Jakate, S., & Keshavarzian, A. (2009). Sleep deprivation worsens inflammation and delays recovery in a mouse model of colitis. Sleep Medicine, 10(6), 597–603. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2008.12.009
Chen, Y., Tan, F., Wei, L., Li, X., Lyu, Z., Feng, X., … Li, N. (2018). Sleep duration and the risk of cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis including dose–response relationship. BMC Cancer, 18(1). http://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-5025-y
Almendros, I., Martinez-Garcia, M. A., Farré, R., & Gozal, D. (2020). Obesity, sleep apnea, and cancer. International Journal of Obesity, 44(8), 1653–1667. http://doi.org/10.1038/s41366-020-0549-z
Erren, T. C., Falaturi, P., Morfeld, P., Knauth, P., Reiter, R. J., & Piekarski, C. (2010). Shift Work and Cancer. Deutsches Aerzteblatt Online. http://doi.org/10.3238/arztebl.2010.0657
Bernert, R. A., Kim, J. S., Iwata, N. G., & Perlis, M. L. (2015). Sleep Disturbances as an Evidence-Based Suicide Risk Factor. Current Psychiatry Reports, 17(3). http://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-015-0554-4
Kim, J.-H., Park, E.-C., Cho, W.-H., Park, J.-Y., Choi, W.-J., & Chang, H.-S. (2013). Association between Total Sleep Duration and Suicidal Ideation among the Korean General Adult Population. Sleep, 36(10), 1563–1572. http://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.3058
Mccall, W. V., & Black, C. G. (2013). The Link Between Suicide and Insomnia: Theoretical Mechanisms. Current Psychiatry Reports, 15(9). http://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-013-0389-9
Li, S. X., Lam, S. P., Zhang, J., Yu, M. W. M., Chan, J. W. Y., Chan, C. S. Y., … Wing, Y.-K. (2016). Sleep Disturbances and Suicide Risk in an 8-Year Longitudinal Study of Schizophrenia-Spectrum Disorders. Sleep, 39(6), 1275–1282. http://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.5852
Littlewood, D. L., Gooding, P., Kyle, S. D., Pratt, D., & Peters, S. (2016). Understanding the role of sleep in suicide risk: qualitative interview study. BMJ Open, 6(8). http://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2016-012113
Lin, H.-T., Lai, C.-H., Perng, H.-J., Chung, C.-H., Wang, C.-C., Chen, W.-L., & Chien, W.-C. (2018). Insomnia as an independent predictor of suicide attempts: a nationwide population-based retrospective cohort study. BMC Psychiatry, 18(1). http://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-018-1702-2
Freeman, D., Sheaves, B., Waite, F., Harvey, A. G., & Harrison, P. J. (2020). Sleep disturbance and psychiatric disorders. The Lancet Psychiatry, 7(7), 628–637. http://doi.org/10.1016/s2215-0366(20)30136-x
Benca, R. M. (1992). Sleep and Psychiatric Disorders. Archives of General Psychiatry, 49(8), 651. http://doi.org/10.1001/archpsyc.1992.01820080059010
Breslau, N., Roth, T., Rosenthal, L., & Andreski, P. (1996). Sleep disturbance and psychiatric disorders: A longitudinal epidemiological study of young Adults. Biological Psychiatry, 39(6), 411–418. http://doi.org/10.1016/0006-3223(95)00188-3
Baglioni, C., Nanovska, S., Regen, W., Spiegelhalder, K., Feige, B., Nissen, C., … Riemann, D. (2016). Sleep and mental disorders: A meta-analysis of polysomnographic research. Psychological Bulletin, 142(9), 969–990. http://doi.org/10.1037/bul0000053
Goldstein, A. N., & Walker, M. P. (2014). The Role of Sleep in Emotional Brain Function. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 10(1), 679–708. http://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-032813-153716
Postuma, R. B., Iranzo, A., Hu, M., Högl, B., Boeve, B. F., Manni, R., … Pelletier, A. (2019). Risk and predictors of dementia and parkinsonism in idiopathic REM sleep behaviour disorder: a multicentre study. Brain, 142(3), 744–759. http://doi.org/10.1093/brain/awz030
Wintler, T., Schoch, H., Frank, M. G., & Peixoto, L. (2020). Sleep, brain development, and autism spectrum disorders: Insights from animal models. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 98(6), 1137–1149. http://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.24619
Shokri-Kojori, E., Wang, G.-J., Wiers, C. E., Demiral, S. B., Guo, M., Kim, S. W., … Volkow, N. D. (2018). β-Amyloid accumulation in the human brain after one night of sleep deprivation. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 115(17), 4483–4488. http://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1721694115
Mantovani, S., Smith, S. S., Gordon, R., & Osullivan, J. D. (2018). An overview of sleep and circadian dysfunction in Parkinsons disease. Journal of Sleep Research, 27(3). http://doi.org/10.1111/jsr.12673
Malhotra, R. K. (2018). Neurodegenerative Disorders and Sleep. Sleep Medicine Clinics, 13(1), 63–70. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsmc.2017.09.006
Huang, L.-B., Tsai, M.-C., Chen, C.-Y., & Hsu, S.-C. (2013). The Effectiveness of Light/Dark Exposure to Treat Insomnia in Female Nurses Undertaking Shift Work during the Evening/Night Shift. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 09(07), 641–646. http://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.2824
Zhang, Y., & Papantoniou, K. (2019). Night shift work and its carcinogenicity. The Lancet Oncology, 20(10). http://doi.org/10.1016/s1470-2045(19)30578-9
Perry-Jenkins, M., Goldberg, A. E., Pierce, C. P., & Sayer, A. G. (2007). Shift Work, Role Overload, and the Transition to Parenthood. Journal of Marriage and Family, 69(1), 123–138. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1741-3737.2006.00349.x
Rodziewicz TL, Hipskind JE. Medical Error Prevention. 2020 May 5. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2020 Jan–. PMID: 29763131. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29763131/
Tanaka, K., Takahashi, M., Hiro, H., Kakinuma, M., Tanaka, M., Kamata, N., & Miyaoka, H. (2010). Differences in Medical Error Risk among Nurses Working Two- and Three-shift Systems at Teaching Hospitals: A Six-month Prospective Study. Industrial Health, 48(3), 357–364. http://doi.org/10.2486/indhealth.48.357
Admi H, Tzischinsky O, Epstein R, Herer P, Lavie P. Shift work in nursing: is it really a risk factor for nurses’ health and patients’ safety?. Nurs Econ. 2008;26(4):250-257. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18777974/
Clendon, J., & Gibbons, V. (2015). 12h shifts and rates of error among nurses: A systematic review. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 52(7), 1231–1242. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2015.03.011
Hammadah, M., Kindya, B. R., Allard‐Ratick, M. P., Jazbeh, S., Eapen, D., Tang, W. W., & Sperling, L. (2017). Navigating air travel and cardiovascular concerns: Is the sky the limit?, Clinical Cardiology, 40 (9), 660–666. http://doi.org/10.1002/clc.22741
Lieber, B. A., Han, J., Appelboom, G., Taylor, B. E., Han, B., Agarwal, N., & Connolly, E. S. (2016). Association of Steroid Use with Deep Venous Thrombosis and Pulmonary Embolism in Neurosurgical Patients: A National Database Analysis. World Neurosurgery, 89, 126–132. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2016.01.033
El-Menyar, A., Asim, M., & Al-Thani, H. (2017). Obesity Paradox in Patients With Deep Venous Thrombosis. Clinical and Applied Thrombosis/Hemostasis, 24(6), 986–992. http://doi.org/10.1177/1076029617727858
Klovaite, J., Benn, M., & Nordestgaard, B. G. (2014). Obesity as a causal risk factor for deep venous thrombosis: a Mendelian randomization study. Journal of Internal Medicine, 277(5), 573–584. http://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12299
Davies, H. O., Popplewell, M., Singhal, R., Smith, N., & Bradbury, A. W. (2016). Obesity and lower limb venous disease – The epidemic of phlebesity. Phlebology: The Journal of Venous Disease, 32(4), 227–233. http://doi.org/10.1177/0268355516649333
Liljeqvist, S., Helldén, A., Bergman, U., & Söderberg, M. (2008). Pulmonary embolism associated with the use of anabolic steroids. European Journal of Internal Medicine, 19(3), 214–215. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejim.2007.03.016
Linton MF, Yancey PG, Davies SS, Jerome WG (Jay), Linton EF, Vickers KC. The Role of Lipids and Lipoproteins in Atherosclerosis. In: De Groot LJ, Chrousos G, Dungan K, et al., eds. Endotext. South Dartmouth (MA): MDText.com, Inc.; 2000. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK343489/.
Rescheduling of meals may ease the effects of jet lag. (2017). Nursing Standard, 31(48), 16–16. http://doi.org/10.7748/ns.31.48.16.s17
Ruscitto, C., & Ogden, J. (2016). The impact of an implementation intention to improve mealtimes and reduce jet lag in long-haul cabin crew. Psychology & Health, 32(1), 61–77. http://doi.org/10.1080/08870446.2016.1240174
Reid, K. J., & Abbott, S. M. (2015). Jet Lag and Shift Work Disorder. Sleep Medicine Clinics, 10(4), 523–535. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsmc.2015.08.006
Srinivasan, V., Spence, D. W., Pandi-Perumal, S. R., Trakht, I., & Cardinali, D. P. (2008). Jet lag: Therapeutic use of melatonin and possible application of melatonin analogs. Travel Medicine and Infectious Disease, 6(1-2), 17–28. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.tmaid.2007.12.002
Edwards, B. J., Atkinson, G., Waterhouse, J., Reilly, T., Godfrey, R., & Budgett, R. (2000). Use of melatonin in recovery from jet-lag following an eastward flight across 10 time-zones. Ergonomics, 43(10), 1501–1513. http://doi.org/10.1080/001401300750003934
Zee, P. C., & Goldstein, C. A. (2010). Treatment of Shift Work Disorder and Jet Lag. Current Treatment Options in Neurology, 12(5), 396–411. http://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-010-0090-9
https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/circadian-rhythm-disorders
Borodkin, K., & Dagan, Y. (2013). Diagnostic Algorithm for Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders. Encyclopedia of Sleep, 66–73. http://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-378610-4.00284-9
Lockley, S. (2013). Special Considerations and Future Directions in Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders Diagnosis. Encyclopedia of Sleep, 138–149. http://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-378610-4.00299-0
Crowley, S., & Youngstedt, S. (2013). Pathophysiology, Associations, and Consequences of Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorder. Encyclopedia of Sleep, 16–21. http://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-12-378610-4.00266-7
Franken, P., & Dijk, D.-J. (2009). Circadian clock genes and sleep homeostasis. European Journal of Neuroscience, 29(9), 1820–1829. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1460-9568.2009.06723.x
Burgess, H. J., & Emens, J. S. (2016). Circadian-Based Therapies for Circadian Rhythm Sleep-Wake Disorders. Current Sleep Medicine Reports, 2(3), 158–165. http://doi.org/10.1007/s40675-016-0052-1
Jones, C. R., Huang, A. L., Ptáček, L. J., & Fu, Y.-H. (2013). Genetic basis of human circadian rhythm disorders. Experimental Neurology, 243, 28–33. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2012.07.012
Toh KL. Basic science review on circadian rhythm biology and circadian sleep disorders. Ann Acad Med Singap. 2008;37(8):662-668. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18797559/
Farhud D, Aryan Z. Circadian Rhythm, Lifestyle and Health: A Narrative Review. Iran J Public Health. 2018;47(8):1068-1076. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6123576/
Dodson, E. R., & Zee, P. C. (2010). Therapeutics for Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders. Sleep Medicine Clinics, 5(4), 701–715. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsmc.2010.08.001
Zhu, L., & Zee, P. C. (2012). Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders. Neurologic Clinics, 30(4), 1167–1191. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.ncl.2012.08.011
Kim MJ, Lee JH, Duffy JF. Circadian Rhythm Sleep Disorders. J Clin Outcomes Manag. 2013;20(11):513-528. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4212693/
Zhong, G., Naismith, S. L., Rogers, N. L., & Lewis, S. J. G. (2011). Sleep-wake disturbances in common neurodegenerative diseases: A closer look at selected aspects of the neural circuitry. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 307(1-2), 9–14. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2011.04.020
Dijk, D.-J., Boulos, Z., Eastman, C. I., Lewy, A. J., Campbell, S. S., & Terman, M. (1995). Light Treatment for Sleep Disorders: Consensus Report. Journal of Biological Rhythms, 10(2), 113–125. http://doi.org/10.1177/074873049501000204
Barion, A., & Zee, P. C. (2007). A clinical approach to circadian rhythm sleep disorders. Sleep Medicine, 8(6), 566–577. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2006.11.017
Horne JA, Ostberg O. A self-assessment questionnaire to determine morningness-eveningness in human circadian rhythms. Int J Chronobiol. 1976;4(2):97-110. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1027738/
Adan, A., & Almirall, H. (1991). Horne & Östberg morningness-eveningness questionnaire: A reduced scale. Personality and Individual Differences, 12(3), 241–253. http://doi.org/10.1016/0191-8869(91)90110-w
Urbán, R., Magyaródi, T., & Rigó, A. (2011). Morningness-Eveningness, Chronotypes and Health-Impairing Behaviors in Adolescents. Chronobiology International, 28(3), 238–247. http://doi.org/10.3109/07420528.2010.549599
https://www.thewep.org/documentations/mctq
Buysse, D. J., Reynolds, C. F., Monk, T. H., Berman, S. R., & Kupfer, D. J. (1989). The Pittsburgh sleep quality index: A new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Research, 28(2), 193–213. http://doi.org/10.1016/0165-1781(89)90047-4
Bastien, C. (2001). Validation of the Insomnia Severity Index as an outcome measure for insomnia research. Sleep Medicine, 2(4), 297–307. http://doi.org/10.1016/s1389-9457(00)00065-4
Yang, M., Morin, C. M., Schaefer, K., & Wallenstein, G. V. (2009). Interpreting score differences in the Insomnia Severity Index: using health-related outcomes to define the minimally important difference. Current Medical Research and Opinion, 25(10), 2487–2494. http://doi.org/10.1185/03007990903167415
Morin, C. M., Belleville, G., Bélanger, L., & Ivers, H. (2011). The Insomnia Severity Index: Psychometric Indicators to Detect Insomnia Cases and Evaluate Treatment Response. Sleep, 34(5), 601–608. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/34.5.601
Castriotta RJ, Wilde MC, Lai JM, Atanasov S, Masel BE, Kuna ST. Prevalence and consequences of sleep disorders in traumatic brain injury. J Clin Sleep Med. 2007;3(4):349-356. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17694722/
Chokroverty S. Overview of sleep & sleep disorders. Indian J Med Res. 2010;131:126-140. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20308738/
Pavlova, M. K., & Latreille, V. (2019). Sleep Disorders. The American Journal of Medicine, 132(3), 292–299. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjmed.2018.09.021
Olejniczak, P. W., & Fisch, B. J. (2003). Sleep disorders. Medical Clinics of North America, 87(4), 803–833. http://doi.org/10.1016/s0025-7125(03)00006-3
https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/sleep-apnea
https://clevemed.com/what-is-sleep-apnea/patient-sleep-apnea-screener/
Spicuzza, L., Caruso, D., & Maria, G. D. (2015). Obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome and its management. Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease, 6(5), 273–285. http://doi.org/10.1177/2040622315590318
Bixler, E. O., Vgontzas, A. N., Lin, H.-M., Liao, D., Calhoun, S., Fedok, F., … Graff, G. (2008). Blood Pressure Associated With Sleep-Disordered Breathing in a Population Sample of Children. Hypertension, 52(5), 841–846. http://doi.org/10.1161/hypertensionaha.108.116756
Campos, A. I., García-Marín, L. M., Byrne, E. M., Martin, N. G., Cuéllar-Partida, G., & Rentería, M. E. (2020). Insights into the aetiology of snoring from observational and genetic investigations in the UK Biobank. Nature Communications, 11(1). http://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14625-1
Morgenthaler, T. I., Kagramanov, V., Hanak, V., & Decker, P. A. (2006). Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Is It a Unique Clinical Syndrome? Sleep, 29(9), 1203–1209. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/29.9.1203
El-Ad, B., & Lavie, P. (2005). Effect of sleep apnea on cognition and mood. International Review of Psychiatry, 17(4), 277–282. http://doi.org/10.1080/09540260500104508
Morgenstern, M., Wang, J., Beatty, N., Batemarco, T., Sica, A. L., & Greenberg, H. (2014). Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America, 43(1), 187–204. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecl.2013.09.002
Sleep–Related Breathing Disorders in Adults: Recommendations for Syndrome Definition and Measurement Techniques in Clinical Research. (1999). Sleep, 22(5), 667–689. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/22.5.667
Ruehland, W. R., Rochford, P. D., O’Donoghue, F. J., Pierce, R. J., Singh, P., & Thornton, A. T. (2009). The New AASM Criteria for Scoring Hypopneas: Impact on the Apnea Hypopnea Index. Sleep, 32(2), 150–157. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/32.2.150
Selim, B. J., Koo, B. B., Qin, L., Jeon, S., Won, C., Redeker, N. S., … Yaggi, H. K. (2016). The Association between Nocturnal Cardiac Arrhythmias and Sleep-Disordered Breathing: The DREAM Study. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 12(06), 829–837. http://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.5880
Ahmed, M. H. (2010). Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and fatty liver: Association or causal link? World Journal of Gastroenterology, 16(34), 4243. http://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v16.i34.4243
Singh, H., Pollock, R., Uhanova, J., Kryger, M., Hawkins, K., & Minuk, G. Y. (2005). Symptoms of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Digestive Diseases and Sciences, 50(12), 2338–2343. http://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-005-3058-y
Lawati, N. M. A., Patel, S. R., & Ayas, N. T. (2009). Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Consequences of Obstructive Sleep Apnea and Short Sleep Duration. Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases, 51(4), 285–293. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.pcad.2008.08.001
Young, T. (2004). Risk Factors for Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Adults. Jama, 291(16), 2013. http://doi.org/10.1001/jama.291.16.2013
Yaggi, H. K., Concato, J., Kernan, W. N., Lichtman, J. H., Brass, L. M., & Mohsenin, V. (2005). Obstructive Sleep Apnea as a Risk Factor for Stroke and Death. New England Journal of Medicine, 353(19), 2034–2041. http://doi.org/10.1056/nejmoa043104
Redline, S., Budhiraja, R., Kapur, V., Marcus, C. L., Mateika, J. H., Mehra, R., … Quan, A. S. F. (2007). The Scoring of Respiratory Events in Sleep: Reliability and Validity. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 03(02), 169–200. http://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.26818
Basheer B, Hegde KS, Bhat SS, Umar D, Baroudi K. Influence of mouth breathing on the dentofacial growth of children: a cephalometric study. J Int Oral Health. 2014;6(6):50-55. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4295456/
Ruhle, K. H., & Nilius, G. (2008). Mouth Breathing in Obstructive Sleep Apnea prior to and during Nasal Continuous Positive Airway Pressure. Respiration, 76(1), 40–45. http://doi.org/10.1159/000111806
Izu, S. C., Itamoto, C. H., Pradella-Hallinan, M., Pizarro, G. U., Tufik, S., Pignatari, S., & Fujita, R. R. (2010). Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome (OSAS) in mouth breathing children. Brazilian Journal of Otorhinolaryngology, 76(5), 552–556. http://doi.org/10.1590/s1808-86942010000500003
Lee, S. H., Choi, J. H., Shin, C., Lee, H. M., Kwon, S. Y., & Lee, S. H. (2007). How Does Open-Mouth Breathing Influence Upper Airway Anatomy? The Laryngoscope, 117(6), 1102–1106. http://doi.org/10.1097/mlg.0b013e318042aef7
Tuomilehto, H. P. I., Seppä, J. M., Partinen, M. M., Peltonen, M., Gylling, H., Tuomilehto, J. O. I., … Uusitupa, M. (2009). Lifestyle Intervention with Weight Reduction. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 179(4), 320–327. http://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.200805-669oc
https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/obesity-overweight.htm
Neill, A. M., Angus, S. M., Sajkov, D., & Mcevoy, R. D. (1997). Effects of sleep posture on upper airway stability in patients with obstructive sleep apnea. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 155(1), 199–204. http://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.155.1.9001312
Loord, H., & Hultcrantz, E. (2007). Positioner–a method for preventing sleep apnea. Acta Oto-Laryngologica, 127(8), 861–868. http://doi.org/10.1080/00016480601089390
Szollosi, I., Roebuck, T., Thompson, B., & Naughton, M. T. (2006). Lateral Sleeping Position Reduces Severity of Central Sleep Apnea / Cheyne-Stokes Respiration. Sleep, 29(8), 1045–1051. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/29.8.1045
Silverberg DS, Iaina A, Oksenberg A. Treating obstructive sleep apnea improves essential hypertension and quality of life. Am Fam Physician. 2002;65(2):229-236. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/11820487/
Aurora, R. N., Chowdhuri, S., Ramar, K., Bista, S. R., Casey, K. R., Lamm, C. I., … Tracy, S. L. (2012). The Treatment of Central Sleep Apnea Syndromes in Adults: Practice Parameters with an Evidence-Based Literature Review and Meta-Analyses. Sleep, 35(1), 17–40. http://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.1580
Hsu, A. A. L., & Lo, C. (2003). Continuous positive airway pressure therapy in sleep apnoea. Respirology, 8(4), 447–454. http://doi.org/10.1046/j.1440-1843.2003.00494.x
Patel, S. R., White, D. P., Malhotra, A., Stanchina, M. L., & Ayas, N. T. (2003). Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Therapy for Treating gess in a Diverse Population With Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Archives of Internal Medicine, 163(5), 565. http://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.163.5.565
Sundaram, S., Lim, J., & Lasserson, T. J. (2005). Surgery for obstructive sleep apnoea in adults. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. http://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.cd001004.pub2
Chen, H., & Lowe, A. A. (2012). Updates in oral appliance therapy for snoring and obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep and Breathing, 17(2), 473–486. http://doi.org/10.1007/s11325-012-0712-4
Gaisl, T., Haile, S. R., Thiel, S., Osswald, M., & Kohler, M. (2019). Efficacy of pharmacotherapy for OSA in adults: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 46, 74–86. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2019.04.009
Ohayon, M., Wickwire, E. M., Hirshkowitz, M., Albert, S. M., Avidan, A., Daly, F. J., … Vitiello, M. V. (2017). National Sleep Foundations sleep quality recommendations: first report. Sleep Health, 3(1), 6–19. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleh.2016.11.006
Youngstedt, S. D., Goff, E. E., Reynolds, A. M., Kripke, D. F., Irwin, M. R., Bootzin, R. R., … Jean-Louis, G. (2016). Has adult sleep duration declined over the last 50 years? Sleep Medicine Reviews, 28, 69–85. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2015.08.004
Chaput, J.-P., Mcneil, J., Després, J.-P., Bouchard, C., & Tremblay, A. (2013). Seven to Eight Hours of Sleep a Night Is Associated with a Lower Prevalence of the Metabolic Syndrome and Reduced Overall Cardiometabolic Risk in Adults. PLoS ONE, 8(9). http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0072832
Wild, C. J., Nichols, E. S., Battista, M. E., Stojanoski, B., & Owen, A. M. (2018). Dissociable effects of self-reported daily sleep duration on high-level cognitive abilities. Sleep, 41(12). http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/zsy182
Hirshkowitz, M., Whiton, K., Albert, S. M., Alessi, C., Bruni, O., Doncarlos, L., … Hillard, P. J. A. (2015). National Sleep Foundation’s sleep time duration recommendations: methodology and results summary. Sleep Health, 1(1), 40–43. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleh.2014.12.010
Cappuccio, F. P., Delia, L., Strazzullo, P., & Miller, M. A. (2010). Sleep Duration and All-Cause Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. Sleep, 33(5), 585–592. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/33.5.585
Gottlieb, D. J., Punjabi, N. M., Newman, A. B., Resnick, H. E., Redline, S., Baldwin, C. M., & Nieto, F. J. (2005). Association of Sleep Time With Diabetes Mellitus and Impaired Glucose Tolerance. Archives of Internal Medicine, 165(8), 863. http://doi.org/10.1001/archinte.165.8.863
Short, M. A., Agostini, A., Lushington, K., & Dorrian, J. (2015). A systematic review of the sleep, sleepiness, and performance implications of limited wake shift work schedules. Scandinavian Journal of Work, Environment & Health, 41(5), 425–440. http://doi.org/10.5271/sjweh.3509
Cappuccio, F. P., Taggart, F. M., Kandala, N.-B., Currie, A., Peile, E., Stranges, S., & Miller, M. A. (2008). Meta-Analysis of Short Sleep Duration and Obesity in Children and Adults. Sleep, 31(5), 619–626. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/31.5.619
Mong, J. A., & Cusmano, D. M. (2016). Sex differences in sleep: impact of biological sex and sex steroids. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 371(1688), 20150110. http://doi.org/10.1098/rstb.2015.0110
Krishnan, V., & Collop, N. A. (2006). Gender differences in sleep disorders. Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine, 12(6), 383–389. http://doi.org/10.1097/01.mcp.0000245705.69440.6a
Mehta, N., Shafi, F., & Bhat, A. (2015). Unique Aspects of Sleep in Women. Missouri medicine, 112(6), 430–434. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6168103/
Moline, M. L., Broch, L., & Zak, R. (2004). Sleep in women across the life cycle from adulthood through menopause. Medical Clinics of North America, 88(3), 705–736. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2004.01.009
He, Y., Jones, C. R., Fujiki, N., Xu, Y., Guo, B., Holder, J. L., … Fu, Y.-H. (2009). The Transcriptional Repressor DEC2 Regulates Sleep Length in Mammals. Science, 325(5942), 866–870. http://doi.org/10.1126/science.1174443
Theorell-Haglöw, J., Berglund, L., Berne, C., & Lindberg, E. (2014). Both habitual short sleepers and long sleepers are at greater risk of obesity: a population-based 10-year follow-up in women. Sleep Medicine, 15(10), 1204–1211. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2014.02.014
Mezick, E. J., Wing, R. R., & Mccaffery, J. M. (2014). Associations of self-reported and actigraphy-assessed sleep characteristics with body mass index and waist circumference in adults: moderation by gender. Sleep Medicine, 15(1), 64–70. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleep.2013.08.784
Kim, S. J. (2011). Relationship Between Weekend Catch-up Sleep and Poor Performance on Attention Tasks in Korean Adolescents. Archives of Pediatrics & Adolescent Medicine, 165(9), 806. http://doi.org/10.1001/archpediatrics.2011.128
Kim, C.-W., Choi, M.-K., Im, H.-J., Kim, O.-H., Lee, H.-J., Song, J., … Park, K.-H. (2012). Weekend catch-up sleep is associated with decreased risk of being overweight among fifth-grade students with short sleep duration. Journal of Sleep Research, 21(5), 546–551. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2869.2012.01013.x
Sun, W., Ling, J., Zhu, X., Lee, T. M.-C., & Li, S. X. (2019). Associations of weekday-to-weekend sleep differences with academic performance and health-related outcomes in school-age children and youths. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 46, 27–53. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2019.04.003
Kang, S.-G., Lee, Y. J., Kim, S. J., Lim, W., Lee, H.-J., Park, Y.-M., … Hong, J. P. (2014). Weekend catch-up sleep is independently associated with suicide attempts and self-injury in Korean adolescents. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 55(2), 319–325. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.comppsych.2013.08.023
Zhao, M., Tuo, H., Wang, S., & Zhao, L. (2020). The Effects of Dietary Nutrition on Sleep and Sleep Disorders. Mediators of Inflammation, 2020, 1–7. http://doi.org/10.1155/2020/3142874
Doherty, Madigan, Warrington, & Ellis. (2019). Sleep and Nutrition Interactions: Implications for Athletes. Nutrients, 11(4), 822. http://doi.org/10.3390/nu11040822
Sutanto CN, Wang MX, Tan D, Kim JE. Association of Sleep Quality and Macronutrient Distribution: A Systematic Review and Meta-Regression. Nutrients. 2020 Jan 2;12(1):126. doi: 10.3390/nu12010126. PMID: 31906452; PMCID: PMC7019667. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31906452/
Peuhkuri, K., Sihvola, N., & Korpela, R. (2012). Diet promotes sleep duration and quality. Nutrition Research, 32(5), 309–319. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.nutres.2012.03.009
Afaghi, A., Oconnor, H., & Chow, C. M. (2007). High-glycemic-index carbohydrate meals shorten sleep onset. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 85(2), 426–430. http://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/85.2.426
Golem, D. L., Martin-Biggers, J. T., Koenings, M. M., Davis, K. F., & Byrd-Bredbenner, C. (2014). An Integrative Review of Sleep for Nutrition Professionals. Advances in Nutrition, 5(6), 742–759. http://doi.org/10.3945/an.114.006809
Grandner, M. A., Jackson, N., Gerstner, J. R., & Knutson, K. L. (2013). Sleep symptoms associated with intake of specific dietary nutrients. Journal of Sleep Research, 23(1), 22–34. http://doi.org/10.1111/jsr.12084
Porter, J., & Horne, J. (1981). Bed-time food supplements and sleep: Effects of different carbohydrate levels. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 51(4), 426–433. http://doi.org/10.1016/0013-4694(81)90106-1
Halson, S. L. (2014). Sleep in Elite Athletes and Nutritional Interventions to Enhance Sleep. Sports Medicine, 44(S1), 13–23. http://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-014-0147-0
Rondanelli, M., Opizzi, A., Monteferrario, F., Antoniello, N., Manni, R., & Klersy, C. (2011). The Effect of Melatonin, Magnesium, and Zinc on Primary Insomnia in Long-Term Care Facility Residents in Italy: A Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 59(1), 82–90. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.2010.03232.x
Tahara, Y., & Shibata, S. (2014). Chrono-biology, Chrono-pharmacology, and Chrono-nutrition. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences, 124(3), 320–335. http://doi.org/10.1254/jphs.13r06cr
Landolt, H.-P., Werth, E., Borbély, A. A., & Dijk, D.-J. (1995). Caffeine intake (200 mg) in the morning affects human sleep and EEG power spectra at night. Brain Research, 675(1-2), 67–74. http://doi.org/10.1016/0006-8993(95)00040-w
Gottesmann, C. (2002). GABA mechanisms and sleep. Neuroscience, 111(2), 231–239. http://doi.org/10.1016/s0306-4522(02)00034-9
Campbell, S. S., Dawson, D., & Anderson, M. W. (1993). Alleviation of Sleep Maintenance Insomnia with Timed Exposure to Bright Light. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society, 41(8), 829–836. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1532-5415.1993.tb06179.x
Zhao, J., Tian, Y., Nie, J., Xu, J., & Liu, D. (2012). Red Light and the Sleep Quality and Endurance Performance of Chinese Female Basketball Players. Journal of Athletic Training, 47(6), 673–678. http://doi.org/10.4085/1062-6050-47.6.08
Smolensky, M. H., Sackett-Lundeen, L. L., & Portaluppi, F. (2015). Nocturnal light pollution and underexposure to daytime sunlight: Complementary mechanisms of circadian disruption and related diseases. Chronobiology International, 32(8), 1029–1048. http://doi.org/10.3109/07420528.2015.1072002
Düzgün, G., & Akyol, A. D. (2017). Effect of Natural Sunlight on Sleep Problems and Sleep Quality of the Elderly Staying in the Nursing Home. Holistic Nursing Practice, 31(5), 295–302. http://doi.org/10.1097/hnp.0000000000000206
Valham, F., Sahlin, C., Stenlund, H., & Franklin, K. A. (2012). Ambient Temperature and Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Effects on Sleep, Sleep Apnea, and Morning Alertness. Sleep, 35(4), 513–517. http://doi.org/10.5665/sleep.1736
Okamoto-Mizuno, K., Tsuzuki, K., & Mizuno, K. (2004). Effects of mild heat exposure on sleep stages and body temperature in older men. International Journal of Biometeorology, 49(1). http://doi.org/10.1007/s00484-004-0209-3
St-Onge, M.-P., & Shechter, A. (2014). Sleep disturbances, body fat distribution, food intake and/or energy expenditure: pathophysiological aspects. Hormone Molecular Biology and Clinical Investigation, 17(1). http://doi.org/10.1515/hmbci-2013-0066
Chaput, J.-P., Després, J.-P., Bouchard, C., & Tremblay, A. (2008). The Association Between Sleep Duration and Weight Gain in Adults: A 6-Year Prospective Study from the Quebec Family Study. Sleep, 31(4), 517–523. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/31.4.517
Dekker, S. A., Noordam, R., Biermasz, N. R., Roos, A., Lamb, H. J., Rosendaal, F. R., … Mutsert, R. (2018). Habitual Sleep Measures are Associated with Overall Body Fat, and not Specifically with Visceral Fat, in Men and Women. Obesity, 26(10), 1651–1658. http://doi.org/10.1002/oby.22289
Tunnicliffe, J. M., Erdman, K. A., Reimer, R. A., Lun, V., & Shearer, J. (2008). Consumption of dietary caffeine and coffee in physically active populations: physiological interactions. Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, 33(6), 1301–1310. http://doi.org/10.1139/h08-124
Mahoney, C. R., Giles, G. E., Marriott, B. P., Judelson, D. A., Glickman, E. L., Geiselman, P. J., & Lieberman, H. R. (2019). Intake of caffeine from all sources and reasons for use by college students. Clinical Nutrition, 38(2), 668–675. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnu.2018.04.004
Binks, H., Vincent, G. E., Gupta, C., Irwin, C., & Khalesi, S. (2020). Effects of Diet on Sleep: A Narrative Review. Nutrients, 12(4), 936. http://doi.org/10.3390/nu12040936
Rao, T. P., Ozeki, M., & Juneja, L. R. (2015). In Search of a Safe Natural Sleep Aid. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 34(5), 436–447. http://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.2014.926153
Abbasi B, Kimiagar M, Sadeghniiat K, Shirazi MM, Hedayati M, Rashidkhani B. The effect of magnesium supplementation on primary insomnia in elderly: A double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Res Med Sci. 2012 Dec;17(12):1161-9. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23853635/
Aspy, D. J., Madden, N. A., & Delfabbro, P. (2018). Effects of Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) and a B Complex Preparation on Dreaming and Sleep. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 003151251877032. http://doi.org/10.1177/0031512518770326
Parazzini F. Resveratrol, tryptophanum, glycine and vitamin E: a nutraceutical approach to sleep disturbance and irritability in peri- and post-menopause. Minerva Ginecol. 2015;67(1):1-5. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25660429/
Siegel JM. The neurotransmitters of sleep. J Clin Psychiatry. 2004;65 Suppl 16:4-7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15575797/
Djeridane, Y., Touitou, Y. Chronic diazepam administration differentially affects melatonin synthesis in rat pineal and Harderian glands. Psychopharmacology154, 403–407 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130000631
Betti L, Palego L, Demontis GC, Miraglia F, Giannaccini G. Hydroxyindole-O-methyltransferase (HIOMT) activity in the retina of melatonin-proficient mice. Heliyon. 2019;5(9):e02417. Published 2019 Sep 14. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02417
Haduch, A., Bromek, E., Wójcikowski, J., Gołembiowska, K., Daniel, W.. Melatonin Supports Serotonin Formation by Brain CYP2D. Drug Metabolism and DispositionMarch 1, 2016, 44 (3) 445-452; DOI: https://doi.org/10.1124/dmd.115.067413
Morton, D. J. (1987). Mechanism of Inhibition of Bovine Pineal Gland Hydroxyindole-O-Methyltransferase (EC 2.1.1.4) by Divalent Cations. Journal of Pineal Research, 4(3), 295–303. http://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-079x.1987.tb00867.x
Markova-Car, E. P., Jurišić, D., Ilić, N., & Pavelić, S. K. (2014). Running for time: circadian rhythms and melanoma. Tumor Biology, 35(9), 8359–8368. http://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-014-1904-2
Slominski AT, Zmijewski MA, Skobowiat C, Zbytek B, Slominski RM, Steketee JD. Sensing the environment: regulation of local and global homeostasis by the skin’s neuroendocrine system. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 2012;212:v-115. doi:10.1007/978-3-642-19683-6_1 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3422784/
Chalupsky, K., Kračun, D., Kanchev, I., Bertram, K., & Görlach, A. (2015). Folic Acid Promotes Recycling of Tetrahydrobiopterin and Protects Against Hypoxia-Induced Pulmonary Hypertension by Recoupling Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling, 23(14), 1076–1091. http://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2015.6329
Dianzani, I., Sanctis, L. D., Smooker, P. M., Gough, T. J., Alliaudi, C., Brusco, A., … Cotton, R. G. H. (1998). Dihydropteridine reductase deficiency: Physical structure of the QDPR gene, identification of two new mutations and genotype–phenotype correlations. Human Mutation, 12(4), 267–273. http://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1098-1004(1998)12:4<267::aid-humu8>3.0.co;2-c
Nichol, C. A., Lee, C. L., Edelstein, M. P., Chao, J. Y., & Duch, D. S. (1983). Biosynthesis of tetrahydrobiopterin by de novo and salvage pathways in adrenal medulla extracts, mammalian cell cultures, and rat brain in vivo. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 80(6), 1546–1550. http://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.80.6.1546
Titus, F., Dávalos, A., Alom, J., & Codina, A. (1986). 5-Hydroxytryptophan versus Methysergide in the Prophylaxis of Migraine. European Neurology, 25(5), 327–329. http://doi.org/10.1159/000116030
Birdsall TC. 5-Hydroxytryptophan: a clinically-effective serotonin precursor. Altern Med Rev. 1998;3(4):271-280. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9727088/
Volpi-Abadie J, Kaye AM, Kaye AD. Serotonin syndrome. Ochsner J. 2013;13(4):533-540. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3865832/
Valadas, J. S., Esposito, G., Vandekerkhove, D., Miskiewicz, K., Deaulmerie, L., Raitano, S., … Verstreken, P. (2018). ER Lipid Defects in Neuropeptidergic Neurons Impair Sleep Patterns in Parkinson’s Disease. Neuron, 98(6). http://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2018.05.022
Chung SY, Moriyama T, Uezu E, et al. Administration of phosphatidylcholine increases brain acetylcholine concentration and improves memory in mice with dementia. J Nutr. 1995;125(6):1484-1489. doi:10.1093/jn/125.6.1484 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7782901/
Montgomery, P., Burton, J. R., Sewell, R. P., Spreckelsen, T. F., & Richardson, A. J. (2014). Fatty acids and sleep in UK children: subjective and pilot objective sleep results from the DOLAB study – a randomized controlled trial. Journal of Sleep Research, 23(4), 364–388. http://doi.org/10.1111/jsr.12135
Alzoubi, K. H., Mayyas, F., & Zamzam, H. I. A. (2019). Omega-3 fatty acids protects against chronic sleep-deprivation induced memory impairment. Life Sciences, 227, 1–7. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.028
Nasehi, M., Mosavi-Nezhad, S.-M., Khakpai, F., & Zarrindast, M.-R. (2018). The role of omega-3 on modulation of cognitive deficiency induced by REM sleep deprivation in rats. Behavioural Brain Research, 351, 152–160. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2018.06.002
Jahangard, L., Sadeghi, A., Ahmadpanah, M., Holsboer-Trachsler, E., Bahmani, D. S., Haghighi, M., & Brand, S. (2018). Influence of adjuvant omega-3-polyunsaturated fatty acids on depression, sleep, and emotion regulation among outpatients with major depressive disorders – Results from a double-blind, randomized and placebo-controlled clinical trial. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 107, 48–56. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2018.09.016
Scorza, F. A., Cavalheiro, E. A., Scorza, C. A., Galduróz, J. C. F., Tufik, S., & Andersen, M. L. (2013). Sleep Apnea and Inflammation – Getting a Good Night’s Sleep with Omega-3 Supplementation. Frontiers in Neurology, 4. http://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2013.00193
Hansen, A. L., Dahl, L., Olson, G., Thornton, D., Graff, I. E., Frøyland, L., … Pallesen, S. (2014). Fish Consumption, Sleep, Daily Functioning, and Heart Rate Variability. Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine, 10(05), 567–575. http://doi.org/10.5664/jcsm.3714
Xie, L., Kang, H., Xu, Q., Chen, M. J., Liao, Y., Thiyagarajan, M., … Nedergaard, M. (2013). Sleep Drives Metabolite Clearance from the Adult Brain. Science, 342(6156), 373–377. http://doi.org/10.1126/science.1241224
Varshavsky, A. (2012). Augmented generation of protein fragments during wakefulness as the molecular cause of sleep: a hypothesis. Protein Science, 21(11), 1634–1661. http://doi.org/10.1002/pro.2148
Mackiewicz, M., Shockley, K. R., Romer, M. A., Galante, R. J., Zimmerman, J. E., Naidoo, N., … Pack, A. I. (2007). Macromolecule biosynthesis: a key function of sleep. Physiological Genomics, 31(3), 441–457. http://doi.org/10.1152/physiolgenomics.00275.2006
Scharf, M. T., Naidoo, N., Zimmerman, J. E., & Pack, A. I. (2008). The energy hypothesis of sleep revisited. Progress in Neurobiology, 86(3), 264–280. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.pneurobio.2008.08.003
Horne, J. (2009). REM sleep, energy balance and ‘optimal foraging.’ Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 33(3), 466–474. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.12.002
Berger, R. J., & Phillips, N. H. (1995). Energy conservation and sleep. Behavioural Brain Research, 69(1-2), 65–73. http://doi.org/10.1016/0166-4328(95)00002-b
Benington, J. H., & Heller, H. C. (1995). Restoration of brain energy metabolism as the function of sleep. Progress in Neurobiology, 45(4), 347–360. http://doi.org/10.1016/0301-0082(94)00057-o
Abel, T., Havekes, R., Saletin, J. M., & Walker, M. P. (2013). Sleep, Plasticity and Memory from Molecules to Whole-Brain Networks. Current Biology, 23(17). http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.07.025
Rasch, B., & Born, J. (2013). About Sleeps Role in Memory. Physiological Reviews, 93(2), 681–766. http://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00032.2012
Cirelli, C., & Tononi, G. (2008). Is Sleep Essential? PLoS Biology, 6(8). http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0060216
Siegel, J. M. (2005). Clues to the functions of mammalian sleep. Nature, 437(7063), 1264–1271. http://doi.org/10.1038/nature04285
Campbell, S. S., & Tobler, I. (1984). Animal sleep: A review of sleep duration across phylogeny. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 8(3), 269–300. http://doi.org/10.1016/0149-7634(84)90054-x
Tobler, I. (1995). Is sleep fundamentally different between mammalian species? Behavioural Brain Research, 69(1-2), 35–41. http://doi.org/10.1016/0166-4328(95)00025-o
Tononi, G., & Cirelli, C. (2006). Sleep function and synaptic homeostasis. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 10(1), 49–62. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.smrv.2005.05.002
Dongen, H. P. A. V., Vitellaro, K. M., & Dinges, D. F. (2005). Individual Differences in Adult Human Sleep and Wakefulness: Leitmotif for a Research Agenda. Sleep, 28(4), 479–498. http://doi.org/10.1093/sleep/28.4.479
Vyazovskiy, V. V., & Delogu, A. (2014). NREM and REM Sleep. The Neuroscientist, 20(3), 203–219. http://doi.org/10.1177/1073858413518152
Mignot, E. (2008). Why We Sleep: The Temporal Organization of Recovery. PLoS Biology, 6(4). http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0060106
Siegel, J. M. (2009). Sleep viewed as a state of adaptive inactivity. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 10(10), 747–753. http://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2697
Horne, J. (2000). REM sleep — by default? Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 24(8), 777–797. http://doi.org/10.1016/s0149-7634(00)00037-3
Baran, B., Pace-Schott, E. F., Ericson, C., & Spencer, R. M. C. (2012). Processing of Emotional Reactivity and Emotional Memory over Sleep. Journal of Neuroscience, 32(3), 1035–1042. http://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.2532-11.2012
Tononi, G., & Cirelli, C. (2014). Sleep and the Price of Plasticity: From Synaptic and Cellular Homeostasis to Memory Consolidation and Integration. Neuron, 81(1), 12–34. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2013.12.025
Li, J., Vitiello, M. V., & Gooneratne, N. S. (2018). Sleep in Normal Aging. Sleep Medicine Clinics, 13(1), 1–11. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsmc.2017.09.001
Murillo-Rodriguez, E., Arias-Carrion, O., Zavala-Garcia, A., Sarro-Ramirez, A., & Huitron-Resendiz, S. (2012). Basic Sleep Mechanisms: An Integrative Review. Central Nervous System Agents in Medicinal Chemistry, 12(1), 38–54. http://doi.org/10.2174/187152412800229107
Weber, F. D. (2018). Sleep: Eye-Opener Highlights Sleep’s Organization. Current Biology, 28(5). http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2018.01.054
Yetton, B. D., Mcdevitt, E. A., Cellini, N., Shelton, C., & Mednick, S. C. (2018). Quantifying sleep architecture dynamics and individual differences using big data and Bayesian networks. Plos One, 13(4). http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0194604
Colrain, I. M., Nicholas, C. L., & Baker, F. C. (2014). Alcohol and the sleeping brain. Handbook of Clinical Neurology Alcohol and the Nervous System, 415–431. http://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-444-62619-6.00024-0
Zisapel, N. (2018). New perspectives on the role of melatonin in human sleep, circadian rhythms and their regulation. British Journal of Pharmacology, 175(16), 3190–3199. http://doi.org/10.1111/bph.14116
Tosini, G., Baba, K., Hwang, C. K., & Iuvone, P. M. (2012). Melatonin: An underappreciated player in retinal physiology and pathophysiology. Experimental Eye Research, 103, 82–89. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.exer.2012.08.009
Blasiak, J., Reiter, R. J., & Kaarniranta, K. (2016). Melatonin in Retinal Physiology and Pathology: The Case of Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity, 2016, 1–12. http://doi.org/10.1155/2016/6819736
Bellingham, J., Chaurasia, S. S., Melyan, Z., Liu, C., Cameron, M. A., Tarttelin, E. E., … Lucas, R. J. (2006). Evolution of Melanopsin Photoreceptors: Discovery and Characterization of a New Melanopsin in Nonmammalian Vertebrates. PLoS Biology, 4(8). http://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0040254
Zaidi, F. H., Hull, J. T., Peirson, S. N., Wulff, K., Aeschbach, D., Gooley, J. J., … Lockley, S. W. (2007). Short-Wavelength Light Sensitivity of Circadian, Pupillary, and Visual Awareness in Humans Lacking an Outer Retina. Current Biology, 17(24), 2122–2128. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2007.11.034
Legates, T. A., Altimus, C. M., Wang, H., Lee, H.-K., Yang, S., Zhao, H., … Hattar, S. (2012). Aberrant light directly impairs mood and learning through melanopsin-expressing neurons. Nature, 491(7425), 594–598. http://doi.org/10.1038/nature11673
Sikka, G., Hussmann, G. P., Pandey, D., Cao, S., Hori, D., Park, J. T., … Berkowitz, D. E. (2014). Melanopsin mediates light-dependent relaxation in blood vessels. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 111(50), 17977–17982. http://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1420258111
Buhr, E. D., Yoo, S.-H., & Takahashi, J. S. (2010). Temperature as a Universal Resetting Cue for Mammalian Circadian Oscillators. Science, 330(6002), 379–385. http://doi.org/10.1126/science.1195262
Robbins, R., Grandner, M. A., Buxton, O. M., Hale, L., Buysse, D. J., Knutson, K. L., … Jean-Louis, G. (2019). Sleep myths: an expert-led study to identify false beliefs about sleep that impinge upon population sleep health practices. Sleep Health, 5(4), 409–417. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.sleh.2019.02.002
Damiola, F. (2000). Restricted feeding uncouples circadian oscillators in peripheral tissues from the central pacemaker in the suprachiasmatic nucleus. Genes & Development, 14(23), 2950–2961. http://doi.org/10.1101/gad.183500
Abel, T., Havekes, R., Saletin, J. M., & Walker, M. P. (2013). Sleep, Plasticity and Memory from Molecules to Whole-Brain Networks. Current Biology, 23(17). http://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2013.07.025
Muzet, A., Ehrhart, J., Candas, V., Libert, J. P., & Vogt, J. J. (1983). Rem Sleep and Ambient Temperature in Man. International Journal of Neuroscience, 18(1-2), 117–125. http://doi.org/10.3109/00207458308985885
Saini, C., Morf, J., Stratmann, M., Gos, P., & Schibler, U. (2012). Simulated body temperature rhythms reveal the phase-shifting behavior and plasticity of mammalian circadian oscillators. Genes & Development, 26(6), 567–580. http://doi.org/10.1101/gad.183251.111
Franco P, Szliwowski H, Dramaix M, Kahn A. Influence of ambient temperature on sleep characteristics and autonomic nervous control in healthy infants. Sleep. 2000 May 1;23(3):401-7. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10811384/
Libert JP, Candas V, Muzet A, Ehrhart J. Thermoregulatory adjustments to thermal transients during slow wave sleep and REM sleep in man. J Physiol (Paris). 1982;78(3):251-7 https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7166740/
Palca, J. W., Walker, J. M., & Berger, R. J. (1986). Thermoregulation, metabolism, and stages of sleep in cold-exposed men. Journal of Applied Physiology, 61(3), 940–947. http://doi.org/10.1152/jappl.1986.61.3.940
Lack. (2009). Chronotype differences in circadian rhythms of temperature, melatonin, and sleepiness as measured in a modified constant routine protocol. Nature and Science of Sleep, 1. http://doi.org/10.2147/nss.s6234
Samson, D. R., Crittenden, A. N., Mabulla, I. A., Mabulla, A. Z. P., & Nunn, C. L. (2017). Chronotype variation drives night-time sentinel-like behaviour in hunter–gatherers. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences, 284(1858), 20170967. http://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2017.0967
Walker, R. J., Kribs, Z. D., Christopher, A. N., Shewach, O. R., & Wieth, M. B. (2014). Age, the Big Five, and time-of-day preference: A mediational model. Personality and Individual Differences, 56, 170–174. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2013.09.003
Bjorness, T., & Greene, R. (2009). Adenosine and Sleep. Current Neuropharmacology, 7(3), 238–245. http://doi.org/10.2174/157015909789152182
Dworak, M., Diel, P., Voss, S., Hollmann, W., & Strüder, H. (2007). Intense exercise increases adenosine concentrations in rat brain: Implications for a homeostatic sleep drive. Neuroscience, 150(4), 789–795. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2007.09.062
Rainnie, D., Grunze, H., Mccarley, R., & Greene, R. (1994). Adenosine inhibition of mesopontine cholinergic neurons: implications for EEG arousal. Science, 263(5147), 689–692. http://doi.org/10.1126/science.8303279
Daly, J. W., Shi, D., Nikodijevic, O., & Jacobson, K. A. (1994). The role of adenosine receptors in the central action of caffeine. Pharmacopsychoecologia, 7(2), 201–213. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4373791/

